
Interstate 93 (I-93) is an Interstate Highway in the New England states of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont in the United States. Spanning approximately 190 miles (310 km) along a north–south axis, it is one of three primary Interstate Highways located entirely within New England; the other two are I-89 and I-91. The largest cities along the route are Boston, Massachusetts, and Manchester, New Hampshire; it also travels through the New Hampshire state capital of Concord.

The Kansas Turnpike is a 236-mile-long (380 km), freeway-standard toll road that lies entirely within the US state of Kansas. It runs in a general southwest–northeast direction from the Oklahoma border to Kansas City. It passes through several major Kansas cities, including Wichita, Topeka, and Lawrence. The turnpike is owned and maintained by the Kansas Turnpike Authority (KTA), which is headquartered in Wichita.

The Beijing–Harbin Expressway, designated as G1 and commonly abbreviated as Jingha Expressway (京哈高速) is an expressway linking the cities of Beijing and Harbin, Heilongjiang.

Jingjintang Expressway, also known as the Jingtang Expressway, links Beijing via central Tianjin to the Tanggu District in eastern Tianjin. 143 kilometres in length, it crosses the jurisdictions of Beijing and Tianjin municipalities and Hebei province.

The 4th Ring Road is a controlled-access expressway ring road in Beijing, China which runs around the city, with a radius of approximately 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) from city centre. The total length of the road is 65.3 kilometres (40.6 mi). There are 147 bridges and viaducts that run the length of the Ring Road.
Highways in Taiwan are classified into five types:

A limited-access road, known by various terms worldwide, including limited-access highway, dual-carriageway, expressway, and partial controlled-access highway, is a highway or arterial road for high-speed traffic which has many or most characteristics of a controlled-access highway, including limited or no access to adjacent property, some degree of separation of opposing traffic flow, use of grade separated interchanges to some extent, prohibition of slow modes of transport, such as bicycles, (draught) horses, or self-propelled agricultural machines; and very few or no intersecting cross-streets or level crossings. The degree of isolation from local traffic allowed varies between countries and regions. The precise definition of these terms varies by jurisdiction.

The Outer Ring Road in Tianjin, China is a city express road, 71.322 kilometres in length, which encircles Tianjin municipality.

A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms include throughway and parkway. Some of these may be limited-access highways, although this term can also refer to a class of highways with somewhat less isolation from other traffic.

The Hong Kong Strategic Route and Exit Number System is a system adopted by the Transport Department of the Hong Kong Government to organise the major roads in the territory into routes 1 to 10 for the convenience of drivers. When the system was implemented in 2004, the government promoted it with a major public campaign, including the slogan "Remember the Numbers; Make Driving Easier".
Transport in Tianjin consists of an extensive network of roads and railways and a major airport. Bicycle is a major means of transport in daily use of the city.

Road signs in Thailand are standardized road signs similar to those used in other nations but much of it resembles road signage systems used in South American countries with certain differences, such as using a blue circle instead of a red-bordered white circle to indicate mandatory actions. Until the early 1980s, Thailand closely followed American, European, Australian, and Japanese practices in road sign design, with diamond-shaped warning signs and circular restrictive signs to regulate traffic. For Romanized, signs usually use the FHWA Series fonts typeface, which is also used on American road signage, but for Thai text, the font used is unknown.

Baodi District is a district of the municipality of Tianjin, People's Republic of China.

The Shanghai–Chengdu Expressway, designated as G42 and commonly referred to as the Hurong Expressway is an east–west bound expressway that connects the eastern metropolis of Shanghai to Chengdu, the capital city of Sichuan. The expressway passes through six provinces and serves major cities such as Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Nanjing, Hefei, Wuhan, and Yichang. The eastern terminus of G42 is at the Wuning Road Interchange of Shanghai Middle Ring Road. At its western terminus, the expressway intersects the East 3rd Ring Road and connects East Erxianqiao Road in Chenghua District, Chengdu. The expressway spans 1,960 km (1,220 mi) in length.

The Changchun–Shenzhen Expressway, designated as G25 and commonly referred to as the Changshen Expressway, is an expressway that connects the cities of Changchun, Jilin, China, and Shenzhen, Guangdong. When complete, it will be 3,585 km (2,228 mi) in length.
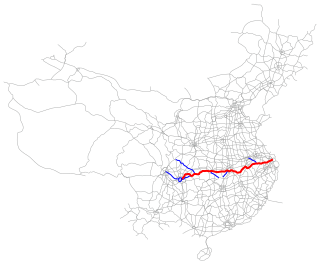
The Shanghai–Chongqing Expressway, designated as G50 and commonly referred to as the Huyu Expressway is an east-west bound expressway that connects the cities of Shanghai, China in Yangtze River Delta, and Chongqing in western China. The expressway runs through six provinces/municipalities and adjoin major cities such as Wuhu, Anqing, Wuhan and Yichang, roughly parallel to G42 Shanghai-Chengdu Expressway to its south. The thoroughfare begins at Huqingping Outer Ring Interchange near Hongqiao International Airport, where it meets S20 Outer Ring Expressway in Shanghai, and terminates at an interchange in Jiangbei District, where the highway joins G75 Lanzhou-Haikou Expressway. It is fully complete and spans 1,900 km (1,200 mi) in length.

The Nanning–Youyiguan Expressway, commonly referred to as the Nanyou Expressway, is a 225.06-kilometre-long expressway (139.85 mi) in the Chinese autonomous region of Guangxi that connects the city of Nanning, the capital of Guangxi, and Friendship Pass, known in Chinese as Youyiguan, a border crossing between China and Vietnam. The Friendship Pass is located in the county-level city of Pingxiang, under the administration of the city of Chongzuo. At the border, the expressway connects with North–South expressway in Vietnam. The expressway is designated G7211, and opened on 28 December 2005.
A wide variety of road signs are displayed in the People's Republic of China.

U.S. Route 59 (US-59) is a part of the U.S. Highway System that runs from the Mexico–US border in Laredo, Texas, as a continuation of Mexican Federal Highway 85D north to the Lancaster–Tolstoi Border Crossing on the Canada–US border, where it continues as Manitoba Highway 59. In the U.S. state of Kansas, US-59 is a main north–south highway that travels from Chetopa to Atchison.



















