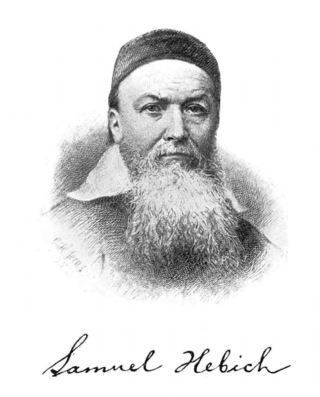James Sowerby was an English naturalist, illustrator and mineralogist. Contributions to published works, such as A Specimen of the Botany of New Holland or English Botany, include his detailed and appealing plates. The use of vivid colour and accessible texts was intended to reach a widening audience in works of natural history. The standard author abbreviation Sowerby is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.

Nathaniel Wolff Wallich was a surgeon and botanist of Danish origin who worked in India, initially in the Danish settlement near Calcutta and later for the Danish East India Company and the British East India Company. He was involved in the early development of the Calcutta Botanical Garden, describing many new plant species and developing a large herbarium collection which was distributed to collections in Europe. Several of the plants that he collected were named after him.

Syzygium cumini, commonly known as Malabar plum, Java plum, black plum, jamun, jaman, jambul, or jambolan, is an evergreen tropical tree in the flowering plant family Myrtaceae, and favored for its fruit, timber, and ornamental value. It is native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It can reach heights of up to 30 m (100 ft) and can live more than 100 years. A rapidly growing plant, it is considered an invasive species in many world regions.
Johann Gerhard König was a Baltic German botanist and physician who served in the Tranquebar Mission, India before joining service under the Nawab of Arcot, and then the English East India Company. He collected natural history specimens including plants, particularly those of medical interest, from the region and several species are named after him including the curry tree (Murrayakoenigii).

The Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden, previously known as Indian Botanic Garden and the Calcutta Botanic Garden, is a botanical garden situated in Shibpur, Howrah near Kolkata. They are commonly known as the Calcutta Botanical Garden and previously as the Royal Botanic Garden, Calcutta. The gardens exhibit a wide variety of rare plants and a total collection of over 12,000 specimens spread over 109 hectares. It is under Botanical Survey of India (BSI) of Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India.

The Basel Mission was a Christian missionary society based in Switzerland. It was active from 1815 to 2001, when it transferred the operative work to Mission 21, the successor organization of Kooperation Evangelischer Kirchen und Missione (KEM), founded in 2001.

James Sykes Gamble was an English botanist who specialized in the flora of the Indian sub-continent; he became Director of the British Imperial Forest School at Dehradun, and a Fellow of the Royal Society.

Hermann Friedrich Mögling (1811–1881), also spelt Herrmann Friedrich Moegling, was a German missionary from the Basel Mission who spent most of his career in the western regions of the state of Karnataka, India. He is credited as the publisher of the first ever newspaper in the Kannada language called as Mangalooru Samachara in 1843. He was awarded a doctorate for his literary work in Kannada called as Bibliotheca Carnataca. He also translated Kannada literature into German. Mögling is acknowledged by Kannada writers and linguists as the first modern Kannada writer, as he produced nearly 36 literary works, considered to be ground-breaking and exceptional Kannada literature, in a short period of 20 years.

Neolamarckia cadamba, with English common names burflower-tree, laran, and Leichhardt pine, and called kadam or cadamba locally, is an evergreen, tropical tree native to South and Southeast Asia. The genus name honours French naturalist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck. It has scented orange flowers in dense globe-shaped clusters. The flowers are used in perfumes. The tree is grown as an ornamental plant and for timber and paper-making. Kadam features in Indian religions and mythologies.

Woodblock printing on textiles is the process of printing patterns on fabrics, typically linen, cotton, or silk, by means of carved wooden blocks.

Alphitonia excelsa, commonly known as the red ash or soap tree, is a species of tree in the family Rhamnaceae. It is endemic to Australia, being found in New South Wales, Queensland, Northern Territory and the northeastern tip of Western Australia. It is used in bush regeneration as a pioneer species and for amenity planting.
A horticultural flora, also known as a garden flora, is a plant identification aid structured in the same way as a native plants flora. It serves the same purpose: to facilitate plant identification; however, it only includes plants that are under cultivation as ornamental plants growing within the prescribed climate zone or region. Traditionally published in book form, often in several volumes, such floras are increasingly likely to be produced as websites or CD ROMs.

William Theobald was a malacologist and naturalist on the staff of the Geological Survey of India serving in Burma, then a part of British India.
Benjamin Heyne FLS was a German botanist, naturalist, and surgeon who worked in British India as a Botanist to Samalkot in the Madras Presidency under the British East India Company. He collected and described plants from southern India, many of which were named after him by European botanists.
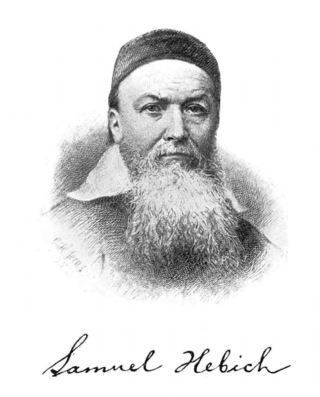
Samuel Hebich (1803–1868) was one of the three pioneer Basel Mission missionaries to Southwestern India--Canara, Coorg, South Mahratta, Malabar, and Nilagiri. He, along with Johann Christoph Lehner and Christian Leonard Greiner commenced Basel Mission station, the first German mission station in India, at Mangalore.
C. L. Furtado is CSI-Bishop Emeritus - in - Karnataka Southern of Church of South India. Furtado became the third Bishop on 25 August 1997, the date on which he was consecrated as Bishop in the diocese that is headquartered in Mangalore with the Cathedra of the Bishop placed at CSI-Shanthi Cathedral, Mangalore.

Christian Ramsay, Countess of Dalhousie informally Lady Dalhousie, néeBroun; was a Scottish botanist and natural historian. She married George Ramsay, 9th Earl of Dalhousie and travelled with him when he was appointed Lieutenant Governor of Nova Scotia, Governor General of Canada and Commander in Chief of the Indian Army. While travelling, she collected and catalogued many species of plants, presented scientific papers to societies and donated many collections to different botanical groups.
William Webb Spicer was an Anglican rector and amateur botanist, economic entomologist, and naturalist. He is known for his 1878 book A Handbook of the Plants of Tasmania, which was the first locally printed handbook for Australian flora.
Basel Mission Press is the first printing press of coastal Karnataka and was established in 1841 at Balmatta, Mangalore, India. This printing press was gifted to Gottfried Weigle by Basel Mission of Switzerland who had been to Bombay to get a booklet printed. Tulu Kirthanegalu by the lithographic process was the first book printed in the Manguluru Branch in 1941. In 1841, Gottfried Weigle obtained a printing press from Bombay and brought it back to Mangalore in 1842 with two Marathi printing assistants. In 1842, they published a Kannada pamphlet by Moegling and made 1500 copies. The next item was Christian Greiner's Tulu translation of St. Matthew's Gospel. In July 1843, the press began the first Kannada newspaper called "Mangalur-samachar" edited by Hermann Moegling. Two issues a month were produced until February 1844, after which it was printed in Bellary. Basel Mission Press celebrated its 175th anniversary celebrations in 2016. Basel Mission Press is now renamed as Balmatta Institute of Printing Technology and Book Craft offers courses in printing technology and book binding. The press is being maintained by Karnataka Christian Education Society (KACES) since 1972