Related Research Articles

Fishbourne Roman Palace is located in the village of Fishbourne, Chichester in West Sussex. The palace is the largest residential Roman building discovered in Britain and has an unusually early date of 75 CE, around thirty years after the Roman conquest of Britain.
Sussex, from the Old English Sūþsēaxe, is a historic county in South East England and was formerly an independent medieval kingdom. It is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the English Channel, and divided for many purposes into the ceremonial counties of West Sussex and East Sussex.
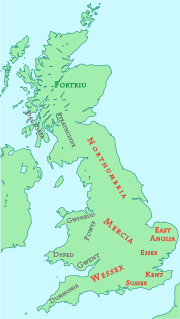
The Kingdom of the South Saxons, today referred to as the Kingdom of Sussex, was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Heptarchy of Anglo-Saxon England. On the south coast of the island of Great Britain, it was originally a sixth-century Saxon colony and later an independent kingdom. The kingdom remains one of the least known of the Anglo-Saxon polities, with no surviving king-list, several local rulers and less centralisation than other Anglo Saxon kingdoms. The South Saxons were ruled by the kings of Sussex until the country was annexed by Wessex, probably in 827, in the aftermath of the Battle of Ellendun.

West Sussex is a county in South East England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the shire districts of Adur, Arun, Chichester, Horsham, and Mid Sussex, and the boroughs of Crawley and Worthing. Covering an area of 1,991 square kilometres, West Sussex borders Hampshire to the west, Surrey to the north, and East Sussex to the east. The county town and only city in West Sussex is Chichester, located in the south-west of the county. Administratively the ancient county of Sussex had been divided into 6 rapes with the 3 western rapes being administered separately from the eastern rapes. This was legally formalised with the establishment of West Sussex Council in 1888 but within the ceremonial Sussex. After the reorganisation of local government in 1974, the ceremonially fictions of the historic county of Sussex was divided into two separate counties, with the western half becoming West Sussex and the eastern half East Sussex. The existing East and West Sussex councils taking control respectively, with Mid Sussex and parts of Crawly being transferred to West Sussex administration from East Sussex. In the 2011 census, West Sussex recorded a population of 806,900.
The Sussex Archaeological Society, founded in 1846, is one of the oldest county-based archaeological societies in the UK. A registered self-funding charity whose charitable aims are to enable people to enjoy, learn about and have access to the heritage of Sussex. This is done by opening six historic sites in Sussex to visitors, providing research facilities in its library, running excavations, providing a finds identification service and offering a variety of walks, talks and conferences on the archaeology and history of Sussex. Its headquarters are at Bull House, High Street, Lewes, Sussex. The current chief executive of the society is Andrew Edwards.

Sir Barrington Windsor Cunliffe,, known as Barry Cunliffe, is a British archaeologist and academic. He was Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford from 1972 to 2007. Since 2007, he has been an Emeritus Professor.
Tiberius Claudius Cogidubnus was a 1st-century king of the Regnenses or Regni tribe in early Roman Britain.

Sussex, from the Old English 'Sūþsēaxe', is a historic county in South East England.
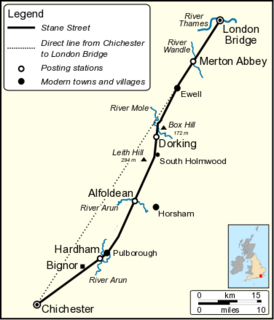
Stane Street is the modern name of the 91 km-long (57 mi) Roman road in southern England that linked Londinium (London) to Noviomagus Reginorum (Chichester). The exact date of construction is uncertain; however, on the basis of archaeological artefacts discovered along the route, it was in use by 70 AD and may have been built in the first decade of the Roman occupation of Britain.

Mount Caburn is a 480-foot (146m) prominent landmark in East Sussex, England, about one mile (1.6 km) east of Lewes overlooking the village of Glynde. It is the highest part of an outlier of the South Downs, separated from the main range by Glynde Reach, a tributary of the River Ouse.
The site of the Claudian invasion of Britain in AD 43 is a matter of academic debate. Although it is generally believed that the force left from Gesoriacum (Boulogne), it is possible that part of the fleet sailed from near the mouth of the Rhine. And while Rutupiæ is often stated as the site of the landing, there are equally plausible arguments in favour of a landing further west along the south coast of Britain.

Bignor Roman Villa is a large Roman courtyard villa which has been excavated and put on public display on the Bignor estate in the English county of West Sussex. It is well known for its high quality mosaic floors, which are some of the most complete and intricate in the country.
Margaret Helen Rule, was a British archaeologist. She led the project that excavated and raised the Tudor warship Mary Rose in 1982.

Fishbourne is a village and civil parish in the Chichester District of West Sussex, England and is situated two miles (3.2 km) west of Chichester.
The Battle of Mercredesburne was one of three battles fought as part of the conquest of what became the Kingdom of Sussex in southern England. The battles were fought between the Saxon leader Ælle's army and the local Britons.

Newmarket Hill is situated in the parish of Kingston near Lewes. It is located midway between, and within walking distance of, two of the most important population centres in East Sussex, Brighton and Lewes.
Miles Russell, is a British archaeologist best known for his work and publications on the prehistoric and Roman periods and for his appearances in television programmes such as Time Team and Harry Hill's TV Burp.

Torberry Hill is an Iron Age hillfort in the county of West Sussex, in southern England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument, with a list entry identification number of 1015966. The hill fort is located within the parish of Harting, within the South Downs National Park. The hill includes the remains of an Early Iron Age univallate hill fort, a Middle Iron Age promontory fort and a post-medieval post mill. The hill is a chalk spur projecting northwards from the South Downs.
This is a timeline of Sussex history. To read about the background to these events, see History of Sussex. See also the list of monarchs of Sussex.
Religion in Sussex has been dominated over the last 1,400 years by Christianity. Like the rest of England, the established church in Sussex is the Church of England, although other Christian traditions exist. After Christianity, the religion with the most adherents is Islam, followed by Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism and Sikhism.
References
- ↑ Russell, Miles (August 2005). "Ruling Britannia (review)". History Today . 55 (8).[ dead link ]