Related Research Articles

The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference across an electrical conductor, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and to an applied magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879. For clarity, the original effect is sometimes called the ordinary Hall effect to distinguish it from other "Hall effects" which have different physical mechanisms.

Magnetic-core memory was the predominant form of random-access computer memory for 20 years between about 1955 and 1975. Such memory is often just called core memory, or, informally, core.

A tachometer is an instrument measuring the rotation speed of a shaft or disk, as in a motor or other machine. The device usually displays the revolutions per minute (RPM) on a calibrated analogue dial, but digital displays are increasingly common.

A Rogowski coil, named after Walter Rogowski, is an electrical device for measuring alternating current (AC) or high-speed current pulses. It consists of a helical coil of wire with the lead from one end returning through the centre of the coil to the other end, so that both terminals are at the same end of the coil. The whole assembly is then wrapped around the straight conductor whose current is to be measured. There is no metal (iron) core. The winding density, the diameter of the coil and the rigidity of the winding are critical for preserving immunity to external fields and low sensitivity to the positioning of the measured conductor.
A Hall effect sensor is a device that is used to measure the magnitude of a magnetic field. Its output voltage is directly proportional to the magnetic field strength through it.
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark ignition internal combustion engines is in petrol (gasoline) road vehicles such as cars and motorcycles.

An ignition coil is an induction coil in an automobile's ignition system that transforms the dynamo's voltage to the thousands of volts needed to create an electric spark in the spark plugs to ignite the fuel. Some coils have an internal resistor, while others rely on a resistor wire or an external resistor to limit the current flowing into the coil from the car's 12-volt supply. The wire that goes from the ignition coil to the distributor and the high voltage wires that go from the distributor to each of the spark plugs are called spark plug wires or high tension leads. Originally, every ignition coil system required mechanical contact breaker points and a capacitor (condenser). More recent electronic ignition systems use a power transistor to provide pulses to the ignition coil. A modern passenger automobile may use one ignition coil for each engine cylinder, eliminating fault-prone spark plug cables and a distributor to route the high voltage pulses.
A wheel speed sensor or vehicle speed sensor (VSS) is a type of tachometer. It is a sender device used for reading the speed of a vehicle's wheel rotation. It usually consists of a toothed ring and pickup.

Electromagnetic suspension (EMS) is the magnetic levitation of an object achieved by constantly altering the strength of a magnetic field produced by electromagnets using a feedback loop. In most cases the levitation effect is mostly due to permanent magnets as they don't have any power dissipation, with electromagnets only used to stabilize the effect.
The Wiegand interface is a de facto wiring standard which arose from the popularity of Wiegand effect card readers in the 1980s. It is commonly used to connect a card swipe mechanism to the rest of an access control system. The sensor in such a system is often a "Wiegand wire", based on the Wiegand effect, discovered by John R. Wiegand. A Wiegand-compatible reader is normally connected to a Wiegand-compatible security panel.

Capacitor discharge ignition (CDI) or thyristor ignition is a type of automotive electronic ignition system which is widely used in outboard motors, motorcycles, lawn mowers, chainsaws, small engines, turbine-powered aircraft, and some cars. It was originally developed to overcome the long charging times associated with high inductance coils used in inductive discharge ignition (IDI) systems, making the ignition system more suitable for high engine speeds. The capacitive-discharge ignition uses capacitor discharge current to the coil to fire the spark plugs.
A keycard lock is a lock operated by a keycard, a flat, rectangular plastic card with identical dimensions to that of a credit card or American and EU driver's license. The card stores a physical or digital pattern that the door mechanism accepts before disengaging the lock.

A proximity sensor is a sensor able to detect the presence of nearby objects without any physical contact.
A current sensor is a device that detects electric current in a wire and generates a signal proportional to that current. The generated signal could be analog voltage or current or even a digital output. The generated signal can be then used to display the measured current in an ammeter, or can be stored for further analysis in a data acquisition system, or can be used for the purpose of control. More information on current sensors can be found here.

An interrupter in electrical engineering is a device used to interrupt the flow of a steady direct current for the purpose of converting a steady current into a changing one. Frequently, the interrupter is used in conjunction with an inductor to produce increased voltages either by a back emf effect or through transformer action. The largest industrial use of the interrupter was in the induction coil, the first transformer, which was used to produce high voltage pulses in scientific experiments and to power arc lamps, spark gap radio transmitters, and the first X-ray tubes, around the turn of the 20th century. Its largest use was the contact breaker or "points" in the distributor of the ignition system of gasoline engines, which served to periodically interrupt the current to the ignition coil producing high voltage pulses which create sparks in the spark plugs. It is still used in this application.
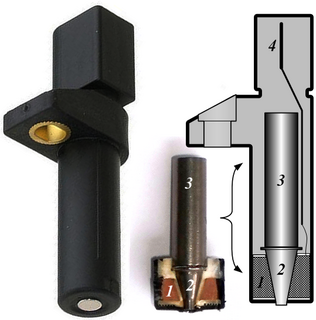
A crank sensor is an electronic device used in an internal combustion engine, both petrol and diesel, to monitor the position or rotational speed of the crankshaft. This information is used by engine management systems to control the fuel injection or the ignition system timing and other engine parameters. Before electronic crank sensors were available, the distributor would have to be manually adjusted to a timing mark on petrol engines.
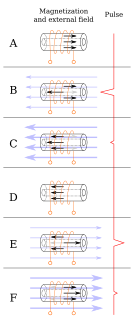
The Wiegand effect is a nonlinear magnetic effect, named after its discoverer John R. Wiegand, produced in specially annealed and hardened wire called Wiegand wire.
Inductive discharge ignition systems were developed in the 19th century as a means to ignite the air–fuel mixture in the combustion chamber of internal combustion engines. The first versions were low tension coils, then low-tension and in turn high-tension magnetos, which were offered as a more effective alternative to the older-design hot-tube ignitors that had been utilized earlier on hot tube engines. With the advent of small stationary engines; and with the development of the automobile, engine-driven tractors, and engine-driven trucks; first the magneto and later the distributor-type systems were utilized as part of an efficient and reliable engine ignition system on commercially available motorized equipment. These systems were in widespread use on all cars and trucks through the 1960s. Manufacturers such as Ford, General Motors, Chrysler, Citroen, Mercedes, John Deere, International Harvester, and many others incorporated them into their products. The inductive discharge system is still extensively used today.

A trembler coil or vibrator coil is a type of high-voltage ignition coil used in the ignition system of early automobiles, most notably the Benz Patent-Motorwagen and the Ford Model T. Its distinguishing feature is a vibrating magnetically-activated contact called a trembler or interrupter, which breaks the primary current, generating multiple sparks during each cylinder's power stroke. Trembler coils were first used on the 1886 Benz automobile, and were used on the Model T until 1927.

Wiegand sensors are magnetic sensors that do not need any external voltage or current, and make use of the Wiegand effect to generate a consistent pulse every time magnetic field polarity reverses. Wiegand sensors are made by wrapping a coil around a Vicalloy wire core, which, due to the hysteresis inherent in the Wiegand effect, induces a pulse in the coil each time the magnetic polarity of the Vicalloy wire core reverses. They can be used in a range of magnetic sensing applications and have the additional advantage that the energy of each pulse can be harvested.
References
- ↑ Brushing Up on Wiegand - he emigrated to the United States in the 1930s to study music (piano and choral conducting) in New York City.
- United States Patent 3780313 First Wiegand Pulse Generator
- United States Patent 3892118 Where it all Started July 1, 1975
- United States Patent 4247601
- United States Patent 4263523
- United States Patent 4484090
- United States Patent 4309628
| This article about an American physicist is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |