Related Research Articles

The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London, England. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is separated from the eastern edge of the square mile of the City of London by the open space known as Tower Hill. It was founded toward the end of 1066 as part of the Norman Conquest. The White Tower, which gives the entire castle its name, was built by William the Conqueror in 1078 and was initially a resented symbol of oppression, inflicted upon London by the new Norman ruling class. The castle was also used as a prison from 1100 until 1952, although that was not its primary purpose. A grand palace early in its history, it served as a royal residence. As a whole, the Tower is a complex of several buildings set within two concentric rings of defensive walls and a moat. There were several phases of expansion, mainly under kings Richard I, Henry III, and Edward I in the 12th and 13th centuries. The general layout established by the late 13th century remains despite later activity on the site.

The Lord Mayor of London is the mayor of the City of London, England, and the leader of the City of London Corporation. Within the City, the Lord Mayor is accorded precedence over all individuals except the sovereign and retains various traditional powers, rights, and privileges, including the title and style The Right Honourable Lord Mayor of London.
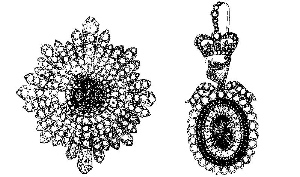
The Jewels of the Order of St Patrick, commonly called the Irish Crown Jewels, were the heavily jewelled badge and star created in 1831 for the Grand Master of the Order of St Patrick, an order of knighthood established in 1783 by George III to be an Irish equivalent of the English Order of the Garter and the Scottish Order of the Thistle. The office of Grand Master was held by the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland.

The Lord Chancellor, formally titled Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom. The lord chancellor is the minister of justice for England and Wales and the highest-ranking Great Officer of State in Scotland and England, nominally outranking the prime minister. The lord chancellor is appointed and dismissed by the sovereign on the advice of the prime minister. Prior to the union of England and Scotland into the Kingdom of Great Britain, there were separate lord chancellors for the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland. Likewise, the Lordship of Ireland and its successor states maintained the office of lord chancellor of Ireland until the establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922, whereupon the office was abolished.

The Crown Jewels of the United Kingdom, originally the Crown Jewels of England, are a collection of royal ceremonial objects kept in the Jewel House at the Tower of London, which include the coronation regalia and vestments worn by British monarchs.
Sir Ralph Sandwich (1235–1308), of Dene, Ham, and Ripple, Kent, Winchfield, Hampshire, etc., was an English administrator and justice. He was Steward of the King's Demesne, Constable of Canterbury (1278), and Royal Warden of London.
Sir John de Benstede KB (c.1275 –1323/4) was a prominent member of the English royal household in the late 13th and early 14th century. He was Prebendary of Sandiacre from 3 February 1297 until, presumably, 1308, when he married. He was also King's Secretary, and he served variously as keeper of the Great Seal and controller of the wardrobe. He also served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1305 to 1306, and as a royal judge from 1309 onwards.

The Jewel House is a vault housing the British Crown Jewels in the Waterloo Block at the Tower of London. It was opened by Queen Elizabeth II in 1994 and refurbished in 2012. Regalia have been kept in various parts of the Tower since the 14th century after a series of successful and attempted thefts at Westminster Abbey.
The King's Remembrancer is an ancient judicial post in the legal system of England and Wales. Since the Lord Chancellor no longer sits as a judge, the Remembrancer is the oldest judicial position in continual existence. The post was created in 1154 by King Henry II as the chief official in the Exchequer Court, whose purpose was "to put the Lord Treasurer and the Barons of Court in remembrance of such things as were to be called upon and dealt with for the benefit of the Crown", a primary duty being to keep records of the taxes, paid and unpaid.

Sir Simon Fraser of Oliver and Neidpath was a Scottish knight who fought in the Wars of Scottish Independence, for which he was hanged, drawn, and quartered in 1306.
The Master of the Jewel Office was a position in the Royal Households of England, the Kingdom of Great Britain and the United Kingdom. The office holder was responsible for running the Jewel House, which houses the Crown Jewels. This role has, at various points in history, been called Master or Treasurer of the Jewel House, Master or Keeper of the Crown Jewels, Master or Keeper of the Regalia, and Keeper of the Jewel House. In 1967, the role was combined with Resident Governor of the Tower of London.

The King's Wardrobe, together with the Chamber, made up the personal part of medieval English government known as the King's household. Originally the room where the king's clothes, armour, and treasure were stored, the term was expanded to describe both its contents and the department of clerks who ran it. Early in the reign of Henry III the Wardrobe emerged out of the fragmentation of the Curia Regis to become the chief administrative and accounting department of the Household. The Wardrobe received regular block grants from the Exchequer for much of its history; in addition, however, the wardrobe treasure of gold and jewels enabled the king to make secret and rapid payments to fund his diplomatic and military operations, and for a time, in the 13th-14th centuries, it eclipsed the Exchequer as the chief spending department of central government.
Richard of Pudlicott, also known as Richard de Podelicote, was an English wool merchant who, down on his luck, became an infamous burglar of King Edward I's Wardrobe treasury at Westminster Abbey in April of 1303. Richard, along with high-ranked accomplices primarily consisting of the monks of Westminster Abbey, stole a large portion of the king's treasury of gems, antique gold and coins, estimated at over 100,000 pounds, or about equal to a year's tax revenue for the Kingdom of England. When priceless objects began flooding pawn shops, houses of prostitution and even fishing nets in the River Thames, the king and his ministers, away at war in Scotland, were alerted. King Edward began his investigation into the incident in June of 1303, which revealed the possible involvement of over 40 monks. Many dozens of people were rounded up and jailed in a wide and indiscriminate net and eventually brought to one of the biggest trials of the High Middle Ages in England. Ultimately most of the loot was recovered and a dozen or so were hanged, including Richard, but most escaped the executioner. Richard gave a false confession that he was the only one involved, saving the clergy—his inside accomplices—from being condemned. After his hanging, his body was flayed, and legend said his skin was nailed to the door of Westminster Abbey as a warning to other would-be criminals. A 2005 study of the door, dating back to the reign of King Edward I revealed the legend to be false. The fragments of hide found under the door's lone surviving iron strap turned out to be from an animal hide which once covered the door.
John FitzThomas was an Anglo-Norman in the Peerage of Ireland, as 4th Lord of Offaly from 1287 and subsequently as 1st Earl of Kildare from 1316.
Events from the 1230s in England.

William Latimer, 4th Baron Latimer, KG was an English noble, soldier and diplomat. After serving in France and for the household of Edward III, he was impeached during the Good Parliament of 1376, the earliest recorded impeachment in the Parliament of England.

Thomas Cantock, Quantock or Cantok was an English-born cleric and judge in medieval Ireland, who held the offices of Bishop of Emly and Lord Chancellor of Ireland.
John Frowyk was an English-born cleric and judge in fourteenth-century Ireland.
Lenton, or de Lenton is a surname, and Anglo-Norman gentry family, originating in the midlands of England. The family are believed to have originated in Lenton in Nottinghamshire, the etymology of which is a "hamlet on the river Leen".
John Devereux, Lord of Munsley, was an Anglo-Norman nobleman living during the reigns of Edward I and Edward II. The Devereux were a prominent knightly family along the Welsh Marches during the thirteenth century, and played an integral role in attempts to control the Welsh Marches during the thirteenth century.
References
- ↑ "Lord Mayors of the City of London from 1189" (PDF). www.citybridgetrust.gov.uk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- ↑ "Chronological list of aldermen: 1222-1300". British History Online. Retrieved 6 October 2016.
- ↑ Paul Doherty, The Great Crown Jewels Robbery of 1303, published by Carroll & Graf Publishers, New York, 2005. It was first published in the U.K. in 2005 by Constable & Robinson, Ltd. ISBN 978-0-78671-664-7
- ↑ White, William "Notes and Queries" pg. 410