Honours and awards
Foreign honours
 Czechoslovakia: Officer of the Order of the White Lion (1946) [5]
Czechoslovakia: Officer of the Order of the White Lion (1946) [5]
Joseph Charles Aub (1890-1973) was an American endocrinologist and professor then chair of medicine at Harvard University. [1] He graduated from Harvard College and Harvard Medical School. [2]
The lead industry funded Aub's research which ignored the health effects of lead on children. [3] [4]

Harvey Williams Cushing was an American neurosurgeon, pathologist, writer, and draftsman. A pioneer of brain surgery, he was the first exclusive neurosurgeon and the first person to describe Cushing's disease. He wrote a biography of physician William Osler in three volumes.

The American University of Beirut is a private, non-sectarian, and independent university chartered in New York with its campus in Beirut, Lebanon. AUB is governed by a private, autonomous board of trustees and offers programs leading to bachelor's, master's, MD, and PhD degrees.
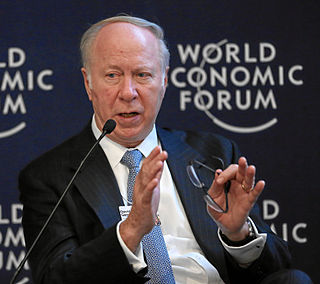
David Richmond Gergen is an American political commentator and former presidential adviser who served during the administrations of Richard Nixon, Gerald Ford, Ronald Reagan, and Bill Clinton. He is currently a senior political analyst for CNN and a professor of public service and the founding director of the Center for Public Leadership at the Harvard Kennedy School. Gergen is also the former editor at large of U.S. News & World Report and a contributor to CNN.com and Parade Magazine. He has twice been a member of election coverage teams that won Peabody awards—in 1988 with MacNeil–Lehrer, and in 2008 with CNN.

Alice Hamilton was an American physician, research scientist, and author. She was a leading expert in the field of occupational health, laid the foundation for health and safety protections, and a pioneer in the field of industrial toxicology.

Mary Corinna Putnam Jacobi was an English-American physician, teacher, scientist, writer, and suffragist. She was the first woman admitted to study medicine at the University of Paris and the first woman to graduate from a pharmacy college in the United States.

William Crawford Gorgas KCMG was a United States Army physician and 22nd Surgeon General of the U.S. Army (1914–1918). He is best known for his work in Florida, Havana and at the Panama Canal in abating the transmission of yellow fever and malaria by controlling the mosquitoes that carry these diseases, for which he used the discoverments made by the cuban doctor Carlos J. Finlay. At first, Finlay's strategy was greeted with considerable skepticism and opposition to such hygiene measures. However, the measures Gorgas put into practice as the head of the Panama Canal Zone Sanitation Commission saved thousands of lives and contributed to the success of the Canal's construction.

Paul Charles Zamecnik was an American scientist who played a central role in the early history of molecular biology. He was a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a senior scientist at Massachusetts General Hospital.

Herbert Leroy Needleman researched the neurodevelopmental damage caused by lead poisoning. He was a pediatrician, child psychiatrist, researcher and professor at the University of Pittsburgh, an elected member of the Institute of Medicine, and the founder of the Alliance to End Childhood Lead Poisoning. Dr. Needleman played a key role in securing some of the most significant environmental health protections achieved during the 20th century, which resulted in a fivefold reduction in the prevalence of lead poisoning among children in the United States by the early 1990s. Despite engendering strong resistance from lead-related industries, which made him the target of frequent attacks, Needleman persisted in campaigning to educate stakeholders, including parents and government panels, about the dangers of lead poisoning. Needleman has been credited with having played a key role in triggering environmental safety measures that have reduced average blood lead levels by an estimated 78 percent between 1976 and 1991. He died in Pittsburgh in 2017.

Arnold Seymour Relman — known as Bud Relman to intimates — was an American internist and professor of medicine and social medicine. He was editor of The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) from 1977 to 1991, where he instituted two important policies: one asking the popular press not to report on articles before publication and another requiring authors to disclose conflicts of interest. He wrote extensively on medical publishing and reform of the U.S. health care system, advocating non-profit delivery of single-payer health care. Relman ended his career as professor emeritus at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts.

The University of Louisville Louis D. Brandeis School of Law, commonly referred to as The University of Louisville School of Law or the Brandeis School of Law, is the law school of the University of Louisville. Established in 1846, it is the oldest law school in Kentucky and the fifth oldest in the country in continuous operation. The law school is named after Justice Louis Dembitz Brandeis, who served on the Supreme Court of the United States and was the school's patron. Following the example of Brandeis, who eventually stopped accepting payment for "public interest" cases, Louis D. Brandeis School of Law was one of the first law schools in the nation to require students to complete public service before graduation.

Carola Blitzman Eisenberg was an Argentine-American psychiatrist who became the first woman to hold the position of Dean of Students at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. From 1978 to 1990, she was the dean of student affairs at Harvard Medical School (HMS). She was a long-time lecturer in the Department of Global Health and Social Medicine at HMS. She was also both a founding member of Physicians for Human Rights and an honorary psychiatrist with the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. After retiring, she was involved in human rights work through Physicians for Human Rights, the Institute for Healthcare Improvement, and elsewhere. She turned 100 in September 2017 and died in Lincoln, Massachusetts, in March 2021 at the age of 103.

Fuller Albright was an American endocrinologist who made numerous contributions to his field, especially to the area of calcium metabolism. Albright made great strides and contributions to the understanding of disorders associated with calcium and phosphate abnormalities in the body. He also was a published author and in his books he detailed his findings.
David Rosner is the Ronald H. Lauterstein Professor of Sociomedical Sciences and professor of history in the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences at Columbia University. He is also co-director of the Center for the History and Ethics of Public Health at Columbia's Mailman School of Public Health. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences' Institute of Medicine in 2010.

Harold Amos was an American microbiologist. He taught at Harvard Medical School for nearly fifty years and was the first African American department chair of the school.

Yandell Henderson was an American physiologist. The New York Times called him an "expert on gases" and "an authority on the physiology of respiration and circulation and on pharmacology and toxicology of gases". He was also noted for new methods in resuscitation. Henderson was a director of the Yale Laboratory of Applied Physiology at Yale University, a member of the National Academy of Sciences, chairman of the section of physiology and pathology of the American Medical Association. He was also a member of the American Philosophical Society. A collection of his papers are held at the National Library of Medicine in Bethesda, Maryland.
Rashi Fein was an American health economist termed "a father of Medicare" in the United States and "an architect of Medicare", was Professor of Economics of Medicine, Emeritus, in the Department of Global Health and Social Medicine at Harvard Medical School, and the author of the book Medical Care, Medical Costs: The Search for a Health Insurance Policy.
Gerald Markowitz is an American historian, currently a Distinguished Professor at John Jay College of Criminal Justice, City University of New York (CUNY) and also a published author.
Ann Stone Minot was an American biochemist and physiologist.
Edward Harold Kass was an American physician, medical school professor, medical researcher in infectious diseases, medical journal editor, and historian of medicine. He is known for his research on toxic shock syndrome and urinary tract infections.