
Palo Duro Canyon is a canyon system of the Caprock Escarpment located in the Texas Panhandle near the cities of Amarillo and Canyon. As one of the largest canyons in the United States, it is roughly 25–40 mi (40–64 km) long and has an average width of 6 mi (9.7 km), but reaches a width of 20 mi (32 km) at places. Its depth is around 800 ft (240 m), but in some locations, valley bottom to surrounding hills increases to 1,000 ft (300 m). Palo Duro Canyon has been named "The Grand Canyon of Texas" both for its size and for its dramatic geological features, including the multicolored layers of rock and steep mesa walls, which are similar to those in the Grand Canyon. It is part of Palo Duro Canyon State Park. The State Park had 442,242 visitors in 2022.
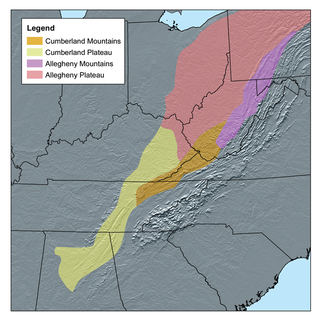
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms "Allegheny Plateau" and the "Cumberland Plateau" both refer to the dissected plateau lands lying west of the main Appalachian Mountains. The terms stem from historical usage rather than geological difference, so there is no strict dividing line between the two. Two major rivers share the names of the plateaus, with the Allegheny River rising in the Allegheny Plateau and the Cumberland River rising in the Cumberland Plateau in Harlan County, Kentucky.
The exposed geology of the Bryce Canyon area in Utah shows a record of deposition that covers the last part of the Cretaceous Period and the first half of the Cenozoic era in that part of North America. The ancient depositional environment of the region around what is now Bryce Canyon National Park varied from the warm shallow sea in which the Dakota Sandstone and the Tropic Shale were deposited to the cool streams and lakes that contributed sediment to the colorful Claron Formation that dominates the park's amphitheaters.

The Cumberland Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern section of the Appalachian Mountains. They are located in western Virginia, southwestern West Virginia, the eastern edges of Kentucky, and eastern middle Tennessee, including the Crab Orchard Mountains. Their highest peak, with an elevation of 4,223 feet (1,287 m) above mean sea level, is High Knob, which is located near Norton, Virginia.

The exposed geology of the Capitol Reef area presents a record of mostly Mesozoic-aged sedimentation in an area of North America in and around Capitol Reef National Park, on the Colorado Plateau in southeastern Utah.

Bear Rocks is a widely recognized symbol of West Virginia wilderness and among the most frequently photographed places in the state. It is a well-known landmark on the eastern edge of the plateau that includes the Dolly Sods Wilderness. It sits in a high-elevation heathland punctuated with wind-carved sandstone outcrops and is home to more than a dozen rare plant and animal species. Situated on the crest of the Allegheny Front, Bear Rocks afford vistas over the South Branch Potomac River. Visibility can extend eastward to the Shenandoah National Park in Virginia.
The geology of Tennessee is as diverse as its landscapes. Politically, Tennessee is broken up into three Grand Divisions: East, Middle, and West Tennessee. Physically, Tennessee is also separated into three main types of landforms: river valley plain, highlands and basins, and mountains.

The Geology of Pennsylvania consists of six distinct physiographic provinces, three of which are subdivided into different sections. Each province has its own economic advantages and geologic hazards and plays an important role in shaping everyday life in the state. From the southeast corner to the northwest corner of the state, they include: the Atlantic Plain Province, the Piedmont Province, the New England Province, the Ridge and Valley Province, the Appalachain Province, and the Central Lowlands Province.

The Silurian Tuscarora Formation — also known as Tuscarora Sandstone or Tuscarora Quartzite — is a mapped bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, Maryland, West Virginia, and Virginia, US.

Hindostan Falls is an extinct unincorporated community in Center Township, Martin County, in the U.S. state of Indiana.

The Pennsylvanian Pottsville Formation is a mapped bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, western Maryland, West Virginia, Ohio, and Alabama. It is a major ridge-former in the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians of the eastern United States. The Pottsville Formation is conspicuous at many sites along the Allegheny Front, the eastern escarpment of the Allegheny or Appalachian Plateau.

Ablation Point, also known as Punta Ablación, is the eastern extremity of a hook-shaped rock ridge marking the north side of the entrance to Ablation Valley, on the east coast of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It was first photographed from the air on 23 November 1935 by Lincoln Ellsworth and mapped from these photographs by W.L.G. Joerg. It was roughly surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) and resurveyed in 1949 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS). It was named by FIDS for nearby Ablation Valley. The site lies within Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.147.
A tableland is an area containing elevated landforms characterized by a distinct, flat, nearly level, or gently undulating surface. They often exhibit steep, cliff-like edges, known as escarpments, that separate them from surrounding lowlands. Depending on either their size, other physical characteristics, or geographic location, the landforms comprising a tableland are individually referred to by a number of names including either butte, mesa, plateau, potrero, tepui, or tuya. Table Mountains are also a type of tableland. A homologous landform under the sea is called either a tablemount or guyot.

Cape Town lies at the south-western corner of the continent of Africa. It is bounded to the south and west by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the north and east by various other municipalities in the Western Cape province of South Africa.

The Danxia landform refers to various landscapes found in southeast, southwest and northwest China that "consist of a red bed characterized by steep cliffs". It is a unique type of petrographic geomorphology found in China. Danxia landform is formed from red-coloured sandstones and conglomerates of largely Cretaceous age. The landforms look very much like karst topography that forms in areas underlain by limestones, but since the rocks that form danxia are sandstones and conglomerates, they have been called "pseudo-karst" landforms. They were formed by endogenous forces and exogenous forces.

The Shinarump Conglomerate is a geologic formation found in the Four Corners region of the United States. It was deposited in the early part of the Late Triassic period.

A pinnacle, tower, spire, needle or natural tower in geology is an individual column of rock, isolated from other rocks or groups of rocks, in the shape of a vertical shaft or spire. is a natural geomorphological shape and a structural denudation shape of the relief. It is about an isolated, tall and often also slender column or prism, reminiscent of a tower in its shape. A specific type of rock tower is the rock needle.
The Mount Simon Sandstone is an Upper Cambrian sandstone and is found in many states in the Midwest such as Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, Illinois, and Missouri.

The Stob Earth Pyramids are rock formations, known as hoodoos, situated at the foothills of the Rila mountain range in south-western Bulgaria. They span an area of 0.7 km2 near the village of Stob, Kyustendil Province. The rock formations are up to 12 m high and up to 40 m thick at the base. Their shape is mostly conical to mushroomlike. Some of the columns are topped by flat stones.

The geology of Virginia began to form at least 1.8 billion years ago. The oldest rocks in the state were metamorphosed during the Grenville orogeny, a mountain-building event beginning 1.2 billion years ago in the Proterozoic, which obscured older rocks. Throughout the Proterozoic and Paleozoic, Virginia experienced igneous intrusions, carbonate and sandstone deposition, and a series of other mountain-building events which defined the terrain of the inland parts of the state. The closing of the Iapetus Ocean formed the supercontinent Pangaea, and created additional small landmasses, some of which are now hidden beneath thick Atlantic Coastal Plain sediments. The region subsequently experienced the rifting open of the Atlantic ocean in the Mesozoic, the development of the Coastal Plain, isolated volcanism, and a series of marine transgressions that flooded much of the area. Virginia has extensive deposits of coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as deposits of other minerals and metals, including vermiculite, kyanite and uranium.

















