Related Research Articles

In graph theory, an isomorphism of graphsG and H is a bijection between the vertex sets of G and H

In graph theory, a vertex cover of a graph is a set of vertices that includes at least one endpoint of every edge of the graph.

Sergei Natanovich Bernstein was a Ukrainian and Russian mathematician of Jewish origin known for contributions to partial differential equations, differential geometry, probability theory, and approximation theory.

Éva Tardos is a Hungarian mathematician and the Jacob Gould Schurman Professor of Computer Science at Cornell University.
In computational complexity theory, the PCP theorem states that every decision problem in the NP complexity class has probabilistically checkable proofs of constant query complexity and logarithmic randomness complexity.

Vijay Virkumar Vazirani is an Indian American distinguished professor of computer science in the Donald Bren School of Information and Computer Sciences at the University of California, Irvine.
In graph theory, a path decomposition of a graph G is, informally, a representation of G as a "thickened" path graph, and the pathwidth of G is a number that measures how much the path was thickened to form G. More formally, a path-decomposition is a sequence of subsets of vertices of G such that the endpoints of each edge appear in one of the subsets and such that each vertex appears in a contiguous subsequence of the subsets, and the pathwidth is one less than the size of the largest set in such a decomposition. Pathwidth is also known as interval thickness, vertex separation number, or node searching number.

Martin Charles Golumbic is a mathematician and computer scientist known for his research on perfect graphs, graph sandwich problems, compiler optimization, and spatial-temporal reasoning. He is a professor emeritus of computer science at the University of Haifa, and was the founder of the journal Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence.
Frances Foong Chu Yao is a Taiwanese-American mathematician and theoretical computer scientist. She is currently a Chair Professor at the Institute for Interdisciplinary Information Sciences (IIIS) of Tsinghua University. She was Chair Professor and Head of the Department of computer science at the City University of Hong Kong, where she is now an honorary professor.
The Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC) is an academic conference in the field of theoretical computer science. STOC has been organized annually since 1969, typically in May or June; the conference is sponsored by the Association for Computing Machinery special interest group SIGACT. Acceptance rate of STOC, averaged from 1970 to 2012, is 31%, with the rate of 29% in 2012.
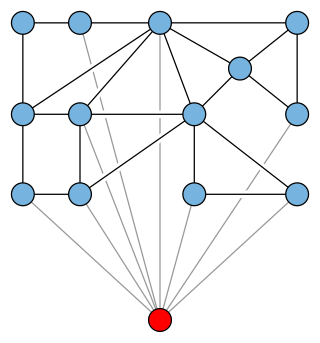
In graph theory, a branch of mathematics, an apex graph is a graph that can be made planar by the removal of a single vertex. The deleted vertex is called an apex of the graph. It is an apex, not the apex because an apex graph may have more than one apex; for example, in the minimal nonplanar graphs K5 or K3,3, every vertex is an apex. The apex graphs include graphs that are themselves planar, in which case again every vertex is an apex. The null graph is also counted as an apex graph even though it has no vertex to remove.
Eugene Michael Luks is an American mathematician and computer scientist, a professor emeritus of computer and information science at the University of Oregon. He is known for his research on the graph isomorphism problem and on algorithms for computational group theory.

Angelika Steger is a mathematician and computer scientist whose research interests include graph theory, randomized algorithms, and approximation algorithms. She is a professor at ETH Zurich.

Virginia Vassilevska Williams is a theoretical computer scientist and mathematician known for her research in computational complexity theory and algorithms. She is currently the Steven and Renee Finn Career Development Associate Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She is notable for her breakthrough results in fast matrix multiplication, for her work on dynamic algorithms, and for helping to develop the field of fine-grained complexity.
Oded Regev is an Israeli-American theoretical computer scientist and mathematician. He is a professor of computer science at the Courant institute at New York University. He is best known for his work in lattice-based cryptography, and in particular for introducing the learning with errors problem.
Benjamin E. Rossman is an American mathematician and theoretical computer scientist, specializing in computational complexity theory. He is currently an associate professor of computer science and mathematics at Duke University.
Envy-free pricing is a kind of fair item allocation. There is a single seller that owns some items, and a set of buyers who are interested in these items. The buyers have different valuations to the items, and they have a quasilinear utility function; this means that the utility an agent gains from a bundle of items equals the agent's value for the bundle minus the total price of items in the bundle. The seller should determine a price for each item, and sell the items to some of the buyers, such that there is no envy. Two kinds of envy are considered:
Tamar (Tami) Tamir is an Israeli computer scientist specializing in approximation algorithms and algorithmic mechanism design, especially for problems in resource allocation, scheduling, and packing problems. She is a professor in the Efi Arazi School of Computer Science of Reichman University.
Tali Kaufman is an Israeli theoretical computer scientist whose research topics have included property testing, expander graphs, coding theory, and randomized algorithms with sublinear time complexity. She is a professor of computer science at Bar-Ilan University, and a fellow of the Israel Institute for Advanced Studies.
Ryan O'Donnell is a Canadian theoretical computer scientist and a professor at Carnegie Mellon University. He is known for his work on the analysis of Boolean functions and for authoring the textbook on this subject. He is also known for his work on computational learning theory, hardness of approximation, property testing, quantum computation and quantum information.
References
- 1 2 3 Curriculum vitae (PDF), retrieved 2017-03-28
- ↑ Julia Chuzhoy at the Mathematics Genealogy Project
- 1 2 Julia Chuzhoy gives invited address at the International Congress of Mathematicians, Department of Computer Science, University of Chicago, June 1, 2015, archived from the original on September 19, 2015, retrieved March 29, 2017
- ↑ Awards and honors, Toyota Technological Institute , retrieved 2017-03-28
- ↑ "Awards", Proceedings of the 53rd Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (PDF), IEEE Computer Society, 2012
- ↑ Lipton, R. J.; Regan, K. W. (June 8, 2015), "Minor Insights Are Useful", Gödel’s Lost Letter and P=NP
- ↑ "ICM Plenary and Invited Speakers since 1897", International Mathematical Union (IMU), archived from the original on 2017-11-08, retrieved 2017-03-28