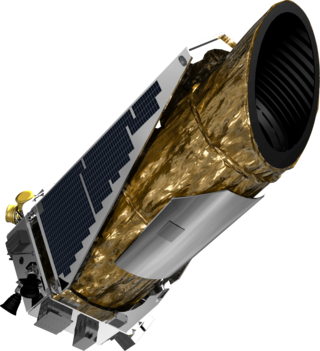
The Kepler space telescope is a defunct space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit. The principal investigator was William J. Borucki. After nine and a half years of operation, the telescope's reaction control system fuel was depleted, and NASA announced its retirement on October 30, 2018.

A Super-Earth is a type of exoplanet with a mass higher than Earth's, but substantially below those of the Solar System's ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, which are 14.5 and 17 times Earth's, respectively. The term "super-Earth" refers only to the mass of the planet, and so does not imply anything about the surface conditions or habitability. The alternative term "gas dwarfs" may be more accurate for those at the higher end of the mass scale, although "mini-Neptunes" is a more common term.

Kepler-9b is one of the first planets discovered outside the solar system (exoplanets) by NASA's Kepler Mission. It revolves around the star Kepler-9 within the constellation Lyra. Kepler-9b is the largest of three planets detected in the Kepler system by transit method; its mass is roughly half that of the planet Saturn, and it is the largest planet in its system. Kepler-9b and Kepler-9c display a phenomenon called orbital resonance, in which gravitational pull from each planet alters and stabilizes the orbit of the other. The planet's discovery was announced on August 26, 2010.

An exoplanet is a planet located outside the Solar System. The first evidence of an exoplanet was noted as early as 1917, but was not recognized as such until 2016; no planet discovery has yet come from that evidence. What turned out to be the first detection of an exoplanet was published among a list of possible candidates in 1988, though not confirmed until 2003. The first confirmed detection came in 1992, with the discovery of terrestrial-mass planets orbiting the pulsar PSR B1257+12. The first confirmation of an exoplanet orbiting a main-sequence star was made in 1995, when a giant planet was found in a four-day orbit around the nearby star 51 Pegasi. Some exoplanets have been imaged directly by telescopes, but the vast majority have been detected through indirect methods, such as the transit method and the radial-velocity method. As of 1 July 2024, there are 6,660 confirmed exoplanets in 4,868 planetary systems, with 995 systems having more than one planet. This is a list of the most notable discoveries.

Kepler-10, formerly known as KOI-72, is a Sun-like star in the constellation of Draco that lies 607 light-years from Earth. Kepler-10 was targeted by NASA's Kepler spacecraft, as it was seen as the first star identified by the Kepler mission that could be a possible host to a small, transiting exoplanet. The star is slightly less massive, slightly larger, and slightly cooler than the Sun; at an estimated 11.9 billion years in age, Kepler-10 is 2.3 times the age of the Sun.

Kepler-20f (also known by its Kepler Object of Interest designation KOI-070.05) is an exoplanet orbiting the Sun-like star Kepler-20, the second outermost of five such planets discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft. It is located approximately 929 light-years (285 parsecs, or about 8.988×1015 km) from Earth in the constellation Lyra. The exoplanet was found by using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. The planet is notable as it has the closest radius to Earth known so far.

Kepler-37b is an exoplanet orbiting the star Kepler-37 in the constellation Lyra. As of February 2013, it is the smallest planet discovered around a main-sequence star, with a radius slightly greater than that of the Moon and slightly smaller than that of Mercury. The measurements do not constrain its mass, but masses above a few times that of the Moon give unphysically high densities.

A mega-Earth is a proposed neologism for a massive terrestrial exoplanet that is at least ten times the mass of Earth. Mega-Earths would be substantially more massive than super-Earths. The term "mega-Earth" was coined in 2014, when Kepler-10c was revealed to be a Neptune-mass planet with a density considerably greater than that of Earth, though it has since been determined to be a typical volatile-rich planet weighing just under half that mass.

K2-33b is a very young super-Neptune exoplanet, orbiting the pre-main-sequence star K2-33. It was discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft on its "Second Light" mission. It is located about 456 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Scorpius. The exoplanet was found by using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured.

K2-33 is an extremely young pre-main-sequence star located about 453 light-years (139 pc) away from the Earth in the constellation of Scorpius. It is known to host one planet, a super-Neptune, named K2-33b. It is also notable for its young age.

K2-148b is a confirmed super-Earth, probably rocky, closely orbiting a small orange dwarf star. It is the innermost of three Super-Earths around the star K2-148, which is in a wide binary pair with the M0.5V red dwarf EPIC 220194953. K2-148b is the smallest planet of the system, at about a third larger than Earth, and could be terrestrial in nature. However, the three planets do not exhibit significant transit timing variations, implying that they could have relatively low masses. The planet was validated in early 2018 by Hirano et al. and is too hot for known life.
K2-141b is a massive rocky exoplanet orbiting extremely close to a K Type orange main-sequence star K2-141. The planet was first discovered by the Kepler space telescope during its K2 “Second Light” mission and later observed by the HARPS-N spectrograph. It is classified as an Ultra-short Period (USP) and is confirmed to be terrestrial in nature. Its high density implies a massive iron core taking up between 30% and 50% of the planet's total mass.
K2-155d is a potentially habitable Super-Earth exoplanet in the K2-155 system. It is the outermost of three known planets orbiting around the K-type star K2-155 in the constellation Taurus. It is one of 15 new exoplanets around red dwarf stars discovered by Japanese astronomer Teruyuki Hirano of the Tokyo Institute of Technology and his team. The team used data from NASA's Kepler Space Telescope during its extended K2 "Second Light" mission. K2-155d orbits near the so-called habitable zone of its system, and has the potential to host liquid water.
K2-229b is an extremely hot, solid, iron-rich exoplanet in a close orbit around the active K-dwarf K2-229 in the constellation Virgo, 335 light years away from Earth.

K2-236b is a Neptune-like exoplanet that orbits an F-type star. It is also called EPIC 211945201 b. Its mass is 27 Earths, it takes 19.5 days to complete one orbit of its star, and is 0.148 AU from its star. Its discovery was announced in 2018. This was the first exoplanet discovered by scientists based in India. The discoverers were Abhijit Chakraborty (PRL), Arpita Roy (Caltech), Rishikesh Sharma (PRL), Suvrath Mahadevan, Priyanka Chaturvedi, Neelam J. S. S. V. Prasad (PRL), and B. G. Anandarao (PRL).

NGTS-3Ab is a gas giant exoplanet that orbits a G-type star. Its mass is 2.38 Jupiters, it takes 1.7 days to complete one orbit of its star, and is 0.023 AU from its star. Its discovery was announced in 2018. The Jupiter-like planet is discovered by 39 astronomers, mainly Max Günther, Didier Queloz, Edward Gillen, Laetitia Delrez, and Francois Bouchy.

HD 89345 b is a Neptune-like exoplanet that orbits a G-type star. It is also called K2-234b. Its mass is equivalent to 35.7 Earths, it takes 11.8 days to complete one orbit of its star, and is 0.105 AU away from its star. It was discovered by a team of 43 astrophysicists, one of which was V. Van Eylen, and was announced in 2018.

K2-288Bb is a super-Earth or mini-Neptune exoplanet orbiting in the habitable zone of K2-288B, a low-mass M-dwarf star in a binary star system in the constellation of Taurus about 226 light-years from Earth. It was discovered by citizen scientists while analysing data from the Kepler spacecraft's K2 mission, and was announced on 7 January 2019. K2-288 is the third transiting planet system identified by the Exoplanet Explorers program, after the six planets of K2-138 and the three planets of K2-233.
K2-66b is a confirmed mega-Earth orbiting the subgiant K2-66, about 520 parsecs (1,700 ly) from Earth in the direction of Aquarius. It is an extremely hot and dense planet heavier than Neptune, but with only about half its radius.

















