C11orf49 is a protein coding gene that in humans encodes for the C11orf49 protein. It is heavily expressed in brain tissue and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, with the latter being an important component of the immune system. It is predicted that the C11orf49 protein acts as a kinase, and has been shown to interact with HTT and APOE2.

C2CD4D, or C2 calcium-dependent domain-containing protein 4D is a protein product of the human genome. The gene that codes for this protein is found on chromosome 1, from 150,076,963 to 150,079,657. The gene contains 2 exons and encodes 353 amino acids. Synonyms for C2CD4D are "FAM148D" and NP_001129475. C2CD4D contains a conserved metal binding domain that is a known as Protein kinase C conserved region 2, subgroup 1. This motif is known to be a member of the C2 superfamily, which is present in phospholipases, protein kinases C, and synaptotagmins. The amino acid sequence of C2CD4D can be accessed at Prior to any post translational modification, C2CD4D has a molecular weight of 37.6 kdal. Although scientists have not yet determined where C2CD4D functions within the cell, C2CD4D has a predicted isoelectric point of 11.636 which severely limits the places in which it can be effective. In addition, C2CD4D does not contain any predicted transmembrane domains or any predicted signal peptides.

METTL26, previously designated C16orf13, is a protein-coding gene for Methyltransferase Like 26, also known as JFP2. Though the function of this gene is unknown, various data have revealed that it is expressed at high levels in various cancerous tissues. Underexpression of this gene has also been linked to disease consequences in humans.

DEP Domain Containing Protein 1B also known as XTP1, XTP8, HBV XAg-Transactivated Protein 8, [formerly referred to as BRCC3] is a human protein encoded by a gene of similar name located on chromosome 5.

Transmembrane protein 134 is a protein encoded by the TMEM134 gene. TMEM134 does not have any other known aliases. There are two transmembrane domains and a domain of unknown function (DUF872). Evolutionary, the majority of the organisms that have this gene are primates and mammals, although there are some organisms dating back to Drosophila and C. elegans. Through current research, there has not been any confirmed function of TMEM134.

PROSER2, also known as proline and serine rich 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PROSER2 gene. PROSER2, or c10orf47(Chromosome 10 open reading frame 47), is found in band 14 of the short arm of chromosome 10 (10p14) and contains a highly conserved SARG domain. It is a fast evolving gene with two paralogs, c1orf116 and specifically androgen-regulated gene protein isoform 1. The PROSER2 protein has a currently uncharacterized function however, in humans, it may play a role in cell cycle regulation, reproductive functioning, and is a potential biomarker of cancer.
C20orf96 is a protein-coding gene in humans. It codes for an unknown protein known as uncharacterized protein C20orf96, predicted to be a nuclear protein. The function and biological processes of the gene is not well understood by the scientific community yet.

C8orf48 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C8orf48 gene. C8orf48 is a nuclear protein specifically predicted to be located in the nuclear lamina. C8orf48 has been found to interact with proteins that are involved in the regulation of various cellular responses like gene expression, protein secretion, cell proliferation, and inflammatory responses. This protein has been linked to breast cancer and papillary thyroid carcinoma.

PRR29 is a protein encoded by the PRR29 gene located in humans on chromosome 17 at 17q23.
Coiled-coil domain containing protein 180 (CCDC180) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC180 gene. This protein is known to localize to the nucleus and is thought to be involved in regulation of transcription as are many proteins containing coiled-coil domains. As it is expressed most highly in the testes and is regulated by SRY and SOX transcription factors, it could be involved in sex determination.

Transmembrane Protein 176B, or TMEM176B is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM176B gene. It is thought to play a role in the process of maturation of dendritic cells.
Cardiac-enriched FHL2-interacting protein (CEFIP) is a protein encoded by the gene C10orf71 on chromosome 10 open reading frame 71. It is primarily understood that this gene is moderately expressed in muscle tissue and cardiac tissue.

CRACD-like protein. previously known as KIAA1211L is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRACDL gene. It is highly expressed in the cerebral cortex of the brain. Furthermore, it is localized to the microtubules and the centrosomes and is subcellularly located in the nucleus. Finally, CRACDL is associated with certain mental disorders and various cancers.
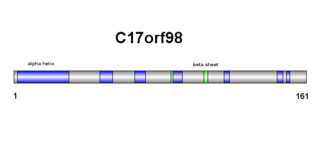
C17orf98 is a protein which in humans is coded by the gene c17orf98. The protein is derived from Homo sapiens chromosome 17. The C17orf98 gene consists of a 6,302 base sequence. Its mRNA has three exons and no alternative splice sites. The protein has 154 amino acids, with no abnormal amino acid levels. C17orf98 has a domain of unknown function (DUF4542) and is 17.6kDa in weight. C17orf98 does not belong to any other families nor does it have any isoforms. The protein has orthologs with high percent similarity in mammals and reptiles. The protein has additional distantly related orthologs across the metazoan kingdom, culminating with the sponge family.

Chromosome 9 open reading frame 43 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C9orf43 gene. The gene is also known as MGC17358 and LOC257169. C9orf43 contains DUF 4647 and a polyglutamine repeat region although protein function is not well understood.

Transmembrane protein 125 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the TMEM125 gene. It has 4 transmembrane domains and is expressed in the lungs, thyroid, pancreas, intestines, spinal cord, and brain. Though its function is currently poorly understood by the scientific community, research indicates it may be involved in colorectal and lung cancer networks. Additionally, it was identified as a cell adhesion molecule in oligodendrocytes, suggesting it may play a role in neuron myelination.

Tubulin epsilon and delta complex 2 (TEDC2), also known as Chromosome 16 open reading frame 59 (C16orf59), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TEDC2 gene. Its NCBI accession number is NP_079384.2.

Transmembrane protein 221 (TMEM221) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM221 gene. The function of TMEM221 is currently not well understood.
C3orf56 is a protein encoding gene found on chromosome 3. Although, the structure and function of the protein is not well understood, it is known that the C3orf56 protein is exclusively expressed in metaphase II of oocytes and degrades as the oocyte develops towards the blastocyst stage. Degradation of the C3orf56 protein suggests that this gene plays a role in the progression from maternal to embryonic genome and in embryonic genome activation.
Lysine-rich nucleolar protein 1 (KNOP1) is a protein which in human's is encoded by the KNOP1 gene. Aliases for KNOP1 include TSG118, C16orf88, and FAM191A.