History
Inal the Great, the King of Circassia from 1427 to 1453 who unified all Circassians into one state, [2] [3] divided Circassia into several provinces, Kabardia being one of them. After his death, Kabardia became independent.
Without a native tradition of written history, most of what is known about Kabardian history comes from their contacts with neighbors. When the Golden Horde broke up about 1500 the steppe nomads became organized as the Nogai Horde. They and the Crimeans began or continued to raid the north Caucasus. Walter Richmond reports raids for the years : ‘no later than 1476’, 1491, 1498, circa 1500 ‘every spring’, 1521, 1518, a 10-year break after 1519, 1539, 1547, 1554, 1567, 1578, 1606-1635 "seven times’, 1670s, 1708, 1720, 1735, 1740s, 1760–61 and [4] 1777.
Alliances 1500–1600
Since the Crimeans were also raiding Russia (see Crimean–Nogai raids into East Slavic lands) the two peoples were natural allies. There had been an isolated group of Cossacks on the lower Terek from perhaps 1520. In 1552 a Kabardian embassy reached Moscow. In 1556 Kabardians and Cossacks took the Turkish fort Temryuk on the Taman peninsula. When Astrakhan was captured in 1556 Russia had a base 250 miles northeast of Kabardia. A few Kabardians entered Russian service. Temryuk came to power some time before 1558 and in 1561 his daughter married Ivan the Terrible. In 1567 Russia founded Sunzha Ostrog at the junction of the Terek and Sunzha in Lesser Kabardia. In 1569, after the Turks failed to take Astrakhan, their retreating troops were killed by the Kabardians. In 1570 Temryuk was killed fighting the Crimeans. In 1588 there was another treaty of alliance. With the death of Temryuk and losses in the Livonian War Russia disengaged from the Caucasus for about 200 years. Sunzha Ostrog was abandoned in 1571, rebuilt in 1578 and abandoned a year later.
1600–1760
In 1645 a regiment was moved to Tersk (it has been re-established early in the century). Kabardia split into two factions, the pro-Russian Baksan and pro-Crimean Kashkatau (originally the alliances were opposite, but they switched sides some time after 1722.). One side brought in Russians from Astrakhan. The Nekrasov Cossacks settled on the Kuban about 1711. More Cossacks settled on the Terek and Kizlyar was founded in 1736. In 1739 Kabardia was declared a buffer state between the Russian and Ottoman empires. [5] In 1744 Koltsov and 400 Cossacks arrived to support the Baksan faction. Another force was sent in 1753.
Conquest
Kabardia came under Russian control between about 1769 and 1830. They moved west from the Terek country, southwest from Astrakhan and to a lesser degree southeast from Azov. From 1769 Russia intervened in Georgia south of the mountains. This required them to hold the Georgian Military Highway which passed through Kabardia. Georgia was annexed in 1800.
Mozdok was established in 1763 and in 1769 Russia attacked Kabardia for the first time. The 1774 Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca declared Kabardia a vassal of the Crimean Khanate. [6] In 1777 the Mozdok line was begun which was to run from Mozdok northwest to Azov. From 1779 a line of forts was run west along the Malka River, cutting off Kabardian pastures. In 1779 von Shtrandman was sent to the north Caucasus and fought 1500 Kabardians at a place called Fort Pavolosk. There was a major battle on the Malka River and later 3000 Kabardians were defeated in the Baksan country. This led to a treaty but there was more fighting in 1780. By 1783 the Georgian Military Highway had been improved sufficiently to be used by wheeled traffic. In 1785-91 Sheikh Mansur attempted to lead an anti-Russian holy war in the north Caucasus. During the Russo-Turkish War (1787–92) Russian forces thrice crossed Circassian territory attempting to take the Black Sea fort of Anapa. Late in this war Batal Pasha invaded the north Caucasus and was defeated. In 1791 Ust-Labinsk was established in Circassia at the junction of the Kuban and Laba rivers. By 1793 25000 Cossacks were settled along the Mozdok line.
In the early nineteenth century a plague struck the north Caucasus which lasted until the 1830s. It is estimated that Kabardia lost 90% of its population, falling from 200,000 in 1790 to 30,000 in 1830. In 1804 there was a general uprising all over the north Caucasus. The Russians won at least three battles mainly because of their artillery. One involved 13000 men on both sides and another involved 7000 Kabardians. Around 1810 Russia destroyed 200 villages. In 1822 new forts were built on the North Caucasus Line. In the 1820s Aleksey Petrovich Yermolov led a campaign which is said to have completely depopulated Lesser Kabardia. After about 1830 the Kabardians had been subdued by plague and war and the Russians turned their attention to the Murid War in the east and the Russo-Circassian War in the west.

Circassia, also known as Zichia, was a country and a historical region in Eastern Europe. It spanned the western coastal portions of the North Caucasus, along the northeastern shore of the Black Sea. Circassia was conquered by the Russian Empire during the Russo-Circassian War (1763–1864), after which approximately 99.5-99.8% of the Circassian people were either exiled or massacred in the Circassian genocide.

The Terek is a major river in the Northern Caucasus. It originates in the Mtskheta-Mtianeti region of Georgia and flows through North Caucasus region of Russia into the Caspian Sea. It rises near the juncture of the Greater Caucasus Mountain Range and the Khokh Range, to the southwest of Mount Kazbek, winding north in a white torrent between the town of Stepantsminda and the village of Gergeti toward the Russian region North Ossetia and the city of Vladikavkaz. It turns east to flow through Chechnya and Dagestan before dividing into two branches which empty into the Caspian Sea. Below the city of Kizlyar it forms a swampy river delta around 100 kilometres (62 mi) wide. The river is a key natural asset in the region, providing irrigation and hydroelectric power in its upper reaches.

The Circassians or Circassian people, also called Cherkess or Adyghe are a Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation who originated in Circassia, a region and former country in the North Caucasus.
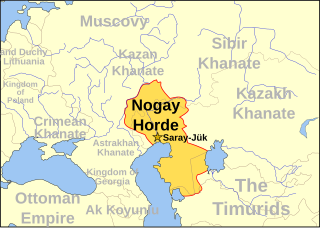
The Nogai Horde was a confederation founded by the Nogais that occupied the Pontic–Caspian steppe from about 1500 until they were pushed west by the Kalmyks and south by the Russians in the 17th century. The Mongol tribe called the Manghuds constituted a core of the Nogai Horde.

The Terek Cossack Host was a Cossack host created in 1577 from free Cossacks who resettled from the Volga to the Terek River. The local aboriginal Terek Cossacks joined this Cossack host later. In 1792 it was included in the Caucasus Line Cossack Host and separated from it again in 1860, with the capital of Vladikavkaz. In 1916 the population of the Host was 255,000 within an area of 1.9 million desyatinas.

The peoples of the Caucasus, or Caucasians, are a diverse group comprising more than 50 ethnic groups throughout the Caucasus.

The Russo-Circassian War, also known as the Russian invasion of Circassia, was the invasion of Circassia by Russia, starting in 1763 (O.S) with the Russian Empire assuming authority in Circassia, followed by the Circassian refusal, and ending 100 years, 10 months and 6 days later with the last army of Circassia defeated on 21 May 1864 (O.S), making it exhausting and casualty-heavy for both sides. The Russo-Circassian War was the longest war both Russia and Circassia have ever fought and the longest war in the Caucasus region.

The Russian conquest of the Caucasus mainly occurred between 1800 and 1864. The Russian Empire sought to control the region between the Black Sea and Caspian Sea. South of the mountains was the territory that is modern Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Iran and Turkey. North of the mountains was the North Caucasus region of modern Russia. The difficult conquest of the intervening mountains is known as the Caucasian War. Multiple wars were fought against the local rulers of the regions, as well as the dominant powers, the Ottoman Empire and Qajar Iran, for control. By 1864 the last regions were brought under Russian control.
Inal Nekhu was the Supreme Prince (King) of Circassia from 1427 to 1453 who unified all Circassians into one state. He led campaigns into several countries and expanded borders on all directions. He was the founder of several Circassian tribes, mainly Kabardia, Besleney, Temirgoy, Zhaney, and Hatuqwai.

The Nogais are a Kipchak people who speak a Turkic language and live in Southeastern Europe, North Caucasus, Volga region, Central Asia and Turkey. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well as in Karachay-Cherkessia, Chechnya and Astrakhan Oblast; some also live in Dobruja, Turkey, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Ukraine and a small Nogai diaspora is found in Jordan. They speak the Nogai language and are descendants of various Mongolic and Turkic tribes who formed the Nogai Horde. There are eight main groups of Nogais: the Ak Nogai, the Karagash, the Kuban-Nogai, the Kundraw-Nogai, the Qara-Nogai, the Utars, Bug-Nogai, and the Yurt-Nogai.

The Kalmyk Khanate was an Oirat Mongol khanate on the Eurasian steppe. It extended over modern Kalmykia and surrounding areas in the North Caucasus, including Stavropol and Astrakhan. During their independence, the Kalmyks both raided and allied with Russia in turn, engaging in numerous military expeditions against the Crimean Tatars, the Ottoman Empire, neighboring Muslim tribes, and the highlanders of the North Caucasus. The Khanate was annexed by the Russian Empire in 1771.
Prince Idar was a Circassian ruler of the Caucasus. He was the son of Prince Inarmaz, and the grandson of Prince Tabula. Prince Inarmaz himself was the eldest of the three grandsons of Prince Inal. His rule spanned over the period of 1525 to 1540.

The Russo-Persian War of 1651–1653 was an armed conflict in the North Caucasus fought between the Safavid Empire and the Tsardom of Russia, associated with the Safavid plans to strengthen its position in the region and to exclude Russia. The main issue involved the expansion of a Russian garrison on the Koy Su River, as well as the construction of several new fortresses, in particular the one built on the Iranian side of the Terek River. The Safavid government then sent troops, and destroyed the fortress while expelling its Russian garrison. In 1653 Alexis of Russia and the Russian government, which thought about sending the Russian Zaporozhian Army, but did not want to disperse its forces, sent an embassy to Persia for a peaceful settlement of the conflict. Shah Abbas II agreed, stating that the conflict was initiated without his consent.

The North Caucasus Line was a line of Russian forts and Cossack settlements along the north side of the Caucasus Mountains. Originating in the mid-16th century with a small number of free Cossacks near the Caspian Sea, from the mid-18th century the line was pushed west and used as a base to conquer the mountains to the south and to settle the steppes to the north.
Kurgoqo Atajuq was the Kabardian Supreme Prince between 1695 and 1709.

Temryuk Idar or Temroqwa Idar was a prince of the Circassian Kabardian princedom and its head of power for part of the sixteenth century. His fame was largely due to the association of his name with the alliance with Ivan IV and the marriage of his daughter, Maria Temryukovna. When Temryuk came to power, he put down the revolts of the disputing princes, and helped Circassia become a military power within the North Caucasus.
The Temryuk War or Crimean-Circassian War of 1551–1556 was a military conflict between the Crimean Khanate and the Kabardian Principality.
Misost Bematiqwa was a member of the Kabardian royal family and the Atajuq family. He was the Grand Prince between 1785 and 1788.
Russian–Kumyk wars — a series of military conflicts between the Russian Tsardom and the Kumyk Tarki Shamkhalate and other Kumyk states and feudal possessions during the 16th–18th centuries. At the end of the 18th century, as well as during and after the Caucasian War, and throughout the end of the 19th and the beginning of the 20th centuries, conflicts continued in the form of uprisings in Shamkhalate, Northern Kumykia, Southern Kumykia, and in the form of anti-colonial protests of individual villages (societies). In the result of these wars and uprisings, some Kumyk areas and villages were destroyed several times over.

The Sheikh Mansur Movement, also known as the 1785–1791 Insurgency in the North Caucasus, was a major war between the Russian Empire and the North Caucasians, caused by the Chechen religious and military leader Sheikh Mansur, who opposed the Russian expansionist policies and wanted to unite the North Caucasians under one, single, Islamic state.

















