
Mindanao is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. According to the 2020 census, Mindanao has a population of 26,252,442 people, while the entire island group has an estimated population of 27,021,036 according to the 2021 census.

The Philippines is an archipelago that comprises 7,641 islands with a total land area of 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi). It is the world's fifth largest island country. The eleven largest islands contain 95% of the total land area. The largest of these islands is Luzon at about 105,000 square kilometers (40,541 sq mi). The next largest island is Mindanao at about 95,000 square kilometers (36,680 sq mi). The archipelago is around 800 kilometers (500 mi) from the Asian mainland and is located between Taiwan and Borneo.
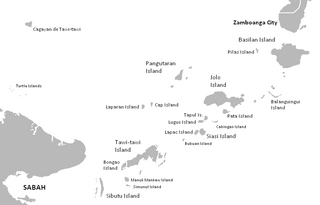
The Sulu Archipelago is a chain of islands in the Pacific Ocean, in the southwestern Philippines. The archipelago forms the northern limit of the Celebes Sea and southern limit of the Sulu Sea. The Sulu Archipelago islands are within the Mindanao island group, consisting of the provinces of Basilan, Sulu, and Tawi-Tawi; hence the archipelago is sometimes referred to as Basulta, derived from the first syllables of the three provinces.

Zamboanga was a province of the Philippines located in the western region of the southern island of Mindanao, Philippines.

The Sulu Sea is a body of water in the southwestern area of the Philippines, separated from the South China Sea in the northwest by Palawan and from the Celebes Sea in the southeast by the Sulu Archipelago. Borneo is found to the southwest and Visayas to the northeast.
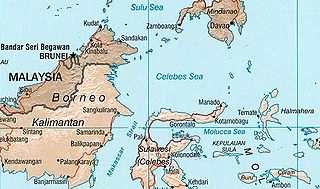
The Celebes Sea, or Sulawesi Sea, of the western Pacific Ocean is bordered on the north by the Sulu Archipelago and Sulu Sea and Mindanao Island of the Philippines, on the east by the Sangihe Islands chain, on the south by Sulawesi's Minahasa Peninsula, and on the west by northern Kalimantan in Indonesia. It extends 420 miles (675 km) north-south by 520 mi (840 km) east-west and has a total surface area of 110,000 square miles (280,000 km2), to a maximum depth of 20,300 feet (6,200 m). South of the Cape Mangkalihat, the sea opens southwest through the Makassar Strait into the Java Sea.
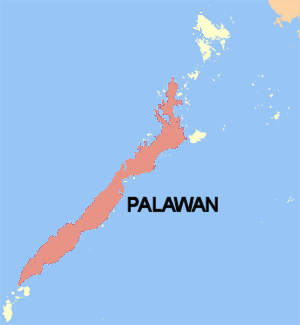
Palawan is the largest island of the province of Palawan in the Philippines and fifth-largest by area and tenth-most populous island of the country, with a total population of 994,101 as of 2020 census. The north west coast of the island is along the South China Sea, while the south east coast forms part of the northern limit of the Sulu Sea. Much of the island remains traditional and is considered by some as under-developed. Abundant wildlife, jungle mountains, and some white sandy beaches attract many tourists, as well as international companies looking for development opportunities.
The Central Philippine languages are the most geographically widespread demonstrated group of languages in the Philippines, being spoken in southern Luzon, Visayas, Mindanao, and Sulu. They are also the most populous, including Tagalog, Bikol, and the major Visayan languages Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Waray, Kinaray-a, and Tausug, with some forty languages all together.

Pamalican Island, also known as Pamalikan, is a small and sandy island of the Cuyo Islands in the Sulu Sea, between Palawan and Panay, in the north part of the Palawan Province of the Philippines. The island is set in the middle of a 7-square-kilometre (2.7 sq mi) coral reef. It has a length of 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi), and measures only 500 metres (1,600 ft) at its widest point. Pamalican can be found 7 miles southwest of Quiniluban island and 3 miles northeast of Manamoc island.

The Moro people or Bangsamoro people are the 13 Muslim-majority ethnolinguistic Austronesian groups of Mindanao, Sulu, and Palawan, native to the region known as the Bangsamoro. As Muslim-majority ethnic groups, they form the largest non-Christian population in the Philippines, and comprise about 5% of the country's total population, or 5 million people.

The Invasion of Palawan, was fought by U.S. liberation forces against the Japanese from 28 February to 22 April 1945, in a series of actions officially designated as Operations Victor I and II, and part of the campaign for the liberation of the Philippines during World War II, was waged to initiate the recapture of the southern islands of the Philippine archipelago, end the Japanese occupation, and secure them from remaining Japanese forces.

The Christian And Missionary Alliance Churches of the Philippines (CAMACOP) is a Christian evangelical group in the Philippines that originated from The Christian and Missionary Alliance (C&MA). It is one of the largest evangelical groups in the Philippines.
Dakut is located in the province of Sulu, in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, of the Philippines.
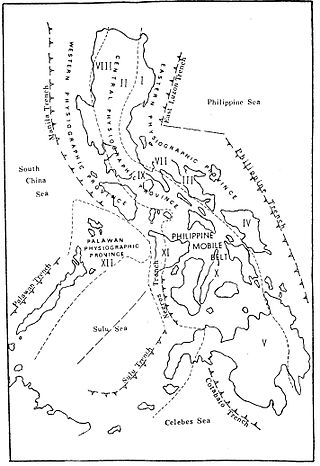
In the geology of the Philippines, the Philippine Mobile Belt is a complex portion of the tectonic boundary between the Eurasian Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate, comprising most of the country of the Philippines. It includes two subduction zones, the Manila Trench to the west and the Philippine Trench to the east, as well as the Philippine Fault System. Within the Belt, a number of crustal blocks or microplates which have been shorn off the adjoining major plates are undergoing massive deformation.

The first USC&GSS Pathfinder, also noted in some NOAA histories as "old Pathfinder", was a United States Coast and Geodetic Survey ship in service from 1899 to 1941, when she was beached in sinking condition on January 30, 1942, after 40 years service in the Philippines.

The Quiniluban Group is a group of islands in Palawan Province of the Philippines situated between the islands of Palawan and Panay in the Sulu Sea. The group is the northernmost in the Cuyo Archipelago, consisting of several islands and rocks. The easternmost of which is a circular group of islands surrounded by reef about 6 nautical miles in diameter. The largest of the circular group is Quiniluban Island. The island group also includes the upscale resort island of Pamican located about 5.6 nautical miles southwest of the circular group, and Manamoc Island located 3.0 nautical miles further southwest of Pamilacan.
Nagubat is an island located in the Antique province of the Philippines. In 1978 its elevation was recorded at 172 feet (52 m).
East Guhuan Island is part of the Philippine territory adjacent to the island of Sabah in the Sulu Sea, 15 km (9.3 mi) from Mangsee Island and is part of Barangay Mangsee under the Municipality of Balabac, Province of Palawan, Philippines.

Separatism in the Philippines refers to bids for secession or greater autonomy for certain areas in the Philippines. The scope of the article includes such efforts since the Philippine Revolution both currently and historical.
The Palawan Passage is a natural waterway in the southeastern South China Sea to the west of the island of Palawan in the Philippine Islands. It is deep and relatively free of navigational hazards, making it an important shipping route. The entire Palawan Passage lies within the exclusive economic zone of the Philippines and in waters the Government of the Philippines refers to as the West Philippine Sea.














