
Hampi or Hampe, also referred to as the Group of Monuments at Hampi, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Hampi (City), Ballari district now Vijayanagara district, east-central Karnataka, India. Hampi predates the Vijayanagara Empire; it is mentioned in the Ramayana and the Puranas of Hinduism as Pampa Devi Tirtha Kshetra. Hampi continues as a religious centre, with the Virupaksha Temple, an active Adi Shankara-linked monastery and various monuments belonging to the old city.

Vijayanagara was a city at the modern location of Hampi, in the Indian state of Karnataka. Vijayanagara was the capital city of the historic Vijayanagara Empire. Located on the banks of the Tungabhadra River, it spread over a large area and included sites in the Vijayanagara district, the Ballari district, and others around these districts. A part of Vijayanagara ruins known as the Group of Monuments at Hampi has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
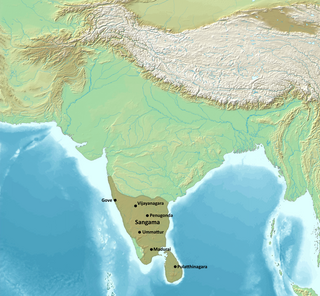
The Vijayanagara Empire was a medieval Hindu empire that covered much of the region of Southern India, ruling the lands of the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa, and some parts of Telangana and Maharashtra. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, members of a pastoralist cowherd community that claimed Yadava lineage. The empire rose to prominence as a culmination of attempts by the southern powers to ward off Turco-Persian Muslim invasions by the end of the 13th century. At its peak, it conquered almost all of Southern India's ruling dynasties and pushed the Turco-Persian sultans of the Deccan beyond the Tungabhadra-Krishna River doab region, in addition to annexing Gajapati Empire (Odisha) up to the Krishna River, thus becoming a notable power.

The Tungabhadra River is a river in India that starts and flows through the state of Karnataka during most of its course, Andhra Pradesh and ultimately joining the Krishna River near Murvakonda in Andhra Pradesh

Hospet or Hosapete is the largest and fastest-growing industrial city and district headquarters of the Vijayanagara district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Hosapete is known as "the steel city of Karnataka". It is located on the bank of the Tungabhadra River and is 13 km (8.1 mi) from Hampi (Vijayanagar). Hampi was once the capital of the Vijayanagara Empire. It has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Hospet is the connecting link between North and South Karnataka. It is 333 km (207 mi) from the state capital Bengaluru.

Lakkundi, also referred to as Lokkugundi, was a major city prior to the 14th century, and is now a village in Gadag District of Karnataka, India. By 10th century, it was already a major economic and commerce center with mint operations for South India, one mentioned in Kannada and Sanskrit inscriptions and texts. By 12th century, many Hindu and Jain temples had been consecrated here, along with public infrastructure such as stepwells and water reservoirs. Among the major temples are the Brahma Jinalaya (oldest), Mallikarjuna, Lakshminarayana, Manikeshwara, Naganatha, Kumbheshvara, Nanneshwara, Someshwara, Narayana, Nilakanteshwara, Kasivisesvara, Virabhadhara, Virupaksha, and others. As its importance and wealth grew, Lakkundi became one of the capitals of the Hoysala Empire.

North Karnataka is a geographical region in Deccan plateau from 300 to 730 metres elevation that constitutes the region of the Karnataka state in India and the region consists of 13 districts. It is drained by the Krishna River and its tributaries the Bhima, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha, and Tungabhadra. North Karnataka lies within the Deccan thorn scrub forests ecoregion, which extends north into eastern Maharashtra.

Virupaksha Temple is located in Hampi in the Vijayanagara district of Karnataka, India. It is part of the Group of Monuments at Hampi, designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The temple is dedicated to Sri Virupaksha. The temple was built by Lakkan Dandesha, a nayaka (chieftain) under the ruler Deva Raya II, also known as Prauda Deva Raya of the Vijayanagara Empire.

Vijayanagara architecture of 1336–1565 CE was a notable building idiom that developed during the rule of the imperial Hindu Vijayanagara Empire. The empire ruled South India, from their regal capital at Vijayanagara, on the banks of the Tungabhadra River in modern Karnataka, India. The empire built temples, monuments, palaces and other structures across South India, with the largest concentration in its capital. The monuments in and around Hampi, in the Vijayanagara district, are listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Karnataka, the sixth largest state in India, has been ranked as the third most popular state in the country for tourism in 2014. It is home to 507 of the 3600 centrally protected monuments in India, second only to Uttar Pradesh. The State Directorate of Archaeology and Museums protects an additional 752 monuments and another 25,000 monuments are yet to receive protection.

The City of Vijayanagara was the urban core of the imperial city and the surrounding principalities of the capital of the Vijayanagara empire during the 14th century to 16th century CE. Notes by foreign travellers such as Abdur Razzak, the Persian who visited Vijayanagara in 1440, mention seven fortifications before the gates to the royal palace. The large area between the first and third fortifications contained agricultural fields, gardens and residences. The notes of Robert Sewell describe countless shops and bazaars (markets) filled with people from different nationalities between this fortification and the palace.

The period of the Vijayanagara Empire is considered an age of prosperity in South India in the 14th century CE. Many travelogues written by visitors, ambassadors and authors of that time provide ample proof of a vibrant era. Agriculture was the main sustenance and the Tungabhadra was the life blood of the capital city.

The History of Karnataka goes back several millennia. Several great empires and dynasties have ruled over Karnataka and have contributed greatly to the history, culture and development of Karnataka as well as the entire Indian subcontinent. The Chindaka Nagas of central India Gangas, Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta, Chalukyas of Vengi, Yadava Dynasty of Devagiri were all of Kannada origin who later took to encouraging local languages.

Temple tanks are wells or reservoirs built as part of the temple complex near Indian temples. They are called pushkarini, kalyani, kunda, sarovara, tirtha, talab, pukhuri, ambalakkuḷam, etc. in different languages and regions of India. Some tanks are said to cure various diseases and maladies when bathed in. It is possible that these are cultural remnants of structures such as the Great Bath of Mohenjo-daro or Dholavira, which was part of the Indus Valley civilization. Some are stepwells with many steps at the sides.

The antiquity of architecture of Karnataka can be traced to its southern Neolithic and early Iron Age, Having witnessed the architectural ideological and utilitarian transformation from shelter- ritual- religion. Here the nomenclature 'Architecture' is as old as c.2000 B.C.E. The upper or late Neolithic people in order to make their shelters by their own they constructed huts made of wattle and doab, that were buttressed by stone boulders, presumably having conical roof resting on the bamboo or wooden posts into red murram or paved granite chips as revealed in archaeological excavations in sites like Brhamagiri, Sanganakallu, Tekkalakota, Piklihal. Megaliths are the dominant archaeological evidence of the early Iron Age. There are more than 2000 early Iron Age burial sites on record, who laid the foundation for a high non-perishable architecture in the form of various distinct architectural styles of stone-built burials, which are ritualistic in its character. The active religious architecture is evident 345 with that of the Kadamba Dynasty. Karnataka is a state in the southern part of India originally known as the State of Mysore. Over the centuries, architectural monuments within the region displayed a diversity of influences, often relaying much about the artistic trends of the rulers of twelve different dynasties. Its architecture ranges dramatically from majestic monolith, such as the Gomateshwara, to Hindu and Jain places of worship, ruins of ancient cities, mausoleums and palaces of different architectural hue. Mysore Kingdom (Wodeyar) rule has also given an architectural master structure in the St. Philomena's Church at Mysore which was completed in 1956, in addition to many Dravidian style architectural temples. Two of the monuments are listed under the UNESCO World Heritage List of 22 cultural monuments in India. Styles of Indo-Saracenic, Renaissance, Corinthian, Hindu, Indo-Greek and Indo-British style palaces were built in Mysore, the city of palaces. Sikh architecture at Bidar (1512) and also in Bangalore in 1956 can also be cited as having an impact on the architectural composition of the state.

The Kanakachalapathi temple is a 16th-century Hindu temple dedicated to the god Vishnu. It is located in the town of Kanakagiri, in the Gangavathi taluk of Koppal district in the Karnataka state, India. Kanakagiri, known in ancient times as "Swarnagiri" is about 3 km from the district headquarters Koppal city, 380 km north of Bangalore city and 200 km east of Belagavi city.

Hampi or Vijayanagara is a town in the Vijayanagara district in the Indian state of Karnataka. Located along the Tungabhadra River in the east and center part of the state, Hampi is near the city of Hosapete. It is famous for hosting the Hampi Group of Monuments, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Vijayanagara district is a district in the southern Indian state of Karnataka, located in the Kalyana-Karnataka region.















