
The Kamchatka Peninsula is a 1,250-kilometre-long (777 mi) peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about 270,000 km2 (104,248 sq mi). The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the 10,500-metre-deep (34,449 ft) Kuril–Kamchatka Trench.

Kronotsky (Кроноцкий) Nature Reserve is a nature area reserved for the study of natural sciences in the remote Russian Far East, on the coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It was created in 1934 and its current boundary contains an area of 10,990 km2 (4,240 sq mi). The largest lake in the reserve is Lake Kronotskoye, which covers an area of 246 square kilometres (95 sq mi). It also has Russia's only geyser basin, plus several mountain ranges with numerous volcanoes, both active and extinct. Due to its often harsh climate and its mix of volcanoes and geysers, it is frequently described as the Land of Fire and Ice.

Koryak Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' Located in the north of the Kamchatka Peninsula, in the valley of the Kuyul River in the Russian Far East, and in separate coastal areas on the coast of the Bering Sea. The reserve includes the surrounding mountains of the Gauvin Peninsula and adjacent waters in Lavrov Bay, and one fourth of the total area covers waters of the Bering Sea. Koryak is an important area for large colonies of nesting waterfowl and migratory seabirds; studies have found that the majority of the seabirds migrating along the Kamchatka Peninsula spend their winters in Japan. Protecting this connection was one of the reasons for the establishment of the reserve in 1995. The rivers of Koryak are important spawning grounds for salmon. Also protected are the floral communities of the reserve, which include prime examples of "Bering forest tundra". The reserve is situated in the Koryak Okrug of Kamchatka Krai. The reserve covers an area of 327,106 ha (1,262.96 sq mi). The site is part of a Ramsar wetland area of international importance.
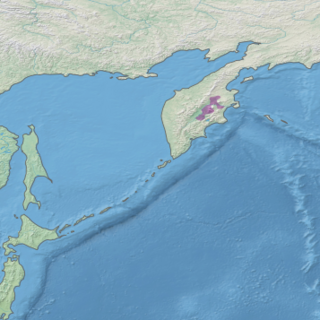
The Kamchatka–Kurile taiga ecoregion is a "conifer island" in the middle of the Kamchatka Peninsula, along the Kamchatka River. It is the easternmost example of Siberian taiga. The region has unusual ecological conditions, a "snow forest" that combines low temperatures, high humidity and boreal forest with heavy snowfall. The local ecology is also affected by volcanic activity. The region is about 300 km long (north-south), and averages about 100 km west-east. It is in the Palearctic realm, and mostly in the Boreal forests/taiga ecoregion with a humid continental climate, cool summer climate. It covers 147,064 km2 (56,782 sq mi).

The Kamchatka-Kurile meadows and sparse forests ecoregion covers the coastal zones of the Kamchatka peninsula, northern section of the Kuril Islands, and the Commander Islands in the Russian Far East. The region noted for its sparse forests of Betula ermanii, and also for extensive tall-herb meadows. It is in the Palearctic realm, and mostly in the boreal forests/taiga biome with a Humid continental climate, cool summer climate. It covers 146,334 km2 (56,500 sq mi).

The Selenge–Orkhon forest steppe ecoregion stretches across north central Mongolia, and follows the Selenga River northeast into Russia. The ecoregion is itself at high elevations, but surrounded by higher mountain ranges. As a transition zone between taiga and steppe, it features conifer forests on the north slopes of mountains, and pine/aspen stands on southern slopes. It has an area of 227,660 square kilometres (87,900 sq mi).

The Altai alpine meadow and tundra ecoregion is a terrestrial ecoregion covering the higher elevation of the Altai Mountains at the center of the "X" formed by the borders separating Russia, Kazakhstan, China, and Mongolia. The mountain peaks are the farthest north in Central Asia, separating the plains of Siberia to the north from the hot, dry deserts to the south. Altitudes above 2,400 meters display characteristics of tundra, with patches of alpine meadows and some trees immediately below the treeline. The ecoregion is in the montane grasslands and shrublands biome, and the Palearctic realm, with a humid continental climate. It covers an area of 90,132 square kilometres (34,800 sq mi).

The Sayan Alpine meadows and tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers the high areas of the Sayan Mountains above the treeline, between the Altai Mountains in the west and Lake Baikal in the east. The area is remote and protects diverse species of alpine flora and fauna. It has an area of 846,149 square kilometres (326,700 sq mi).

The Bering tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers a portion of northeastern Russia, between the Kolyma Mountains on the west, and the Bering Sea coast to the east. The area is an important stopping place for migratory birds. It has an area of 474,227 square kilometres (183,100 sq mi).

The Cherskii–Kolyma mountain tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers the higher elevations of the Chersky Range and the Kolyma Mountains, the only large mountain range in northern Russia. It is in the Palearctic realm, and tundra biome. It has an area of 556,589 square kilometres (214,900 sq mi).

The Chukchi Peninsula tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers the northern coast of Russia along the East Siberian Sea, a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. The climate is somewhat milder than would be expected for its latitude, but the moderating effects of the East Siberian Sea and Bering Sea permits summer daytime temperatures above 50 °F (10 °C). Many colonies of migrating birds visit the area. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm, and tundra biome. It has an area of 298,367 square kilometres (115,200 sq mi).

The Kola Peninsula tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers the northeastern half of the Kola Peninsula, along the coast of the White Sea, a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. The maritime effects of the White Sea create a milder climate than would be expected for a region of this latitude. It is in the Palearctic realm, and the tundra biome. It has an area of 58,793 square kilometres (22,700 sq mi).

The Northwest Russian-Novaya Zemlya tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion on the north coast of European Russia. It covers the southern shores of the White Sea, the coast of the Barents Sea east to the Yamal Peninsula, the southern half of Novaya Zemlya, and numerous inlets and islands. The low tundra wetlands are important breeding grounds for waterfowl. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm, and the tundra biome. It has an area of 284,122 square kilometres (109,700 sq mi).

The Taimyr-Central Siberian tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that broadly covers the Taymyr Peninsula in the Russian Far North. It ranges from the delta of the Yenisei River in the west, across the Taymyr Peninsula and Khatanga Gulf, to the Lena River delta in the east. The region is an important area for breeding birds. It is in the Palearctic realm in the tundra biome, and is mostly located in Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District of Krasnoyarsk Krai. It has an area of 954,670 square kilometres (368,600 sq mi).

The Trans-Baikal Bald Mountain tundra ecoregion covers the high-altitude peak zones above the treeline in a series of mountain ranges that stretch from the northern reaches of Lake Baikal to the western coastal ranges of the Okhotsk Sea. Floral communities are those of mountain tundra, with bare rock or permafrost under layers of moss and lichen. Because the ecoregion is aligned along a common latitude, it acts as a route for the transmission of species across Siberia. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm and the tundra biome. It has an area of 217,559 square kilometres (84,000 sq mi).

The Yamal–Gydan tundra ecoregion is an ecoregion that covers the Yamal Peninsula and Gydan Peninsula in northern Russia. Plants and animals are sparse, although the area is an important one for migratory birds, and for coastal sea mammals. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm, and the tundra biome. It has an area of 412,067 square kilometres (159,100 sq mi).

Pacific Coastal Mountain icefields and tundra is a tundra ecoregion in Alaska, British Columbia, and Yukon, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) categorization system.

The Interior Yukon-Alaska alpine tundra ecoregion covers alpine, sub-alpine, and boreal forest areas along the cordillera of Interior Alaska and south-central Yukon Territory. Geologically, they are the disjunct uplands of the Yukon-Tanana Terrane plus a southern extension of the Brooks Range. The cover is extensive 'dark taiga' of closed spruce forest, open forest of other species, and alpine vegetation at higher altitudes. The region is mostly wilderness and relatively untouched by human development.

The Ogilvie–MacKenzie alpine tundra ecoregion covers the mountainous middle of the Yukon Territory in Canada, with extensions into the Northwest Territories. The vegetation is alpine and subalpine open forest of stunted spruce, fir and pine. The area is rugged but sections appear to have been unglaciated in the late Pleistocene and there are therefore relic species in the region. The area is remote and supports large, sustainable predator-prey systems.

The Torngat Mountain tundra ecoregion covers the Torngat Mountains on the northeastern tip of the Labrador Peninsula where the provinces of Quebec and Newfoundland and Labrador meet. The mountains feature glacially carved U-shaped valleys and deep fjords. The vegetation over most of the territory is that of arctic tundra, herbaceous cover, or bare rock. The region supports seasonal polar bears, black bears, and caribou. The Atlantic coast is on the Atlantic Flyway for migratory birds.




















