| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| Languages | |
| English, formerly Karkin | |
| Religion | |
| Traditional tribal religion |
The Karkin people (also called Los Carquines in Spanish) are one of eight Ohlone peoples, indigenous peoples of California.
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| Languages | |
| English, formerly Karkin | |
| Religion | |
| Traditional tribal religion |
The Karkin people (also called Los Carquines in Spanish) are one of eight Ohlone peoples, indigenous peoples of California.
The Karkin people have historically lived in the Carquinez Strait region in the northeast portion of the San Francisco Bay estuary. [1] They spoke the Karkin language, the only documentation of which is a single vocabulary obtained by linguist-missionary Felipe Arroyo de la Cuesta at Mission Dolores in 1821 [2] from Karkin speaker Mariano Antonio Sagnegse. [3] According to de la Cuesta, karkin means 'to trade.' [4] [5] Although meager, the records of Karkin show that it constituted a distinct branch of Costanoan/Ohlone, strikingly different from the neighboring Chochenyo and other Ohlone languages spoken farther south and across the bay. [4] It is believed that there were about 200 Karkin speakers before colonization. [6]
Starting in 1787, some Karkin people began moving to Mission Dolores in present-day San Francisco. [7] In 1804 and 1807, Karkins resisted attempts by Mission Indians to recapture fugitive Indians who had escaped the mission. [8] The last Karkins moved to the mission between 1809 and 1810. [9] At the end of 1817, 49 Karkins were living at Mission Dolores. [10] By the end of 1823, 35 Karkin people lived at Mission Dolores, Mission San Francisco Solano, and Mission San Jose, seven of whom had been born in the missions. [11]
In 1925, Alfred Kroeber, then director of the Hearst Museum of Anthropology, declared the Ohlone extinct, which directly led to its losing federal recognition and land rights. [12]
The Confederated Villages of Lisjan is a tribe made up of Karkin and six other neighboring indigenous groups. [13]
Corrina Gould is a Karkin and Chochenyo activist who co-founded Indian People Organizing for Change and the Sogorea Te’ Land Trust, [14] and is the spokesperson for the Confederated Villages of Lisjan. [13]
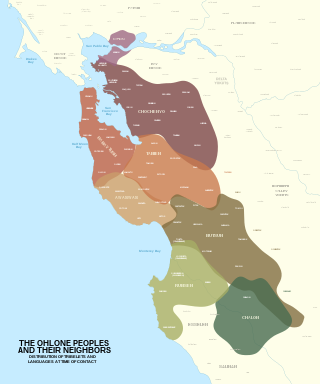
The Ohlone, formerly known as Costanoans, are a Native American people of the Northern California coast. When Spanish explorers and missionaries arrived in the late 18th century, the Ohlone inhabited the area along the coast from San Francisco Bay through Monterey Bay to the lower Salinas Valley. At that time they spoke a variety of related languages. The Ohlone languages make up a sub-family of the Utian language family. Older proposals place Utian within the Penutian language phylum, while newer proposals group it as Yok-Utian.

The Rumsen language is one of eight Ohlone languages, historically spoken by the Rumsen people of Northern California. The Rumsen language was spoken from the Pajaro River to Point Sur, and on the lower courses of the Pajaro, as well as on the Salinas and Carmel Rivers, and the region of the present-day cities of Salinas, Monterey and Carmel.
The Bay Miwok are a cultural and linguistic group of Miwok, a Native American people in Northern California who live in Contra Costa County. They joined the Franciscan mission system during the early nineteenth century, suffered a devastating population decline, and lost their language as they intermarried with other native California ethnic groups and learned the Spanish language.
The Lamchin were one of many tribes of the Ohlone (Coastanoan) people, Native Americans who lived along the San Francisco Peninsula. The Lamchin were the native inhabitants of what is now San Carlos, California. Information is sparse and dispersed, coming mostly from Spanish mission records – as the natives had no written language. The collected information follows over 100 years of research by many noted historians. The Lamchin are believed to be extinct – as historical, statistical and limited written accounts would seem to indicate.
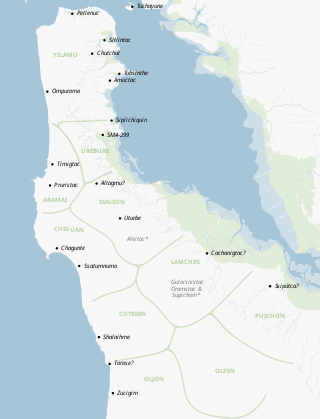
The Ramaytush or Rammay-tuš people are a linguistic subdivision of the Ohlone people of Northern California. The term Ramaytush was first applied to them in the 1970s, but the modern Ohlone people of the peninsula have claimed it as their ethnonym. The ancestors of the Ramaytush Ohlone people have lived on the peninsula—specifically in the area known as San Francisco and San Mateo county—for thousands of years. Prior to the California Genocide, the Ohlone people were not consciously united as a singular socio-political entity. In the early twentieth century anthropologists and linguists began to refer to the Ramaytush Ohlone as San FranciscoCostanoans—the people who spoke a common dialect or language within the Costanoan branch of the Utian family. Anthropologists and linguists similarly called the Tamyen people Santa Clara Costanoans, and the Awaswas people Santa Cruz Costanoans.

The Yelamu are a local tribe of Ohlone people from the San Francisco Bay Area in Northern California. The Yelamu speak a language called Ramaytush. The modern Association of Ramaytush Ohlone (ARO) are the descendants of the Ramaytush.

The Karkin language is an extinct Ohlone language. It was formerly spoken in north central California, but by the 1950s there were no more native speakers. The language was historically spoken by the Karkin people, who lived in the Carquinez Strait region in the northeast portion of the San Francisco Bay estuary. The name 'Karkin' means 'trader' in some varieties of Ohlone.

The Chalon people are one of eight divisions of the Ohlone (Costanoan) people of Native Americans who lived in Northern California. Chalon is also the name of their spoken language, listed as one of the Ohlone languages of the Utian family. Recent work suggests that Chalon may be transitional between the northern and southern groups of Ohlone languages.

The Awaswas, also known as the Santa Cruz people, were a group of the Indigenous peoples of California in North America, with subgroups historically numbering about 600 to 1,400. Academic research suggests that their ancestors had lived within the Santa Cruz Mountains region for approximately 12,000 years. The Awaswas maintained regular trade networks with regional cultures before the Spanish colonists began settling in the area from the 18th century.

The Tamien people are one of eight linguistic divisions of the Ohlone (Costanoan) people groups of Native Americans who live in Northern California. The Tamien traditionally lived throughout the Santa Clara Valley. The use of the name Tamien is on record as early as 1777; it comes from the Ohlone name for the location of the first Mission Santa Clara on the Guadalupe River. Father Pena mentioned in a letter to Junipero Serra that the area around the mission was called Thamien by the native people. The missionary fathers erected the mission on January 17, 1777, at the native village of So-co-is-u-ka.
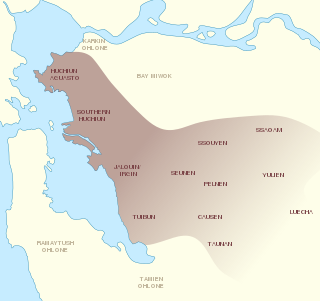
The Chochenyo are one of the divisions of the Indigenous Ohlone (Costanoan) people of Northern California. The Chochenyo reside on the east side of the San Francisco Bay, primarily in what is now Alameda County, and also Contra Costa County, from the Berkeley Hills inland to the western Diablo Range.

The Ohlone languages, also known as Costanoan, form a small Indigenous language family historically spoken in Northern California, both in the southern San Francisco Bay Area and northern Monterey Bay area, by the Ohlone people. Along with the Miwok languages, they are members of the Utian language family. The most recent work suggests that Ohlone, Miwok, and Yokuts are branches of a Yok-Utian language family.
The Chalon language is one of eight Ohlone languages, historically spoken by the Chalon people of Native Americans who lived in Northern California. Also called Soledad, it belongs to the one of the Ohlone languages of the Utian family.It is poorly attested, the only documentation originating from wordlists in the 19th century and a fragment of a catechism. Recent work suggests that Chalon may be transitional between the northern and southern groups of Ohlone languages.

The Tamyen language is one of eight Ohlone languages, once spoken by Tamien people in Northern California.
The Ramaytush language is one of the eight Ohlone languages, historically spoken by the Ramaytush people who were indigenous to California. Historically, the Ramaytush inhabited the San Francisco Peninsula between San Francisco Bay and the Pacific Ocean in the area which is now San Francisco and San Mateo Counties. Ramaytush is a dialect or language within the Ohlone branch of the Utian family. The term Ramaytush was first applied to it during the 1970s, and is derived from the term rammay-tuš "people from the west". It is extinct, but efforts are being taken to revive it.

The Rumsen are one of eight groups of the Ohlone, an indigenous people of California. Their historical territory included coastal and inland areas within what is now Monterey County, California, including the Monterey Peninsula.

Awaswas, or Santa Cruz, is one of eight Ohlone languages. It was historically spoken by the Awaswas people, an indigenous people of California. The last speaker of Awaswas died in the 19th century, and the language has been extinct ever since.
The Sogorea Te Land Trust is an urban land trust founded in 2012 with the goals of returning traditionally Chochenyo and Karkin lands in the San Francisco Bay Area to Indigenous stewardship and cultivating more active, reciprocal relationships with the land. The land trust inspired the work of the Tongva Taraxat Paxaavxa Conservancy in the Los Angeles region of Southern California.

Corrina Gould is a spokeswoman and Tribal Chair of the Confederated Villages of Lisjan/Ohlone, a non-profit organization. She identifies as a Chochenyo and a Karkin Ohlone woman and is a long-time activist who works to protect, preserve, and reclaim ancestral lands of the Ohlone peoples. The Ohlone people live in the greater San Francisco Bay Area, and Gould's organization, specifically, is located in the East Bay, in regions now occupied by Oakland, Berkeley, and beyond.