Related Research Articles
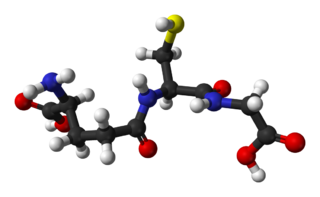
Glutathione is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOCOCH(NH2)CH2CH2CONHCH(CH2SH)CONHCH2COOH. It is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine.
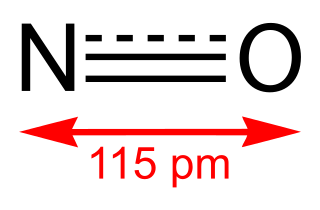
Nitric oxide is a colorless gas with the formula NO. It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula. Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding.

In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (O2), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (O2H), superoxide (O2-), hydroxyl radical (OH.), and singlet oxygen. ROS are pervasive because they are readily produced from O2, which is abundant. ROS are important in many ways, both beneficial and otherwise. ROS function as signals, that turn on and off biological functions. They are intermediates in the redox behavior of O2, which is central to fuel cells. ROS are central to the photodegradation of organic pollutants in the atmosphere. Most often however, ROS are discussed in a biological context, ranging from their effects on aging and their role in causing dangerous genetic mutations.
Thioredoxin reductases are enzymes that reduce thioredoxin (Trx). Two classes of thioredoxin reductase have been identified: one class in bacteria and some eukaryotes and one in animals. In bacteria TrxR also catalyzes the reduction of glutaredoxin like proteins known as NrdH. Both classes are flavoproteins which function as homodimers. Each monomer contains a FAD prosthetic group, a NADPH binding domain, and an active site containing a redox-active disulfide bond.
Redox therapy is an experimental therapy that aims to effect an outcome by modifying the levels of pro-oxidant and antioxidant agents in cells. The term "redox" is a contraction of "reduction-oxidation". For cancer patients, the therapy is predicated on the idea that the redox state of cells may have an effect on cancer development.

Heme oxygenase, or haem oxygenase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the degradation of heme to produce biliverdin, ferrous iron, and carbon monoxide.
Gasotransmitters is a class of neurotransmitters. The molecules are distinguished from other bioactive endogenous gaseous signaling molecules based on a need to meet distinct characterization criteria. Currently, only nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide are accepted as gasotransmitters. According to in vitro models, gasotransmitters, like other gaseous signaling molecules, may bind to gasoreceptors and trigger signaling in the cells.
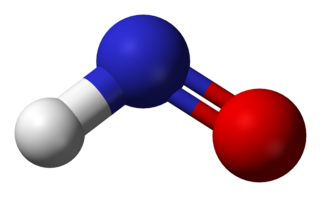
Nitroxyl or azanone is the chemical compound HNO. It is well known in the gas phase. Nitroxyl can be formed as a short-lived intermediate in the solution phase. The conjugate base, NO−, nitroxide anion, is the reduced form of nitric oxide (NO) and is isoelectronic with dioxygen. The bond dissociation energy of H−NO is 49.5 kcal/mol (207 kJ/mol), which is unusually weak for a bond to the hydrogen atom.

Ronald T. Raines is an American chemical biologist. He is the Roger and Georges Firmenich Professor of Natural Products Chemistry at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He is known for using ideas and methods of physical organic chemistry to solve important problems in biology.

Endothelial NOS (eNOS), also known as nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3) or constitutive NOS (cNOS), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS3 gene located in the 7q35-7q36 region of chromosome 7. This enzyme is one of three isoforms that synthesize nitric oxide (NO), a small gaseous and lipophilic molecule that participates in several biological processes. The other isoforms include neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which is constitutively expressed in specific neurons of the brain and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), whose expression is typically induced in inflammatory diseases. eNOS is primarily responsible for the generation of NO in the vascular endothelium, a monolayer of flat cells lining the interior surface of blood vessels, at the interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the remainder of the vessel wall. NO produced by eNOS in the vascular endothelium plays crucial roles in regulating vascular tone, cellular proliferation, leukocyte adhesion, and platelet aggregation. Therefore, a functional eNOS is essential for a healthy cardiovascular system.

Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are a family of antimicrobial molecules derived from nitric oxide (•NO) and superoxide (O2•−) produced via the enzymatic activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase 2 (NOS2) and NADPH oxidase respectively. NOS2 is expressed primarily in macrophages after induction by cytokines and microbial products, notably interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
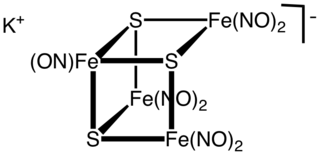
Roussin's black salt is a chemical compound with the formula KFe4S3(NO)7. It consists of the potassium salt of the [Fe4S3(NO)7]− anion, metal nitrosyl compound. First described by Zacharie Roussin in 1858, it is one of the first synthetic iron-sulfur clusters along with the red salt also bearing his name.
Thioredoxin, mitochondrial also known as thioredoxin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TXN2 gene on chromosome 22. This nuclear gene encodes a mitochondrial member of the thioredoxin family, a group of small multifunctional redox-active proteins. The encoded protein may play important roles in the regulation of the mitochondrial membrane potential and in protection against oxidant-induced apoptosis.

In organic chemistry, S-nitrosothiols, also known as thionitrites, are organic compounds or functional groups containing a nitroso group attached to the sulfur atom of a thiol. S-Nitrosothiols have the general formula R−S−N=O, where R denotes an organic group.
In biochemistry, S-nitrosylation is the covalent attachment of a nitric oxide group to a cysteine thiol within a protein to form an S-nitrosothiol (SNO). S-Nitrosylation has diverse regulatory roles in bacteria, yeast and plants and in all mammalian cells. It thus operates as a fundamental mechanism for cellular signaling across phylogeny and accounts for the large part of NO bioactivity.

PD-102,807 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4. It is used in scientific research for studying the effects of the different muscarinic receptor subtypes in the body and brain.
Kate Carroll is an American professor of chemistry, chemical biology, and biochemistry at Florida Atlantic University. She was previously a tenure-track assistant professor at the University of Michigan and was a Professor at Scripps Research in Jupiter, FL from 2010 - 2024

Jonathan Solomon Stamler is an English-born American physician and scientist. He is known for his discovery of protein S-nitrosylation, the addition of a nitric oxide (NO) group to cysteine residues in proteins, as a ubiquitous cellular signal to regulate enzymatic activity and other key protein functions in bacteria, plants and animals, and particularly in transporting NO on cysteines in hemoglobin as the third gas in the respiratory cycle.

Yimon Aye is an American chemist and molecular biologist. Currently she is a professor of chemistry & chemical biology at University of Oxford.

Otenaproxesul is a analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug being developed by Antibe Therapeutics. An NSAID structurally derived from naproxen, in 2016 it received approval to commence phase II clinical trials as a treatment for osteoarthritis after completing phase I clinical trials in 2015. In 2018, the drug completed trials for gastrointestinal safety, and in 2020 completed phase IIb trials on efficacy of pain reduction. Initial phase III clinical trials in 2021 failed to meet the necessary criteria to advance to the next phase.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Katrina Miranda | cbc.arizona.edu". cbc.arizona.edu. Archived from the original on 2019-02-06. Retrieved 2018-12-11.
- ↑ Vázquez-Torres, Andrés (November 2012). "Redox Active Thiol Sensors of Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress". Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 17 (9): 1201–1214. doi:10.1089/ars.2012.4522. ISSN 1523-0864. PMC 3430479 . PMID 22257022.
- 1 2 Blue, Alexis; Communications, University (5 January 2009). "Chemistry Professor Honored in Washington, D.C." UANews. Retrieved 2018-12-11.
- ↑ Cheng, Robert Y.S.; Basudhar, Debashree; Ridnour, Lisa A.; Heinecke, Julie L.; Kesarwala, Aparna H.; Glynn, Sharon; Switzer, Christopher H.; Ambs, Stefan; Miranda, Katrina M. (December 2014). "Gene expression profiles of NO- and HNO-donor treated breast cancer cells: insights into tumor response and resistance pathways". Nitric Oxide. 43: 17–28. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2014.08.003. ISSN 1089-8603. PMC 4250314 . PMID 25153034.
- ↑ Johnson, Gail M.; Chozinski, Tyler J.; Gallagher, Elyssia S.; Aspinwall, Craig A.; Miranda, Katrina M. (November 2014). "Glutathione sulfinamide serves as a selective, endogenous biomarker for nitroxyl after exposure to therapeutic levels of donors". Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 76: 299–307. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.07.022. ISSN 0891-5849. PMC 4254043 . PMID 25064322.
- 1 2 "Katrina M-Miranda | BIO5". www.bio5.org. Archived from the original on 2018-12-14. Retrieved 2018-12-11.
- ↑ "Developing Anticancer Drugs | Benefunder". www.benefunder.com. Archived from the original on 2018-12-14. Retrieved 2018-12-11.
- 1 2 "The Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers: Recipient Details | NSF - National Science Foundation". www.nsf.gov. Retrieved 2018-12-11.
- ↑ Miranda, Katrina (2008-03-31). Chemical Biology of Nitric Oxide (1st ed.). Garland Science. ISBN 9780815341475.
- ↑ "The University of Arizona Foundation - Gift Impact Article". www.uafoundation.org. Archived from the original on 2018-12-14. Retrieved 2018-12-11.
- ↑ December 2018, Rebecca Trager11. "Chemistry prof sues for $20m over alleged gender discrimination". Chemistry World. Retrieved 2018-12-11.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "U of Arizona is being sued once again for alleged discrimination against women in terms of salary and promotions". www.insidehighered.com. Archived from the original on 2018-12-07. Retrieved 2018-12-11.