| Katz syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hyperostosis frontalis interna |
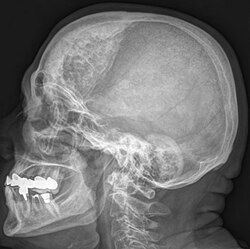 | |
| Hyperostosis frontalis interna in a 74-year-old woman | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Katz syndrome is a rare congenital disorder, presenting as a polymalformative syndrome characterized by enlarged viscera, hepatomegaly, diabetes, and skeletal anomalies that result in a short stature, cranial hyperostosis, and typical facial features. It is probably a variant of the autosomal recessive type of craniometaphyseal dysplasia. [1]