
The Cocopah are Native Americans who live in Baja California, Mexico, and Arizona, United States.

Imperial County is a county located on the southeast border of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 179,702, making it the least populous county in Southern California. The county seat and largest city is El Centro. Imperial is the most recent California county to be established, as it was created in 1907 out of portions of San Diego County.

Yuma County is a county in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of Arizona. As of the 2020 census, its population was 203,881. The county seat is Yuma.
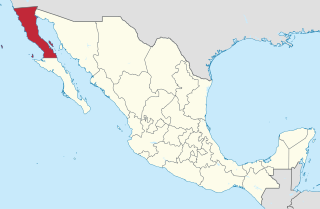
Baja California, officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of Baja California. It has an area of 70,113 km2 (27,071 sq mi) and comprises the northern half of the Baja California Peninsula, north of the 28th parallel, plus oceanic Guadalupe Island. The mainland portion of the state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean; on the east by Sonora, the U.S. state of Arizona, and the Gulf of California; on the north by the U.S. state of California; and on the south by Baja California Sur.

Mexicali is the capital city of the Mexican state of Baja California. The city, which is the seat of the Mexicali Municipality, has a population of 689,775, according to the 2010 census, while the Calexico–Mexicali metropolitan area is home to 1,000,000 inhabitants on both sides of the Mexico–United States border. Mexicali is a regional economic and cultural hub for the border region of The Californias.

The Sonoran Desert is a hot desert in North America and ecoregion that covers the northwestern Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur, as well as part of the southwestern United States. It is the hottest desert in both Mexico and the United States. It has an area of 260,000 square kilometers (100,000 sq mi).

Colorado Desert is a part of the larger Sonoran Desert located in California, United States and Baja California, Mexico. It encompasses approximately 7 million acres, including the heavily irrigated Coachella, Imperial and Mexicali valleys. It is home to many unique flora and fauna.

The All-American Canal is an 82-mile-long (132 km) aqueduct, located in southeastern California. It conveys water from the Colorado River into the Yuma Project, the Imperial Valley, and to nine cities. It is the Imperial Valley's only water source, and replaced the Alamo Canal, which was located mostly in Mexico. The Imperial Dam, about 30 miles (48 km) northeast of Yuma, Arizona on the Colorado River, diverts water into the All-American Canal, which runs to just west of Calexico, California before its last branch heads mostly north into the Imperial Valley. Smaller canals branching off the All-American Canal move water into the Yuma Valley and the Imperial Valley. These canal systems irrigate up to 630,000 acres (250,000 ha) of crop land and have made possible a greatly increased crop yield in this area, originally one of the driest on earth. It is the largest irrigation canal in the world, carrying a maximum of 26,155 cubic feet per second (740.6 m3/s). Agricultural runoff from the All-American Canal drains into the Salton Sea.

The Barry M. Goldwater Air Force Range or Barry M. Goldwater Range (BMGR), formerly known as Luke Air Force Range, is a bombing range in the U.S. state of Arizona, between the Mexico–United States border and Interstate 8 straddling the Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge and the Tohono Oʼodham Nation.

San Luis Río Colorado is a city and also the name of its surrounding municipality in the state of Sonora, Mexico. In the 2020 census, the city had a population of 176,685. The city is the fourth-largest community in the state, and the municipality is also the fourth-largest in terms of population. Lying in the northwestern corner of Sonora, the city marks the state border with Baja California. It also stands on the international border with the United States, adjacent to San Luis, Arizona. It is located about 75 km from Mexicali. The municipality covers an area of 8,412.75 km² in the Sonoran Desert.

The Juan Bautista de Anza National Historic Trail is a 1,210-mile (1,950 km) trail extending from Nogales on the U.S.-Mexico border in Arizona, through the California desert and coastal areas in Southern California and the Central Coast region to San Francisco. The trail commemorates the 1775–1776 land route that Spanish commander Juan Bautista de Anza took from the Sonora y Sinaloa Province of New Spain in Colonial Mexico through to Las Californias Province. The goal of the trip was to establish a mission and presidio on the San Francisco Bay. The trail was an attempt to ease the course of Spanish colonization of California by establishing a major land route north for many to follow. It was used for about five years before being closed by the Quechan (Yuma) Indians in 1781 and kept closed for the next 40 years. It is a National Historic Trail administered by the National Park Service and was also designated a National Millennium Trail.

The Mexico–United States border is an international border separating Mexico and the United States, extending from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. It traverses a variety of terrains, ranging from urban areas to deserts. The Mexico–U.S. border is the most frequently crossed border in the world with approximately 350 million documented crossings annually. Illegal crossing of the border to enter the United States has caused the Mexico–United States border crisis. It is one of two international borders that the United States has, the other being the northern Canada–United States border; Mexico has two other borders: with Belize and with Guatemala. The Mexico-U.S. border is the tenth-longest border between two countries in the world.

Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge (CPNWR) is located in southwestern Arizona in the United States, along 56 miles (90 km) of the Mexico–United States border. It is bordered to the north and to the west by the Barry M. Goldwater Air Force Range, to the south by Mexico's El Pinacate y Gran Desierto de Altar Biosphere Reserve, to the northeast by the town of Ajo, and to the southeast by Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument.
In United States immigration enforcement, "catch and release" refers to a practice of releasing a migrant to the community while he or she awaits hearings in immigration court, as an alternative to holding them in immigration detention. The migrants whom U.S. immigration enforcement agencies have allowed to remain in the community pending immigrant hearings have been those deemed low risk, such as children, families, and those seeking asylum.

Immigration policy, including illegal immigration to the United States, was a signature issue of former U.S. president Donald Trump's presidential campaign, and his proposed reforms and remarks about this issue generated much publicity. Trump has repeatedly said that illegal immigrants are criminals.

Central American migrant caravans, also known as the Viacrucis del migrante, are migrant caravans that travel from Central America to the Mexico–United States border to demand asylum in the United States. The largest and best known of these were organized by Pueblo Sin Fronteras that set off during Holy Week in early 2017 and 2018 from the Northern Triangle of Central America (NTCA), but such caravans of migrants began arriving several years earlier, and other unrelated caravans continued to arrive into late 2018.

The United States family separation policy under the Trump administration was presented to the public as a "zero tolerance" approach intended to deter illegal immigration and to encourage tougher legislation. In some cases, families following the legal procedure to apply for asylum at official border crossings were also separated. It was officially adopted across the entire US–Mexico border from April 2018 until June 2018. Under the policy, federal authorities separated children and infants from parents or guardians with whom they had entered the US. The adults were prosecuted and held in federal jails or deported, and the children were placed under the supervision of the US Department of Health and Human Services. More than 5,500 children, including infants, were removed and up to 2,000 still have not been reunited as of March 2024.

The Mexico–United States bordercrisis is an ongoing migrant crisis in North America concerning the migration of illegal immigrants from Latin America and other countries including China through Mexico and into the United States.
Remain in Mexico is a United States immigration policy originally implemented in January 2019 under the administration of President Donald Trump, affecting immigration across the border with Mexico. Administered by the Department of Homeland Security, it requires migrants seeking asylum to remain in Mexico until their US immigration court date.
Joe Biden's immigration policy initially focused on reversing many of the immigration policies of the previous Trump administration, before implementing stricter enforcement mechanisms later in his first term.
















