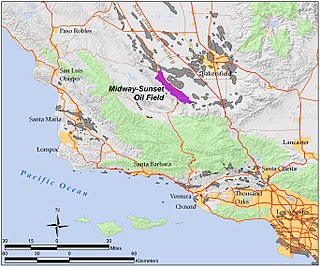
The Midway-Sunset Oil Field is a large oil field in Kern County, San Joaquin Valley, California in the United States. It is the largest known oilfield in California and the third largest in the United States.

The South Belridge Oil Field is a large oil field in northwestern Kern County, San Joaquin Valley, California, about forty miles west of Bakersfield. Discovered in 1911, and having a cumulative production of over 1,500 million barrels (240,000,000 m3) of oil at the end of 2008, it is the fourth-largest oil field in California, after the Midway-Sunset Oil Field, Kern River Oil Field, and Wilmington Oil Field, and is the sixth-most productive field in the United States. Its estimated remaining reserves, as of the end of 2008, were around 494 million barrels (78,500,000 m3), the second-largest in the state, and it had 6,253 active wells. The principal operator on the field was Aera Energy LLC, a joint venture between Royal Dutch Shell and ExxonMobil. Additionally, the field included the only onshore wells in California owned and operated by ExxonMobil.
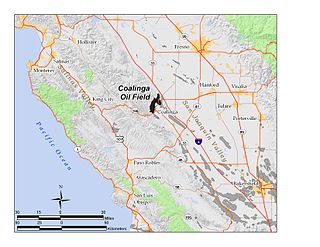
The Coalinga Oil Field is a large oil field in western Fresno County, California, in the United States. It surrounds the town of Coalinga, about halfway between Los Angeles and San Francisco, to the west of Interstate 5, at the foot of the Diablo Range. Discovered in the late 19th century, it became active around 1890, and is now the eighth-largest oil field in California, with reserves totaling approximately 58 million barrels (9,200,000 m3), and over 1,600 active oil wells. The principal operators on the field, as of 2008, were Chevron Corp. and Aera Energy LLC.

The Buena Vista Oil Field, formerly the Naval Petroleum Reserve No. 2 (NPR-2) is a large oil field in Kern County, San Joaquin Valley, California in the United States. Discovered in 1909, and having a cumulative production of approximately 667 million barrels (106,000,000 m3), it is the tenth-largest oil field in California. It is also one of the closest to being exhausted, having a total reserve of only about one percent of its original oil, and having produced a mere 713,000 barrels (113,400 m3) in 2006.

The Cymric Oil Field is a large oil field in Kern County, California in the United States. While only the 14th-largest oil field in California in total size, in terms of total remaining reserves it ranks fifth, with the equivalent of over 119 million barrels (18,900,000 m3) still in the ground. Production at Cymric has been increasing faster than at any other California oil field.

The Lost Hills Oil Field is a large oil field in the Lost Hills Range, north of the town of Lost Hills in western Kern County, California, in the United States.

The Mount Poso Oil Field is a large oil and gas field in the lower foothills of the Sierra Nevada in Kern County, California, United States. Discovered in 1926, and relatively close to exhaustion with less than three percent of its original oil remaining, it is the 21st largest field in California by total ultimate oil recovery, having a cumulative production of close to 300 million barrels (48,000,000 m3). The current principal operator of the field is Plains Exploration & Production; 652 wells remained active at the end of 2006, while production had dwindled to 554,000 barrels (88,100 m3) during that year, from a peak of over 9 million barrels (1,400,000 m3) in 1981.

The McKittrick Oil Field is a large oil and gas field in western Kern County, California. The town of McKittrick overlies the northeastern portion of the oil field. Recognized as an oil field in the 19th century, but known by Native Americans for thousands of years due to its tar seeps, the field is ranked 19th in California by total ultimate oil recovery, and has had a cumulative production of over 303 million barrels (48,200,000 m3) of oil. The principal operators of the field as of 2008 were Chevron Corp. and Aera Energy LLC, but many independent oil exploration and production companies were also active on the field. The California Department of Oil, Gas and Geothermal Resources (DOGGR) estimates approximately 20 million recoverable barrels of oil remain in the ground.
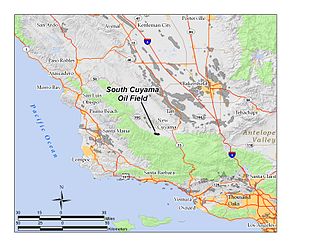
The South Cuyama Oil Field is a large oil and gas field in the Cuyama Valley and the adjacent northern foothills of the Sierra Madre Mountains in northeastern Santa Barbara County, California. Discovered in 1949, and with a cumulative production of around 225 million barrels (35,800,000 m3) of oil, it ranks 27th in size in the state, but is believed to retain only approximately two percent of its original oil, according to the official estimates of the California Department of Oil, Gas, and Geothermal Resources (DOGGR). Of the top forty onshore oil fields in California, it is the most recent to be discovered, but by the end of 2008 only 87 wells remained in production.

The Fruitvale Oil Field is a large oil and gas field in the southern San Joaquin Valley, California, within and just northwest of the city of Bakersfield, along and north of the Kern River. It is one of the few oil fields in the California Central Valley which is mostly surrounded by a heavily populated area. Discovered in 1928, and with a cumulative total recovery of more than 124 million barrels (19,700,000 m3) of oil at the end of 2006, it is 41st in size among California oil fields, and according to the California Department of Oil, Gas, and Geothermal Resources (DOGGR) its total reserve amounts to a little less than ten percent of its original oil.

The Round Mountain Oil Field is a large oil and gas field in the foothills of the Sierra Nevada, about 10 miles (16 km) northeast of Bakersfield, California, United States. It is east of the giant Kern River Oil Field, one of the largest in the United States, and also close to the Mount Poso Oil Field and Kern Front Oil Field. With a cumulative total recovery of more than 110 million barrels (17,000,000 m3) of oil, it is the 48th largest oil field in California, but remains relatively productive with still about ten percent of its reserves remaining in the ground, according to the California Department of Oil, Gas, and Geothermal Resources (DOGGR).

The North Belridge Oil Field is a large oil field along California State Route 33 in the northwestern portion of Kern County, California, about 45 miles west of Bakersfield. It is contiguous with the larger South Belridge Oil Field to the southeast, in a region of highly productive and mature fields. Discovered in 1912, it has had a cumulative production of 136,553,000 barrels (21,710,200 m3) of oil, and retains 27,443,000 barrels (4,363,100 m3) in reserve, as of the end of 2006, making it the 40th largest oil field in the state.
The Ventura Oil Field is a large and currently productive oil field in the hills immediately north of the city of Ventura in southern California in the United States. It is bisected by California State Route 33, the freeway connecting Ventura to Ojai, and is about eight miles (13 km) long by two across, with the long axis aligned east to west. Discovered in 1919, and with a cumulative production of just under a billion barrels of oil as of 2008, it is the tenth-largest producing oil field in California, retaining approximately 50 million barrels in reserve, and had 423 wells still producing. As of 2009 it was entirely operated by Aera Energy LLC.
The Oxnard Oil Field is a large and currently productive oil field in and adjacent to the city of Oxnard, in Ventura County, California in the United States. Its conventional oil reserves are close to exhaustion, with only an estimated one percent of the original oil recoverable with current technology remaining: 434,000 barrels (69,000 m3) out of an original 43.5 million. However, the reservoir includes an enormous deposit of tar sands, ultra-heavy oil classed as an unconventional petroleum reserve, and potentially containing 400 million barrels (64,000,000 m3) of oil equivalent, should it become economically feasible to extract. Present operators on the field include Tri-Valley Oil & Gas Co., Anterra Energy Services, Inc., Chase Production Co., and Occidental Petroleum through its Vintage Production subsidiary. As of the beginning of 2009, there were 34 active wells on the field.

The Russell Ranch Oil Field is an oil and gas field in the Cuyama Valley of northern Santa Barbara and southern San Luis Obispo Counties, California, in the United States. Discovered in 1948, and reaching peak production in 1950, it has produced over 68 million barrels (10,800,000 m3) of oil in its lifetime; with only an estimated 216,000 barrels (34,300 m3) of recoverable oil remaining, and having produced around 66,000 in 2008, it is considered to be close to exhaustion. The primary operator on the field as of 2010 is E&B Natural Resources, which also runs the nearby South Cuyama Oil Field.
The Semitropic Oil Field is an oil and gas field in northwestern Kern County in California in the United States, within the San Joaquin Valley. Formerly known as the Semitropic Gas Field, it was discovered by the Standard Oil Company of California in 1935, and first understood to be primarily a natural gas reservoir; however, in 1956 a much deeper oil-bearing zone was discovered. The field contains the deepest oil well ever drilled in California, at 18,876 feet (5,753 m). At the end of 2008 the field still had 56 active oil wells, most of which were owned by Occidental Petroleum, and the field had an estimated 343,000 barrels of oil still recoverable with current technology.

The Guijarral Hills Oil Field is a formerly-productive oil and gas field near Coalinga on the western side of the Central Valley in central California in the United States. Discovered in 1948, and having produced 5.4 million barrels (860,000 m3) of oil during its peak year in 1950, it now has but one active oil well producing a little over a barrel of oil a day, and is very near to exhaustion, with only 343,000 recoverable barrels of oil remaining throughout its 2,515-acre (10.18 km2) extent according to the official California State Department of Conservation estimate. As of 2010, the only active operator was Longview Production Company.

The Mountain View Oil Field is a large, mature, but still-productive oil field in Kern County, California, in the United States, in the extreme southern part of the San Joaquin Valley southeast of Bakersfield. It underlies the town of Arvin, as well as some smaller agricultural communities. The field is spread out across a large area, covering just under 8 square miles (21 km2), with wells and storage facilities widely dispersed throughout the area, scattered among working agricultural fields of broccoli and carrots as well as citrus orchards. Discovered in 1933, it has produced over 90 million barrels (14,000,000 m3) of oil in its lifetime, and although declining in production is one of the few inland California fields in which new oil is still being discovered.

The Edison Oil Field is a large oil field in Kern County, California, in the United States, in the southeastern part of the San Joaquin Valley and adjacent foothills east-southeast of Bakersfield. The field has a total productive area of over 8,000 acres (32 km2), most of which is intermingled with agricultural land uses; oil pumps and storage tanks are surrounded with row crops and orchards in much of the field's extent. Discovered in 1928, and with a cumulative production of 149 million barrels (23,700,000 m3) of oil as of 2008, and having over 6 million barrels (950,000 m3) in reserve, it is ranked 38th among California's oil fields by total ultimate recovery. It is a mature field in decline, and is run entirely by small independent operators. As of 2008, there were 40 different oil companies active on the field, one of the most in the state for a single field. 914 wells remained active on the field, averaging only two barrels of oil per well per day from the dwindling reservoirs.