
The John F. Kennedy Space Center, located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten field centers. Since December 1968, KSC has been NASA's primary launch center of American spaceflight, research, and technology. Launch operations for the Apollo, Skylab and Space Shuttle programs were carried out from Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 and managed by KSC. Located on the east coast of Florida, KSC is adjacent to Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS). The management of the two entities work very closely together, share resources and operate facilities on each other's property.

Leelanau County is a county located in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the population was 22,301. Since 2008, the county seat has been located within Suttons Bay Township, one mile east of the unincorporated village of Lake Leelanau. Before 2008, Leelanau County's seat was Leland. Leelanau County is included in the Traverse City metropolitan area of Northern Michigan. The largest settlement in Leelanau County by population is Greilickville, itself a suburb of Traverse City.

Calumet is a village in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The village is located within Calumet Township, Houghton County, and had a population of 621 at the 2020 census.

Calumet Township, officially the Charter Township of Calumet, is a charter township of Houghton County in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 6,263 at the 2020 census. Even with a decreasing population, the township remains the largest township by population in Houghton County.
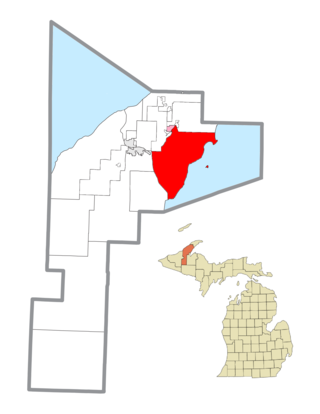
Torch Lake Township is a civil township of Houghton County in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the population of the township was 1,893. The township was established in 1886 and is one of the largest townships in Houghton County by area. It is surrounded by the Torch Lake, the Portage Lake, and Lake Superior. As well as a large number of unincorporated communities, the township also includes a portion of the Baraga State Forest which lies along the shores of Keweenaw Bay. The township borders Schoolcraft Township to the north, Osceola Township to the northwest, and Chassell Township to the southwest. The community of Hubbell serves as the major population center of the township, as well as hosting the Township Hall itself. The mostly uninhabited 91-acre Rabbit Island, located offshore in Lake Superior, is a part of the township.

Allouez Township is a civil township of Keweenaw County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 1,428 at the 2020 census.

Eagle Harbor Township is a civil township of Keweenaw County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 217 at the 2020 census. The township is located on the Keweenaw Peninsula and also includes the southwestern portion of Isle Royale National Park.

Grant Township is a civil township of Keweenaw County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 275 at the 2020 census. Grant Township is one of the most isolated municipalities in Michigan, as it forms the tip of the Keweenaw Peninsula, which projects into Lake Superior.
The Keweenaw Peninsula is a peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. Part of the greater landmass of the Upper Peninsula, the Keweenaw Peninsula projects about 65 miles (105 km) northeasterly into Lake Superior, forming Keweenaw Bay. The peninsula is part of Michigan's Copper Country region, as the region was home to the first major copper mining boom in the United States. Copper mining was active in this region from the 1840s to the 1960s.

Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore is a U.S. national lakeshore in the northwestern Lower Peninsula of Michigan. Located within Benzie and Leelanau counties, the park extends along a 35-mile (56 km) stretch of Lake Michigan's eastern coastline, as well as North and South Manitou islands, preserving a total of 71,199 acres. The park is known for its outstanding natural features, including dune formations, forests, beaches, and ancient glacial phenomena. The lakeshore also contains many cultural features, including the 1871 South Manitou Island Lighthouse, three former stations of the Coast Guard, and an extensive rural historic farm district.

South Manitou Island is located in Lake Michigan, approximately 16 miles (26 km) west of Leland, Michigan. It is part of Leelanau County and the Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore. The uninhabited island is 8.277 sq mi (21.44 km2) in land area and can be accessed by a ferry service from Leland. Guided tours on open-air vehicles are available to visitors, but most traffic is on foot. Larger North Manitou Island lies to its north.
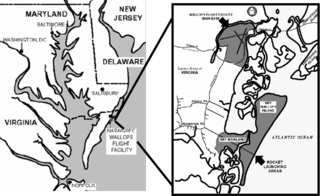
Wallops Flight Facility (WFF) is a rocket launch site on Wallops Island on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States, just east of the Delmarva Peninsula and approximately 100 miles (160 km) north-northeast of Norfolk. The facility is operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and primarily serves to support science and exploration missions for NASA and other Federal agencies. WFF includes an extensively instrumented range to support launches of more than a dozen types of sounding rockets; small expendable suborbital and orbital rockets; high-altitude balloon flights carrying scientific instruments for atmospheric and astronomical research; and, using its Research Airport, flight tests of aeronautical research aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles.

Alberta is an unincorporated community in L'Anse Township of Baraga County in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is situated on US Highway 41 (US 41) about eight miles (13 km) south of the village of L'Anse at 46°38′37″N88°28′46″W. Alberta is the site of the Ford Center, managed by the Michigan Technological University College of Forest Resources and Environmental Science.

The Poker Flat Research Range (PFRR) is a launch facility and rocket range for sounding rockets in the U.S. state of Alaska, located on a 5,132-acre (20.77 km2) site at Chatanika, about 30 miles (50 km) northeast of Fairbanks and 1.5 degrees south of the Arctic Circle. More than 1,700 launches have been conducted at the range to study the Earth's atmosphere and the interaction between the atmosphere and the space environment. Areas studied at PFRR include the aurora, plasma physics, the ozone layer, solar proton events, Earth's magnetic field, and ultraviolet radiation. Rockets launched at PFRR have attained an apogee of 930 miles (1,500 km).

Keweenaw National Historical Park is a unit of the U.S. National Park Service. Established in 1992, the park celebrates the life and history of the Keweenaw Peninsula in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is a federal-local cooperative park made up of two primary units, the Calumet Unit and the Quincy Unit, and almost two dozen cooperating "Heritage Sites" located on federal, state, and privately owned land in and around the Keweenaw Peninsula. The National Park Service owns approximately 1,700 acres (690 ha) in the Calumet and Quincy Units. Units are located in Baraga, Houghton, Keweenaw, and Ontonagon counties.
Brockway Mountain Drive is an 8.8-mile-long (14.2 km) scenic roadway just west of Copper Harbor in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan in the United States. Drivers can access the road from State Highway M-26 on either end near Eagle Harbor to the west or Copper Harbor to the east in the Keweenaw Peninsula. The drive runs along the ridge of Brockway Mountain on the Keweenaw Fault and climbs to 1,320 feet (402 m) above sea level, 720 feet (219 m) above the surface of Lake Superior. Several viewpoints along the route allow for panoramas of Copper Harbor, Lake Superior, and undeveloped woodland. On a clear day, Isle Royale is visible approximately 50 miles (80 km) in distance from the top of the mountain.
Manitou Island is a small island in Lake Superior, off the northeastern tip of the Keweenaw Peninsula in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is part of Grant Township, in Keweenaw County. Located approximately three miles from the mainland, it encompasses around 1,000 acres (4.0 km2). Manitou has seen limited impact from human activity because of its remote location and the often-treacherous waters caused by a strong current at the peninsula's tip. It is mostly forested, with scattered bogs and an inland lake known as "Perch Lake". Dense underbrush can make travel around the island rather difficult, though a few unimproved trails do exist. The Keweenaw Land Trust protects 93 acres (0.38 km2) of the island as the Manitou Island Light Station Preserve.

The Copper Harbor Light is a lighthouse located in the harbor of Copper Harbor, Michigan USA on the Keweenaw Peninsula of Upper Michigan inside Fort Wilkins Historic State Park. It is a Michigan State Historic Site and listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

In Michigan, copper mining became an important industry in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Its rise marked the start of copper mining as a major industry in the United States.

The Gull Rock Light Station is an active lighthouse located on Gull Rock, just west of Manitou Island, off the tip of Michigan's Keweenaw Peninsula in Lake Superior. The light was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984, even as its condition deteriorated, resulting in its placement on the Lighthouse Digest Doomsday List.




















