
Deir el-Medina, or Dayr al-Madīnah, is an ancient Egyptian workmen's village which was home to the artisans who worked on the tombs in the Valley of the Kings during the 18th to 20th Dynasties of the New Kingdom of Egypt The settlement's ancient name was Setmaat, and the workmen who lived there were called "Servants in the Place of Truth". During the Christian era, the temple of Hathor was converted into a Monastery of Saint Isidorus the Martyr from which the Egyptian Arabic name Deir el-Medina is derived.

Seti II was the fifth pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt and reigned from c. 1203 BC to 1197 BC. His throne name, Userkheperure Setepenre, means "Powerful are the manifestations of Re, the chosen one of Re." He was the son of Merneptah and Isetnofret II and occupied the throne during a period known for dynastic intrigue and short reigns, and his rule was no different. Seti II had to deal with many serious plots, most significantly the accession of a rival king named Amenmesse, possibly a half brother, who seized control over Thebes and Nubia in Upper Egypt during his second to fourth regnal years.

An ostracon is a piece of pottery, usually broken off from a vase or other earthenware vessel. In an archaeological or epigraphical context, ostraca refer to sherds or even small pieces of stone that have writing scratched into them. Usually these are considered to have been broken off before the writing was added; ancient people used the cheap, plentiful, and durable broken pieces of pottery around them as a convenient medium to write on for a wide variety of purposes, mostly very short inscriptions, but in some cases very long.

Ramesses VI Nebmaatre-Meryamun was the fifth ruler of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt. He reigned for about eight years in the mid-to-late 12th century BC and was a son of Ramesses III and queen Iset Ta-Hemdjert. As a prince, he was known as Ramesses Amunherkhepeshef and held the titles of royal scribe and cavalry general. He was succeeded by his son, Ramesses VII Itamun, whom he had fathered with queen Nubkhesbed.

The Theban Necropolis is a necropolis on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes (Luxor) in Upper Egypt. It was used for ritual burials for much of the Pharaonic period, especially during the New Kingdom.

Sennedjem was an Ancient Egyptian artisan who was active during the reigns of Seti I and Ramesses II. He lived in Set Maat, contemporary Deir el-Medina, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes. Sennedjem had the title "Servant in the Place of Truth". He was buried along with his wife, Iyneferti, and members of his family in a tomb in the village necropolis. His tomb was discovered January 31, 1886. When Sennedjem's tomb was found, it contained furniture from his home, including a stool and a bed, which he used when he was alive.

TT1 is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Sennedjem and members of his family in Deir el-Medina, on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor. The funerary complex consists of three pyramid-shaped chapels dedicated to, from south to north, Sennedjem's father or brother, Sennedjem himself, and to Sennedjem's son Khonsu. Of the three shafts associated with the chapels, only the shaft in front of Sennedjem's chapel was unrobbed. It led to a series of underground rooms, including the extensively decorated burial chamber.
Qen was an Ancient Egyptian artisan. Qen lived in Deir el-Medina on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes, during the reigns of Ramesses II. His titles included Servant in the Place of Truth, meaning that he worked on the excavation and decoration of nearby royal tombs. He was buried in a tomb in the village necropolis.
sḏm-ꜥš m st mꜣꜥt, usually translated as Servant in the Place of Truth is an ancient Egyptian title that is used to refer to someone who worked in the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile in Thebes. Set-Maat was the name of the workmen's settlement today known as Deir el-Medina. Several artisans had nicely decorated tombs here.

Pashedu was an ancient Egyptian artisan. Pashedu lived in Deir el-Medina on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes, during the reign of Seti I. Pashedu was a son of Menna and Huy. His wife was named Nedjmet-behdet. Pashedu was the owner of tomb TT3 and likely TT326. His titles included Servant in the Place of Truth, meaning that he worked on the excavation and decoration of the nearby royal tombs. Pashedu seems to have succeeded Baki as foreman for the left side during the reign of Ramesses II.

Theban Tomb TT2 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Khabekhnet and his family. Khabekhnet was Servant in the Place of Truth, during the reign of Ramesses II.

Ramose was an ancient Egyptian scribe and artisan who lived in Deir el-Medina on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes, during the reigns of Ramesses II. He held the position of Scribe of the Tomb, the highest administrative position for a scribe in Deir el-Medina, from around years 5 to 38 of Ramesses II's reign. He was buried in a tomb in the village necropolis.

The Theban Tomb TT10 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian artisan named Penbuy, who lived during the 19th Dynasty. Penbuy shared his tomb with Kasa, also a Servant in the Place of Truth.
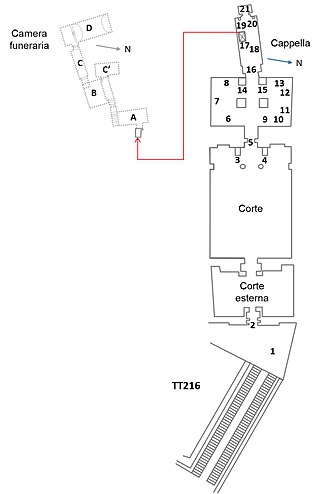
The Theban Tomb TT216 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian artisan named Neferhotep, who lived during the 19th Dynasty. Neferhotep would have lived in Deir el-Medina during the reigns of Ramesses II, Merenptah and Sethi II.
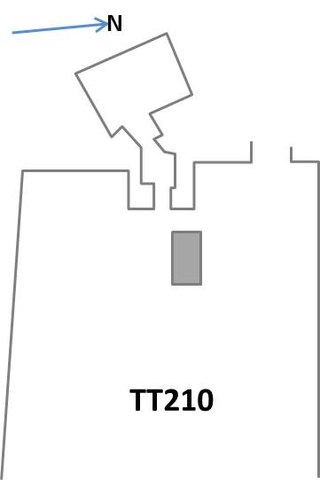
The Theban Tomb TT210, part of the Theban Necropolis, is located in Deir el-Medina, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. TT210 is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian artisan named Raweben, who lived during the 19th Dynasty. Raweben would have lived in Deir el-Medina during the reign of Ramesses II.

The Theban Tomb TT212 is located in Deir el-Medina, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor.
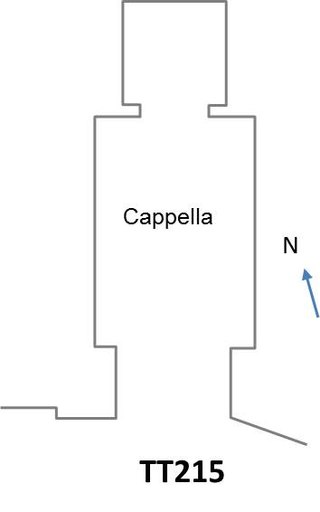
The Theban Tomb TT215 is located in Deir el-Medina. It forms part of the Theban Necropolis, situated on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor.
The Papyrus Salt 124 is an ancient Egyptian papyrus dating to the beginning of the 20th Dynasty. This papyrus is a copy of a letter addressed to the vizier of the time, most likely Hori.
Renpetneferet is a minor goddess who is credited as being either the sister or the wife of Imhotep in Late Period Egyptian texts. There is no evidence of an individual by this name existing during the reign of King Djoser, although similar names were being used for women during the fourth dynasty.
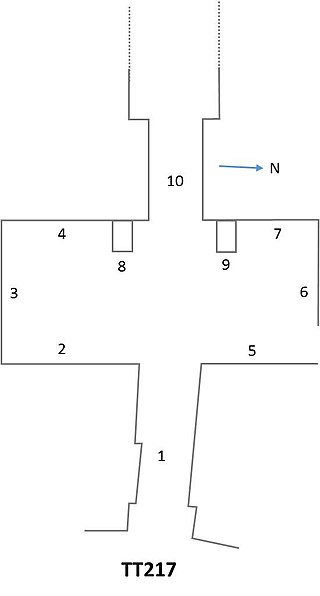
TT217, or Tomb of Ipuy, is the tomb of the ancient Egyptian artisan Ipuy and members of his family in Deir el-Medina, near modern Luxor, Egypt. Ipuy was a sculptor active in the reign of Ramesses II of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt.















