
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt is the period in the history of ancient Egypt following a period of political division known as the First Intermediate Period. The Middle Kingdom lasted from approximately 2040 to 1782 BC, stretching from the reunification of Egypt under the reign of Mentuhotep II in the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Twelfth Dynasty. The kings of the Eleventh Dynasty ruled from Thebes and the kings of the Twelfth Dynasty ruled from el-Lisht.

Amenemhat I, also known as Amenemhet I, was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the first king of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom.

Nubkaure Amenemhat II, also known as Amenemhet II, was the third pharaoh of the 12th Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Although he ruled for at least 35 years, his reign is rather obscure, as well as his family relationships.

Senusret I also anglicized as Sesostris I and Senwosret I, was the second pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt. He ruled from 1971 BC to 1926 BC, and was one of the most powerful kings of this Dynasty. He was the son of Amenemhat I. Senusret I was known by his prenomen, Kheperkare, which means "the Ka of Re is created." He expanded Egypt that allowed him to rule over an age of prosperity.

Khakheperre Senusret II was the fourth pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt. He ruled from 1897 BC to 1878 BC. His pyramid was constructed at El-Lahun. Senusret II took a great deal of interest in the Faiyum oasis region and began work on an extensive irrigation system from Bahr Yussef through to Lake Moeris through the construction of a dike at El-Lahun and the addition of a network of drainage canals. The purpose of his project was to increase the amount of cultivable land in that area. The importance of this project is emphasized by Senusret II's decision to move the royal necropolis from Dahshur to El-Lahun where he built his pyramid. This location would remain the political capital for the 12th and 13th Dynasties of Egypt. The king also established the first known workers' quarter in the nearby town of Senusrethotep (Kahun).

Beni Hasan is an ancient Egyptian cemetery. It is located approximately 20 kilometers (12 mi) to the south of modern-day Minya in the region known as Middle Egypt, the area between Asyut and Memphis.
Khnumhotep is an ancient Egyptian personal theophoric name which may refer to:

Khnumhotep III was an ancient Egyptian high steward and vizier of the 12th Dynasty.

Baqet III was an ancient Egyptian official and Great Chief of the Oryx nome during the 11th Dynasty in the 21st century BCE. Apart from the position of governor of the entire nome, Baqet III also held the titles haty-a, treasurer of the king of Lower Egypt, confidential friend, true royal acquaintance, and mayor of Nekheb.

Segerseni was an ancient Egyptian or Nubian chieftain of Nubia, likely reigning concurrently with the end of the 11th and beginning of the 12th Dynasty during the early Middle Kingdom.

Khnumhotep II was an ancient Egyptian Great Chief of the Oryx nome during the reign of pharaohs Amenemhat II and Senusret II of the 12th Dynasty, Middle Kingdom. He is well known for his tomb at Beni Hasan and its decorations.

Amenemhat, often reported with his short form Ameny (Jmnjj), was an ancient Egyptian "Overlord of the Oryx nome" and chief priest during the reign of pharaoh Senusret I of the 12th Dynasty.

The Oryx nome was one of the 42 nomoi in ancient Egypt. The Oryx nome was the 16th nome of Upper Egypt, and was named after the scimitar oryx. It was located, approximately, in the territories surrounding the modern city of Minya in Middle Egypt.

The Hare nome, also called the Hermopolite nome was one of the 42 nomoi in ancient Egypt; more precisely, it was the 15th nome of Upper Egypt.

Djefaihapi was an ancient Egyptian official during the reign of pharaoh Senusret I of the 12th Dynasty. In literature, his name is found written in many other variants such as Hepzefa, Hapidjefa, Hapdjefai, and Djefaihap.
Zatipy was an ancient Egyptian woman who lived around 2000 BC at the beginning of the 12th Dynasty under king Amenemhat I. She was the wife of Khnumhotep I who was local governor in the Oryx nome. Zatipy is depicted in the tomb of her husband at Beni Hasan. There she is shown behind him, both watching activities of peasants in the marshes. Behind her depiction, her name and titles are written. She was member of the elite (iryt-pat), wife of the ruler and lady of the house. She is also called mistress of all women. The relative high number of titles is remarkable. Especially the title member of the elite is rare for women and only better attested for women with royal connections. It was therefore proposed that Zatipy came from a royal or highly important family. If she was a princess, king Amenemhat I might have tried with this marriage to keep close ties to an important local family.
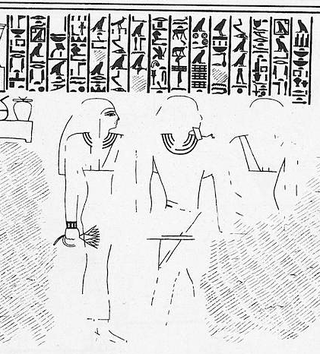
Netjernakht was an Ancient Egyptian official known from his tomb chapel at Beni Hasan in Middle Egypt. He lived most likely in the Twelfth Dynasty. His exact date and position are disputed.
Ramushenti was an ancient Egyptian local governor of the Oryx nome in Middle Egypt. He is only known from his decorated tomb chapel at Beni Hasan. In the decoration of his tomb chapel appear several inscriptions providing the name and titles of Ramushenti. He was great overlord of the Oryx nome. This is the main title of the local governors. Other titles include count (Haty-a), royal sealer, sole friend, king's acquaintance, who is in the chamber, who belongs to Nekhen and overlord of Nekheb,. Not much is known about his family. However, the parents of the local governor Baqet III are a person called Ramushenti and a woman called Heteperau. The two Ramushentis might be the same person. According to this, Ramushenti was the father of Baqet III who was most likely his successor.

Khety was an ancient Egyptian local governor of the Oryx nome in Middle Egypt in the Twelfth Dynasty. He is only known from his decorated tomb chapel at Beni Hasan. In the decoration of his tomb chapel appear several inscriptions providing the name and titles of Khety. He was great overlord of the entire Oryx nome. This is the main title of the local governors of the Oryx nome. Other titles include count (Haty-a), royal sealer, sole friend, king's acquaintance, who is in the chamber, who belongs to Nekhen and overlord of Nekheb, but also overseer of troops at all secret places. Not much is known about his family. His father was a person called Baqet, his wife was called Khnumhotep and there is one son attested with the name Khety. Naguib Kanawati wonders whether Khety was the son of Baqet III. The latter's tomb and those of Khety share the same plan and are close to each other.
Nakht was an ancient Egyptian local governor in Men'at Khufu in Middle Egypt in the Twelfth Dynasty. He is known from his decorated tomb chapel at Beni Hasan. The decoration of his tomb chapel is most likely unfinished. Only one wall is partly decorated with paintings, showing him standing in front of workers in the marshes. The inscriptions there provide the name and titles of Nakht. He was mayor and overseer of the eastern desert. Nakht is also mentioned in the tomb chapel of Khnumhotep II (BH3). In his chapel is a long biographical inscription reporting on the life of the governor but also on his family. There is stated that Khnumhotep I installed Nakht as governor in Men'at Khufu.

















