Related Research Articles

Native Americans, sometimes called American Indians, First Americans or Indigenous Americans, are the Indigenous peoples of the United States or portions thereof, such as American Indians from the contiguous United States and Alaska Natives. The United States Census Bureau defines Native American as "all people indigenous to the United States and its territories, including Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islanders, whose data are published separately from American Indians and Alaska Natives". The US census tracks data from American Indians and Alaska Native separately from Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islanders, who include Samoan Americans and Chamorros.

The Tuscarora are a Native American tribe and First Nations band government of the Iroquoian family, with members today in New York, USA, and Ontario, Canada. They coalesced as a people around the Great Lakes, likely about the same time as the rise of the Five Nations of the historic Iroquois Confederacy, also Iroquoian-speaking and based then in present-day New York.

The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the start of the war, the French colonies had a population of roughly 60,000 settlers, compared with 2 million in the British colonies. The outnumbered French particularly depended on their native allies.

The Cherokee are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, southwestern Virginia, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia and northeastern Alabama.

The Lakota are a Native American people. Also known as the Teton Sioux, they are one of the three prominent subcultures of the Sioux people, with the Eastern Dakota (Santee) and Western Dakota (Wičhíyena). Their current lands are in North and South Dakota. They speak Lakȟótiyapi—the Lakota language, the westernmost of three closely related languages that belong to the Siouan language family.

The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin are groups of Native American tribes and First Nations peoples in North America. The modern Sioux consist of two major divisions based on language divisions: the Dakota and Lakota; collectively they are known as the Očhéthi Šakówiŋ. The term "Sioux" is an exonym created from a French transcription ("Nadouessioux") of the Ojibwe term "Nadowessi", and can refer to any ethnic group within the Great Sioux Nation or to any of the nation's many language dialects.

The Cheyenne are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enrolled in the Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes in Oklahoma, and the Northern Cheyenne, who are enrolled in the Northern Cheyenne Tribe of the Northern Cheyenne Indian Reservation in Montana. The Cheyenne comprise two Native American tribes, the Só'taeo'o or Só'taétaneo'o and the Tsétsêhéstâhese. The tribes merged in the early 19th century.

Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States government for the relocation of Native Americans who held original Indian title to their land as a sovereign independent state. The tribes ceded land they occupied in exchange for land grants in 1803. The concept of an Indian territory was an outcome of the U.S. federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the U.S. government was one of assimilation.

The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and Arabian Desert but spread across the rest of the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa after the spread of Islam. The English word bedouin comes from the Arabic badawī, which means "desert dweller", and is traditionally contrasted with ḥāḍir, the term for sedentary people. Bedouin territory stretches from the vast deserts of North Africa to the rocky sands of the Middle East. They are traditionally divided into tribes, or clans, and historically share a common culture of herding camels and goats. The vast majority of Bedouins adhere to Islam, although there are some fewer numbers of Christian Bedouins present in the Fertile Crescent.

The Seminoles are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, and the Miccosukee Tribe of Indians of Florida, as well as independent groups. The Seminole people emerged in a process of ethnogenesis from various Native American groups who settled in Spanish Florida beginning in the early 1700s, most significantly northern Muscogee Creeks from what is now Georgia and Alabama.

The Noctuidae, commonly known as owlet moths, cutworms or armyworms, are a family of moths. They are considered the most controversial family in the superfamily Noctuoidea because many of the clades are constantly changing, along with the other families of the Noctuoidea. It was considered the largest family in Lepidoptera for a long time, but after regrouping Lymantriinae, Catocalinae and Calpinae within the family Erebidae, the latter holds this title now. Currently, Noctuidae is the second largest family in Noctuoidea, with about 1,089 genera and 11,772 species. This classification is still contingent, as more changes continue to appear between Noctuidae and Erebidae.
The Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians (EBCI), is a federally recognized Indian Tribe based in Western North Carolina in the United States. They are descended from the small group of 800–1000 Cherokee who remained in the Eastern United States after the US military, under the Indian Removal Act, moved the other 15,000 Cherokee to west of the Mississippi River in the late 1830s, to Indian Territory. Those Cherokee remaining in the East were to give up tribal Cherokee citizenship and to assimilate. They became US citizens.

The Sentinelese, also known as the Sentineli and the North Sentinel Islanders, are an indigenous people who inhabit North Sentinel Island in the Bay of Bengal in the northeastern Indian Ocean. Designated a particularly vulnerable tribal group and a Scheduled Tribe, they belong to the broader class of Andamanese peoples.

Uncontacted peoples are groups of indigenous peoples living without sustained contact with neighbouring communities and the world community. Groups who decide to remain uncontacted are referred to as indigenous peoples in voluntary isolation. Legal protections make estimating the total number of uncontacted peoples challenging, but estimates from the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights in the UN and the non-profit group Survival International point to between 100 and 200 uncontacted peoples numbering up to 10,000 individuals total. A majority of uncontacted peoples live in South America, particularly northern Brazil, where the Brazilian government and National Geographic estimate between 77 and 84 tribes reside.

The Kuki people are an ethnic group in the Northeastern Indian states of Manipur, Nagaland, Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram, as well as neighbouring countries of Bangladesh and Myanmar. The Kuki constitute one of several hill tribes within India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. In Northeast India, they are present in all states except Arunachal Pradesh.

Berber Jews are the Jewish communities of the Maghreb, in North Africa, who historically spoke Berber languages. Between 1950 and 1970 most emigrated to France, the United States, or Israel.
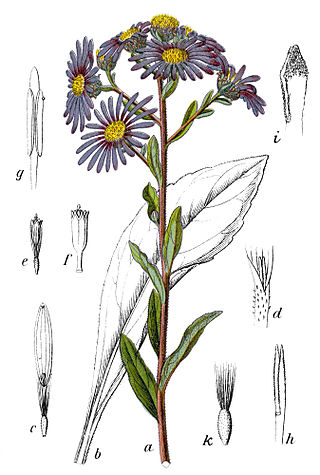
Asteroideae is a subfamily of the plant family Asteraceae. It contains about 70% of the species of the family. It consists of several tribes, including Astereae, Calenduleae, Eupatorieae, Gnaphalieae, Heliantheae, Senecioneae and Tageteae. Asteroideae contains plants found all over the world, many of which are shrubby. There are about 1,135 genera and 17,200 species within this subfamily; the largest genera by number of species are Helichrysum (500–600) and Artemisia (550).
References
- ↑ "U.S. Is Opening a Second Front As Paratroopers Land in North". The Wall Street Journal. 27 March 2003. Retrieved 23 August 2020.