Sources
- Madelung, W. (1975). "The Minor Dynasties of Northern Iran". In Frye, R. N. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 198–249. ISBN 978-0-521-20093-6.
Khurshid was a Justanid king who ruled briefly over Daylam in 865. He was the son and successor of Vahsudan of Daylam. Right after his accession, because of his opposition to his Alid overlord, he was deposed by the Alid Hasan ibn Zayd, who then made Khurshid's brother Justan III the new ruler of the Justanid dynasty.

Alid dynasties of northern Iran or Alavids. In the 9th–14th centuries, the northern Iranian regions of Tabaristan, Daylam and Gilan, sandwiched between the Caspian Sea and the Alborz range, came under the rule of a number of Arab Alid dynasties, espousing the Zaydi branch of Shia Islam.

Mardavij was an Iranian prince, who established the Ziyarid dynasty, ruling from 930 to 935.

The Sallarid dynasty, was a Muslim dynasty, of Daylami origin, which ruled in Tarom, Samiran, Daylam, Gilan and subsequently Azerbaijan, Arran, and some districts in Eastern Armenia in the 2nd half of the 10th century. They constitute part of the period in history that has been named the Iranian Intermezzo, a period that saw the rise of native Iranian dynasties during the 9th to the 11th centuries.
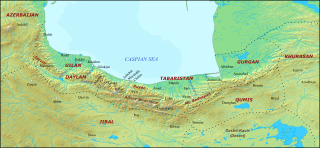
Tabaristan or Tabarestan, was the name applied to a mountainous region located on the Caspian coast of northern Iran. It corresponded to the present-day province of Mazandaran, which became the predominant name of the area from the 11th-century onwards.

The Justanids or Jostanids were an Iranian Zaydi Shia dynasty that ruled a part of Daylam from 791 to the late 11th century.
The Daylamites or Dailamites were an Iranian people inhabiting the Daylam—the mountainous regions of northern Iran on the southwest coast of the Caspian Sea, now comprising the southeastern half of Gilan Province.
Abu Mansur Makan ibn Kaki was a Daylamite military leader active in northern Iran in the early 10th century. He became involved in the succession disputes of the Alids of Tabaristan, and managed to establish himself as the ruler of Tabaristan and Gurgan for short periods of time, in competition to other Daylamite warlords such as Asfar ibn Shiruya or the Ziyarid brothers Mardavij and Vushmgir. He alternately opposed and secured support from the Samanid governors of Khurasan, and eventually fell in battle against a Samanid army.

Khurshid, erroneously designated Khurshid II by earlier scholars, was the last Dabuyid ispahbadh of Tabaristan. He succeeded to the throne at an early age, and was supervised by his uncle as regent until he reached the age of fourteen. Khurshid tried to assert his independence from his vassalage to the Caliphate, supported various rebellions and maintained diplomatic contacts with Tang China. Finally, the Abbasids conquered his country in 759–760, and captured most members of his family. Khurshid fled to Daylam, where he ended his life.

Abū Muḥammad al-Ḥasan ibn Zayd ibn Muḥammad ibn Ismaʿīl ibn al-Ḥasan ibn Zayd, also known as al-Dāʿī al-Kabīr, was an Alid who became the founder of the Zaydid dynasty of Tabaristan.

Abū Muḥammad al-Ḥasan ibn ʿAlī ibn al-Ḥasan ibn ʿAlī ibn ʿUmar al-Ashraf ibn ʿAlī Zayn al-ʿĀbidīn, better known as al-Ḥasan al-Uṭrūsh, was an Alid missionary of the Zaydi Shia sect who re-established Zaydi rule over the province of Tabaristan in northern Iran in 914, after fourteen years of Samanid rule. He ruled Tabaristan until his death under the regnal name of al-Nāṣir liʾl-Ḥaqq, and became known as al-Nāṣir al-Kabīr to distinguish him from his descendants who bore the same surname. He is still known and recognized as an imam among the Zaydis of Yemen.
Surkhab II was the fourth ruler of the Bavand dynasty from 755 to 772.
Vindadhhurmuzd, also known by the more correct form of Vandad Hormozd, was the ruler of the Qarinvand dynasty from 765 to 809.
Qarin I, was the eighth ruler of the Bavand dynasty from 839 to 867.
The Firuzanids (Perozanids) were an Iranian princely family of Daylamite origin which ruled Shukur, and at their greatest extent ruled all of Tabaristan.

The Qarinvand dynasty, or simply the Karenids, was an Iranian dynasty that ruled in parts of Tabaristan (Mazandaran) in what is now northern Iran from the 550s until the 11th-century. They considered themselves as the inheritors of the Dabuyid dynasty, and were known by their titles of Gilgilan and Ispahbadh. They were descended from Sukhra, a Parthian nobleman from the House of Karen, who was the de facto ruler of the Sasanian Empire from 484 to 493.
Justan III was the sixth king of the Justanid dynasty, ruling from 865 to 919. He was the brother and successor of Khurshid of Dailam.
Asfar ibn Shiruya was an Iranian military leader of Gilaki origin, active in northern Iran in the early 10th century. He played a major role in the succession disputes of the Alids of Tabaristan, and managed to establish himself as the ruler of Tabaristan and northern Jibal briefly from 928 to 930.

Ruyan, later known as Rustamdar (رستمدار), was the name of a mountainous district that encompassed the western part of Tabaristan/Mazandaran, a region on the Caspian coast of northern Iran.
Yaḥyā ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn al-Ḥasan ibn al-Ḥasan ibn ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib was an Alid and Zaydi leader who led a rebellion against the Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid in Daylam in 792. He was soon obliged to capitulate, but his activity began the spread of Zaydi Islam in the remote mountains of Daylam. After his surrender, he was initially treated with much honour, but Harun remained deeply suspicious of his popularity and intentions, and recalled him to Baghdad, where he spent the remainder of his life in prison. In 802, the Barmakid Ja'far ibn Yahya helped him escape, but he was captured; the event led to the execution of the Barmakids, once Harun's closest companions. Yahya died in prison, probably in 803.

The Forgotten Kings is a Chronicle account by Ahmad Kasravi. it is wrote since late 1928 to 1929, which includes documentary research on several At that time unknown and anonymous post-Islamic to pre-Seljuk Empire Iranian dynasties.