
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea, and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Cameroon's population of nearly 31 million people speak 250 native languages, in addition to the national tongues of English and French, or both. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area Rio dos Camarões, which became Cameroon in English. Fulani soldiers founded the Adamawa Emirate in the north in the 19th century, and various ethnic groups of the west and northwest established powerful chiefdoms and fondoms.

The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown, due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide.

A beret is a soft, round, flat-crowned cap made of hand-knitted wool, crocheted cotton, wool felt, or acrylic fibre.

The Akha are an ethnic group who live in small villages at higher elevations in the mountains of Thailand, Myanmar, Laos and Yunnan Province in China. They made their way from China into Southeast Asia during the early 20th century. Civil war in Burma and Laos resulted in an increased flow of Akha immigrants and there are now 80,000 people living in Thailand's northern provinces of Chiang Rai and Chiang Mai.
Hill tribe is a term used in Thailand for all of the various ethnic groups who mostly inhabit the high mountainous northern and western regions of Thailand, including both sides of the border areas between northern Thailand, Laos and Burma, the Phi Pan Nam Range, the Thanon Range, the latter a southern prolongation of the Shan Hills, as well as the Tenasserim Hills in Western Thailand. These areas exhibit mountainous terrain which is in some areas covered by thick forests, while in others it has been heavily affected by deforestation.

Adamawa State is a state in the North-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria, bordered by Borno to the northwest, Gombe to the west, and Taraba to the southwest while its eastern border forms part of the national border with Cameroon. It takes its name from the historic emirate of Adamawa, with the emirate's old capital of Yola serving as the capital city of Adamawa State. The state was formed in 1991 when the former Gongola State was broken up into Adamawa and Taraba states. The state is one of the most heterogeneous in Nigeria, having over 100 indigenous ethnic groups.
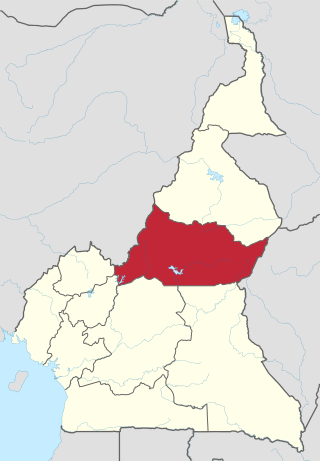
The Adamawa Region is a constituent region of the Republic of Cameroon. It borders the Centre and East regions to the south, the Northwest and West regions to the southwest, Nigeria to the west, the Central African Republic (CAR) to the east, and the North Region to the north.

The Kogi, or Cogui, or Kágaba, meaning "jaguar" in the Kogi language, are an indigenous group that resides in the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta mountains in northern Colombia. Their culture has continued since the Pre-Columbian era.

The Yakan people are among the major Filipino ethnolinguistic groups in the Sulu Archipelago. Having a significant number of followers of Islam, it is considered one of the 13 Muslim groups in the Philippines. The Yakans mainly reside in Basilan but are also in Zamboanga City. They speak a language known as Bissa Yakan, which has characteristics of both Sama-Bajau Sinama and Tausug. It is written in the Malayan Arabic script, with adaptations to sounds not present in Arabic.

The Hausa are a native ethnic group in West Africa. They speak the Hausa language, which is the second most spoken language after Arabic in the Afro-Asiatic language family. The Hausa are a culturally homogeneous people based primarily in the Sahelian and the sparse savanna areas of southern Niger and northern Nigeria respectively, numbering around 86 million people, with significant populations in Benin, Cameroon, Ivory Coast, Chad, Central African Republic, Togo, Ghana, as well as smaller populations in Sudan, Eritrea, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Senegal, Gambia. Predominantly Hausa-speaking communities are scattered throughout West Africa and on the traditional Hajj route north and east traversing the Sahara, with an especially large population in and around the town of Agadez. Other Hausa have also moved to large coastal cities in the region such as Lagos, Port Harcourt, Accra, Abidjan, Banjul and Cotonou as well as to parts of North Africa such as Libya over the course of the last 500 years. The Hausa traditionally live in small villages as well as in precolonial towns and cities where they grow crops, raise livestock including cattle as well as engage in trade, both local and long distance across Africa. They speak the Hausa language, an Afro-Asiatic language of the Chadic group. The Hausa aristocracy had historically developed an equestrian based culture. Still a status symbol of the traditional nobility in Hausa society, the horse still features in the Eid day celebrations, known as Ranar Sallah. Daura is the cultural center of the Hausa people. The town predates all the other major Hausa towns in tradition and culture.
Kamwe is a Chadic language native to Adamawa State and Borno State of Nigeria as well as to North-Western Cameroon.
The Gwèri or Vere language Were also known as Kobo or Mom Jango, is a member of the Duru branch of Savanna languages. It is spoken across the northern Nigerian–Cameroonian border.
Chamba Leko is one of two languages spoken by the Chamba people, the other being Chamba Daka. It is a member of the Leko branch of Savanna languages, and is spoken across the northern Nigerian–Cameroonian border.
The Koma language is a language cluster belonging to the Duru branch of Savannas languages of Cameroon. Blench (2004) includes three varieties separated in Ethnologue, Koma Ndera, Gɨmne, and Gɨmnɨme; within Koma Ndera, speakers of the marginal dialects, Gomnome and Ndera, can scarcely understand one another, though both understand the central dialect, Gomme.
Sikhism was founded in Punjab in 1469 by Guru Nanak on the foundations that everyone is equal, regardless of caste, age, or gender. Both men and women are supposed to follow the Five Ks: Kesh, Kangha (comb), Kara, Kachera and Kirpan, and there was never a distinction between what a woman should be allowed to do versus a man at theological level. Men and women are treated equally in the temple (gurdwara), and everyone eats and prays side-by-side. Both men and women are meant to carry the Kirpan with them as they are responsible for their own physical protection, and should not depend on others. Sikhs are strictly against the caste system and many chose to use Kaur or Singh as a last name to push against the problematic caste system in India. There is only one god (Waheguru) in Sikhism and they are without form or gender, and everyone is equal in the eyes of God. Many Sikh women believe that this absence of assignment of code of conduct for a woman versus a man proves that their religion is historically committed to gender equality. Presently, the culture does not always follow these traditions and equality is often more true in ideals rather than daily practice. According to Kiman Kaur: "It is essential to take into account the diverse Kaur narratives in order to critically understand the violence Sikh women experience due to religious, ethnic, and gender minoritization through enabling more intersectional conversations."

Cave dwelling Jews, also cave Jews or troglodyte Jews, were Jewish communities that dwelled in man-made caves in the mountains. The best known communities of this type existed in the Gharyan Plateau area of the Nafusa Mountains in Libya, and are commonly referred to as Gharyan Jews. These communities no longer exist today.

Waist beads is a type of jewelry worn around the waist or on the hips originating from West Africa, they are traditionally worn by women as a symbol of beauty, sexuality, femininity, fertility, well-being or maturity.
The Kamwe people is a Chadic language speaking group, native to Adamawa State and Borno State of Nigeria and Northwest Cameroon. The Kamwe Language is called Vecemwe in the native tongue. Kamwe is a compound word formed of 'Ka' and 'Mwe' meaning people of the same consanguinity and affinity. The Kamwe are industrious and enterprising. They are usually equated to the Igbos of South Eastern Nigeria
Yandang people are one of the tribes in Nigeria. They are located in Mayo-belwa in Adamawa state and Lau, Ardo Kola, Gasol in Taraba state.
This is a timeline of the Anglophone Crisis in Cameroon during 2023.










