In commerce, supply chain management (SCM) deals with a system of procurement, operations management, logistics and marketing channels, through which raw materials can be developed into finished products and delivered to their end customers. A more narrow definition of supply chain management is the "design, planning, execution, control, and monitoring of supply chain activities with the objective of creating net value, building a competitive infrastructure, leveraging worldwide logistics, synchronising supply with demand and measuring performance globally". This can include the movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, finished goods, and end to end order fulfilment from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Interconnected, interrelated or interlinked networks, channels and node businesses combine in the provision of products and services required by end customers in a supply chain.
Material requirements planning (MRP) is a production planning, scheduling, and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. Most MRP systems are software-based, but it is possible to conduct MRP by hand as well.

Pricing is the process whereby a business sets the price at which it will sell its products and services, and may be part of the business's marketing plan. In setting prices, the business will take into account the price at which it could acquire the goods, the manufacturing cost, the marketplace, competition, market condition, brand, and quality of product.

Porter's Five Forces Framework is a method of analysing the operating environment of a competition of a business. It draws from industrial organization (IO) economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and, therefore, the attractiveness of an industry in terms of its profitability. An "unattractive" industry is one in which the effect of these five forces reduces overall profitability. The most unattractive industry would be one approaching "pure competition", in which available profits for all firms are driven to normal profit levels. The five-forces perspective is associated with its originator, Michael E. Porter of Harvard University. This framework was first published in Harvard Business Review in 1979.
A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.
Market penetration refers to the successful selling of a good or service in a specific market. It is measured by the amount of sales volume of an existing good or service compared to the total target market for that product or service. Market penetration is the key for a business growth strategy stemming from the Ansoff Matrix (Richardson, M., & Evans, C.. H. Igor Ansoff first devised and published the Ansoff Matrix in the Harvard Business Review in 1957, within an article titled "Strategies for Diversification". The grid/matrix is utilized across businesses to help evaluate and determine the next stages the company must take in order to grow and the risks associated with the chosen strategy. With numerous options available, this matrix helps narrow down the best fit for an organization.
Procurement is the process of locating and agreeing to terms and purchasing goods, services, or other works from an external source, often with the use of a tendering or competitive bidding process. The term may also refer to a contractual obligation to "procure", i.e. to "ensure" that something is done. When a government agency buys goods or services through this practice, it is referred to as government procurement or public procurement.
Drop shipping is a form of retail business in which the seller accepts customer orders without keeping stock on hand. Instead, in a form of supply chain management, the seller transfers the orders and their shipment details either to the manufacturer, a wholesaler, another retailer, or a fulfillment house, which then ships the goods directly to the customer.
Purchasing is the procurement process a business or organization uses to acquire goods or services to accomplish its goals. Although there are several organizations that attempt to set standards in the purchasing process, processes can vary greatly between organizations.
Artificial scarcity is scarcity of items despite the technology for production or the sufficient capacity for sharing. The most common causes are monopoly pricing structures, such as those enabled by laws that restrict competition or by high fixed costs in a particular marketplace. The inefficiency associated with artificial scarcity is formally known as a deadweight loss.
The Information Services Procurement Library (ISPL) is a best practice library for the management of Information Technology related acquisition processes. It helps both the customer and supplier organization to achieve the desired quality using the corresponded amount of time and money by providing methods and best practices for risk management, contract management, and planning. ISPL focuses on the relationship between the customer and supplier organization: It helps constructing the request for proposal, it helps constructing the contract and delivery plan according to the project situation and risks, and it helps monitoring the delivery phase. ISPL is a unique Information Technology method because where most other Information Technology methods and frameworks focus on development, ISPL focuses purely on the procurement of information services. The target audience for ISPL consists of procurement managers, acquisition managers, programme managers, contract managers, facilities managers, service level managers, and project managers in the IT area. Because of ISPL's focus on procurement it is very suitable to be used with ITIL and PRINCE2.
Strategic sourcing is the process of developing channels of supply at the lowest total cost, not just the lowest purchase price. It expands upon traditional organisational purchasing activities to embrace all activities within the procurement cycle, from specification to receipt, payment for goods and services to sourcing production lines where the labor market would increase firms' ROI. Strategic sourcing processes aim for continuous improvement and re-evaluation of the purchasing activities of an organisation.
Industrial market segmentation is a scheme for categorizing industrial and business customers to guide strategic and tactical decision-making. Government agencies and industry associations use standardized segmentation schemes for statistical surveys. Most businesses create their own segmentation scheme to meet their particular needs. Industrial market segmentation is important in sales and marketing.
Field inventory management, commonly known as inventory management, is the task of understanding the stock mix of a company and the handling of the different demands placed on that stock. The demands are influenced by both external and internal factors and are balanced by the creation of purchase order requests to keep supplies at a reasonable or prescribed level. Inventory management is important for every other business enterprise.
Global sourcing is the practice of sourcing from the global market for goods and services across geopolitical boundaries. Global sourcing often aims to exploit global efficiencies in the delivery of a product or service. These efficiencies include low cost skilled labor, low cost raw material, extreme international competition, new technology and other economic factors like tax breaks and low trade tariffs. A large number of Information Technology projects and Services, including IS Applications and mobile phone apps and database services are outsourced globally to countries like India and Pakistan for more economical pricing.

A supply-chain network (SCN) is an evolution of the basic supply chain. Due to rapid technological advancement, organizations with a basic supply chain can develop this chain into a more complex structure involving a higher level of interdependence and connectivity between more organizations, this constitutes a supply-chain network.
Supply-chain sustainability is the management of environmental, social and economic impacts and the encouragement of good governance practices, throughout the lifecycles of goods and services. There is a growing need for integrating sustainable choices into supply-chain management. An increasing concern for sustainability is transforming how companies approach business. Whether motivated by their customers, corporate values or business opportunity, traditional priorities such as quality, efficiency and cost regularly compete for attention with concerns such as working conditions and environmental impact. A sustainable supply chain seizes value chain opportunities and offers significant competitive advantages for early adopters and process innovators.

An ‘‘‘electronic bidding system ‘‘‘ is an electronic bidding event according to defined negotiation rules (eAgreement). A buyer and two or more suppliers take part in this online event.
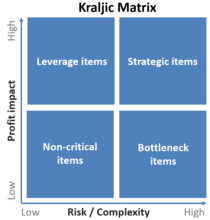
Category management is an approach to the organisation of purchasing within a business organisation. Applying category management to purchasing activity benefits organisations by providing an approach to reduce the cost of buying goods and services, reduce risk in the supply chain, increase overall value from the supply base and gain access to more innovation from suppliers. It is a strategic approach which focuses on the vast majority of organisational spend. If applied effectively throughout an entire organisation, the results can be significantly greater than traditional transactional based purchasing negotiations, however the discipline of category management is sorely misunderstood.
In commerce, global supply-chain management is defined as the distribution of goods and services throughout a trans-national companies' global network to maximize profit and minimize waste. Essentially, global supply chain-management is the same as supply-chain management, but it focuses on companies and organizations that are trans-national.