
The Queen Elizabeth Range is a rugged mountain range of the Transantarctic Mountains System, located in the Ross Dependency region of Antarctica.

The Usarp Mountains is a major Antarctic mountain range, lying westward of the Rennick Glacier and trending N-S for about 190 kilometres (118 mi). The feature is bounded to the north by Pryor Glacier and the Wilson Hills. Its important constituent parts include Welcome Mountain, Mount Van der Hoeven, Mount Weihaupt, Mount Stuart, Mount Lorius, Smith Bench, Mount Roberts, Pomerantz Tableland, Daniels Range, Emlen Peaks, Helliwell Hills and Morozumi Range.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies. Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains together with other scattered peaks form an arc about 260 miles long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.
Wohlthat Mountains is a large group of associated mountain features consisting of the Humboldt Mountains, Petermann Ranges, and the Gruber Mountains, located immediately east of the Orvin Mountains in Fimbulheimen in the central Queen Maud Land. Discovered by the Third German Antarctic Expedition (1938–1939), led by Capt. Alfred Ritscher, and named for Councilor of state Helmuth C.H. Wohlthat, who as economist and fiscal officer dealt with the organization of the expedition.
Ritscher Upland is a large ice-covered upland of western Queen Maud Land, bounded by Kraul Mountains and Heimefront Range to the west and southwest, and by Borg Massif and Kirwan Escarpment to the east. It was discovered by the Third German Antarctic Expedition (1938–1939), and named for Capt. Alfred Ritscher, leader of the expedition. It was remapped from air photos taken by the Norwegian-British-Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE) (1949–1952), led by John Schjelderup Giæver.
The Herbert Mountains are a conspicuous group of rock summits on the east side of Gordon Glacier in the Shackleton Range of Antarctica. They were first mapped in 1957 by the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (and named for Sir Edwin S. Herbert, Chairman of the Finance Committee and a Member of the Committee of Management of the expedition, 1955-58.

Icebreaker Glacier is a large valley glacier 10 miles (16 km) northeast of Mount Monteagle that flows southeast from the Mountaineer Range to Lady Newnes Bay, Victoria Land, Antarctica. Below Hermes Point its flow coalesces with that of Fitzgerald Glacier. The glacier was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1958–59, as a tribute to the work of the complements of U.S. Navy, and U.S. Coast Guard icebreakers in Antarctic exploration, in supporting scientists and in aiding other ships.

Jacka Glacier is a 0.8-mile (1.3 km) long glacier which flows northeast from Hayter Peak and terminates in icefalls opposite Vanhoffen Bluff on the north side of Heard Island in the southern Indian Ocean. The glacier appears to be roughly charted on an 1860 sketch map compiled by Captain H.C. Chester, an American sealer operating in the area during this period. It was surveyed in 1948 by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions, and named by them for Fred J. Jacka, an expedition physicist.
Daspit Glacier is a glacier 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, flowing east-northeast along the south side of Mount Shelby to the head of Trail Inlet, on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by members of the East Base of the United States Antarctic Service, 1939–41, and was originally named Fleming Glacier after Rev. W.L.S. Fleming. It was photographed from the air in 1947 by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne, and charted in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. It was renamed by Ronne for Captain Lawrence R. Daspit, U.S. Navy, who assisted in obtaining Navy support for the Ronne expedition, the original name being transferred to Fleming Glacier on the Rymill Coast.
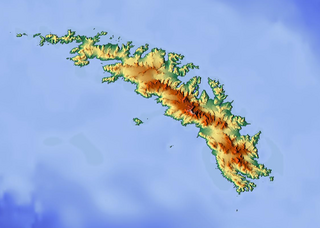
König Glacier is a glacier, 3 nautical miles (6 km) long and 1.5 nautical miles (3 km) wide, flowing in a northerly direction from the north side of Neumayer Glacier to the head of Fortuna Bay, South Georgia. It was first surveyed in 1928–29 by a German expedition under Kohl-Larsen, who named it for Austrian mountaineer Felix König, who took part in the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12, under Wilhelm Filchner.

Barrett Glacier is a glacier draining from the north slopes of the Prince Olav Mountains, about 15 nautical miles (30 km) long, flowing between the Longhorn Spurs and the Gabbro Hills to the Ross Ice Shelf. It was named by the Southern Party of the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (1963–64) for Peter J. Barrett, a geologist with that party.

Mushketov Glacier is a large glacier trending northeastward, draining the area between the Wohlthat Mountains on the west and the Weyprecht, Payer and Lomonosov Mountains on the east, in Queen Maud Land. Discovered and plotted from air photos by German Antarctic Expedition, 1938-39. Replotted from air photos and surveys by Soviet Antarctic Expedition, 1958–59, and named after Ivan V. Mushketov (1850–1902), Russian geologist and geographer.
Mount Guernsey is an isolated, mainly ice-covered mountain, 1,250 metres (4,100 ft) high, standing 6 nautical miles (11 km) north of the summit of Mount Edgell, on the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. The name "Ile Guernesey" was given in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, after the island of Guernsey off the coast of France. The position of "Ile Guernesey" on the French expedition maps does not agree with that of the mountain described above, but from the narrative and sketches by Maurice Bongrain, the expedition surveyor, it has been determined that this mountain was the feature seen in 1909 by Charcot from a position near the center of the entrance to Marguerite Bay. The mountain was surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition, but no name was assigned. It was further surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1948.
Mount Grieg is a snow-covered mountain, rising to about 800 metres (2,600 ft), with a rock-exposed west face, overlooking the southeast part of Brahms Inlet and is situated on the base of the Derocher Peninsula, on the north side of the Beethoven Peninsula in the southwest part of Alexander Island, Antarctica. A number of mountains in this vicinity first appear on maps by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48. This mountain, apparently one of these, was mapped from RARE air photos by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1960, and was remapped by the United States Geological Survey, 1988. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Edvard Grieg, the Norwegian composer.

Peter Glacier is a short, broad glacier draining northeast into Jutulstraumen Glacier just east of Neumayer Cliffs and Melleby Peak in Queen Maud Land. Mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by Norwegian-British-Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE) (1949–52) and air photos by the Norwegian expedition (1958–59). Named for Peter Melleby who was in charge of sledge dogs with the NBSAE.
Edwards Pillar is a large rock pillar on the western face of Mount Stinear in the Prince Charles Mountains of Antarctica. The feature is in the vicinity of a geodetic survey station established by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions Prince Charles Mountains survey party in 1971. It was named for N.F. Edwards, a surveyor with the party.
Mount Pawson is a mountain 7 nautical miles (13 km) southeast of Mohn Peaks, on the east coast of Palmer Land. First mapped by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS)-RARE joint sledge party of 1947-48. Remapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961-67. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for David L. Pawson, biologist with the Palmer Station-Eastwind Expedition, summer 1965-66.
French Passage is a passage through the Wilhelm Archipelago, extending in a northwest–southeast direction between Petermann Island, the Stray Islands, the Vedel Islands and the Myriad Islands to the north and the Argentine Islands, the Anagram Islands, the Roca Islands, and the Cruls Islands to the south. It was so named by the British Graham Land Expedition, 1934–37, because the passage was navigated for the first time in 1909 by the Pourquoi-Pas?, the ship of the French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot. Bradley Rock is an isolated rock which lies about 9 nautical miles (17 km) northwest of the entrance to French Passage.
Skarvhalsen Saddle is an ice saddle just south of Neumayer Cliffs, between Peter Glacier and Swithinbank Slope, in Queen Maud Land. Mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by Norwegian-British-Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE) (1949–52) and air photos by the Norwegian expedition (1958–59) and named Skarvhalsen.









