
Signy Island is a small subantarctic island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was named by the Norwegian whaler Petter Sørlle (1884–1933) after his wife, Signy Therese.

Alexander Island, which is also known as Alexander I Island, Alexander I Land, Alexander Land, Alexander I Archipelago, and Zemlja Alexandra I, is the largest island of Antarctica. It lies in the Bellingshausen Sea west of Palmer Land, Antarctic Peninsula from which it is separated by Marguerite Bay and George VI Sound. The George VI Ice Shelf entirely fills George VI Sound and connects Alexander Island to Palmer Land. The island partly surrounds Wilkins Sound, which lies to its west. Alexander Island is about 390 kilometres (240 mi) long in a north–south direction, 80 kilometres (50 mi) wide in the north, and 240 kilometres (150 mi) wide in the south. Alexander Island is the second-largest uninhabited island in the world, after Devon Island.
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica.

Marguerite Bay or Margaret Bay is an extensive bay on the west side of the Antarctic Peninsula, which is bounded on the north by Adelaide Island and on the south by Wordie Ice Shelf, George VI Sound and Alexander Island. The mainland coast on the Antarctic Peninsula is Fallières Coast. Islands within the bay include Pourquoi Pas Island, Horseshoe Island, Terminal Island, and Lagotellerie Island. Marguerite Bay was discovered in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, who named the bay for his wife.

Adelaide Island is a large, mainly ice-covered island, 139 kilometres (75 nmi) long and 37 kilometres (20 nmi) wide, lying at the north side of Marguerite Bay off the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. The Ginger Islands lie off the southern end. Mount Bodys is the easternmost mountain on Adelaide Island, rising to over 1,220 m. The island lies within the Argentine, British and Chilean Antarctic claims.
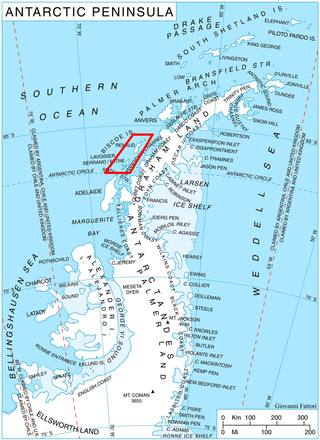
Renaud Island is an ice-covered island in the Biscoe Islands of Antarctica, 40 km (25 mi) long and from 6.4 to 16.1 km wide, lying between the Pitt Islands and Rabot Island. It is separated from the Pitt Islands to the northeast by Mraka Sound, and from Lavoisier Island to the southwest by Pendleton Strait.

Coronation Island is the largest of the South Orkney Islands, 25 nautical miles (46 km) long and from 3 to 8 nautical miles wide. The island extends in a general east–west direction, is mainly ice-covered and comprises numerous bays, glaciers and peaks, the highest rising to 1,265 metres (4,150 ft).

The Dailey Islands are a group of small volcanic islands lying off the coast of Victoria Land, 9 kilometres (5 nmi) northeast of Cape Chocolate, in the northern part of the ice shelf bordering McMurdo Sound. They were discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott, and named for Fred E. Dailey, the expedition carpenter.

The McMurdo Ice Shelf is the portion of the Ross Ice Shelf bounded by McMurdo Sound and Ross Island on the north and Minna Bluff on the south. Studies show this feature has characteristics quite distinct from the Ross Ice Shelf and merits individual naming. A.J. Heine, who made investigations in 1962–63, suggested the name for the ice shelf bounded by Ross Island, Brown Peninsula, Black Island and White Island. The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names has extended the application of this name to include the contiguous ice shelf southward to Minna Bluff.

Snow Hill Island is an almost completely snowcapped island, 33 km (21 mi) long and 12 km (7.5 mi) wide, lying off the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from James Ross Island to the north-east by Admiralty Sound and from Seymour Island to the north by Picnic Passage. It is one of several islands around the peninsula known as Graham Land, which is closer to Chile, Argentina and South America than any other part of the Antarctic continent.
Blaiklock Island is a high and rugged, irregular-shaped island 17 kilometres (9 nmi) long, lying between Bigourdan Fjord and Bourgeois Fjord. It is separated from Pourquoi Pas Island by The Narrows and from the west coast of Graham Land by Jones Channel. The feature was partially surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition under Rymill, at which time it was charted as a promontory. It was determined to be an island in 1949 by Kenneth V. Blaiklock, a Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) surveyor for whom it is named.

Smyley Island is an Antarctic island lying off the Antarctic Peninsula. The island is 61 km (38 mi) long and from 13 to 34 km wide, and lies about 20 km (12 mi) north of Case Island. It connects to the Stange Ice Shelf and is separated from Alexander Island by the Ronne Entrance. Smyley Island is one of the 27 islands of Palmer Land, Antarctica.

Flask Glacier, is a gently-sloping glacier, 25 nautical miles long, flowing east from Bruce Plateau to enter Scar Inlet between Daggoo Peak and Spouter Peak in Graham Land, Antarctica. The lower reaches of this glacier were surveyed and photographed by the Falklands Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1947. The entire glacier was photographed by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition in 1955–56, and mapped by the FIDS in 1957. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee after the third mate on the Pequod in Herman Melville's Moby-Dick; or, The White Whale.

Posadowsky Glacier is a glacier about 9 nautical miles long, flowing north to Posadowsky Bay immediately east of Gaussberg. Posadowsky Bay is an open embayment, located just east of the West Ice Shelf and fronting on the Davis Sea in Kaiser Wilhelm II Land. Kaiser Wilhelm II Land is the part of East Antarctica lying between Cape Penck, at 87°43'E, and Cape Filchner, at 91°54'E, and is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. Other notable geographic features in this area include Drygalski Island, located 45 mi NNE of Cape Filchner in the Davis Sea, and Mirny Station, a Russian scientific research station.

Wright Peninsula is a peninsula on the east coast of Adelaide Island, Antarctica, lying between Stonehouse Bay to the north and Ryder Bay to the south. On its northern coastline the peninsula is fringed by the Stokes Peaks; on its southern side by the Reptile Ridge. The Princess Royal Range separates the peninsula from the rest of Adelaide Island; the only 'gap' is provided by McCallum Pass.

Borceguí Island is an ice-free island in the South Shetland Islands, midway between Cape Yelcho and the Gibbous Rocks, 2 kilometres (1 nmi) off the north coast of Elephant Island. The name was applied by the command of the Argentine sea-going tug Chiriguano in the 1954–55 cruise; in Spanish "borceguí" means half-boot and describes the shape of the island.
Brash Island is an isolated island lying 9.3 kilometres (5 nmi) northwest of Darwin Island, off the southeast end of Joinville Island. It was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1953, and so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee because the island lies in an area where there is a frequent occurrence of "brash ice".
Fuchs Ice Piedmont is an ice piedmont 70 nautical miles (130 km) long, extending in a northeast–southwest direction along the entire west coast of Adelaide Island. It was first mapped in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot. It was named by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) for Sir Vivian E. Fuchs, FIDS base leader and geologist at Stonington Island in 1948–49.
Tsiolkovskiy Island is an ice-covered island in the Fimbul Ice Shelf, Queen Maud Land. The summit of the island rises about 200 m above the general level of the ice shelf. Kroshka Island lies close southwest and is similar but smaller. First mapped by the Soviet Antarctic Expedition in 1961 and named for Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (1857–1935), Russian scientist and inventor.
Haswell Island is the largest of the Haswell Islands, lying off the coast of Antarctica, about 3 kilometres (1.5 nmi) north of Mabus Point in Queen Mary Land. It was discovered by the Western Base Party of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition, 1911–14, under Mawson, and named by him for Professor William A. Haswell, a zoologist at Sydney University and a member of the expedition's Advisory Committee.













