
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg.
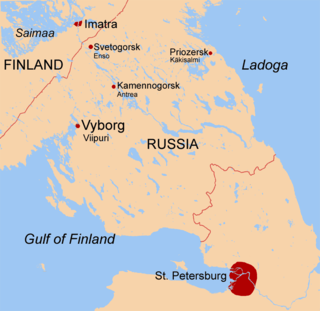
The Karelian Isthmus is the approximately 45–110-kilometre-wide (30–70 mi) stretch of land, situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the westernmost point of Lake Ladoga, Pekonlahti. If the Karelian Isthmus is defined as the entire territory of present-day Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast to the north of the Neva and also a tiny part of the Republic of Karelia, the area of the isthmus is about 15,000 km2 (5,800 sq mi).

Imatra is a town and municipality in southeastern Finland. Imatra is dominated by Lake Saimaa, the Vuoksi River and the border with Russia. On the other side of the border, 7 kilometres (4 mi) away from the centre of Imatra, lies the Russian town of Svetogorsk. St Petersburg is situated 210 km (130 mi) to the southeast, Finland's capital Helsinki is 230 km (140 mi) away and Lappeenranta, the nearest Finnish town, is 37 km (23 mi) away. Imatra belongs to the administrative province of Southern Finland and the region of South Karelia.

Lappeenranta is a city and municipality in the region of South Karelia, about 30 kilometres from the Russian border and 64 kilometres (40 mi) from the town of Vyborg (Viipuri). It is situated on the shore of the Lake Saimaa in southeastern Finland, and is one of the most significant urban centers in the whole Saimaa region, along with the towns of Imatra, Mikkeli and Savonlinna. With approximately 73,000 inhabitants Lappeenranta is the 13th largest city in Finland, after incorporating the previous municipalities of Lappee and Lauritsala in 1967, Nuijamaa in 1989, Joutseno in 2009, and Ylämaa in 2010.

Saimaa is a lake located in the Finnish Lakeland area in southeastern Finland. At approximately 4,279 square kilometres (1,652 sq mi), it is the largest lake in Finland, and the fourth largest natural freshwater lake in Europe.

Mikkeli is a town and municipality in Finland. It is located in what used to be the province of Eastern Finland and is part of the Etelä-Savo region. The municipality has a population of 51,976 and covers an area of 3,229.57 square kilometres (1,246.94 sq mi) of which 424.7 km2 (164.0 sq mi) is water. The population density is 30.58 inhabitants per square kilometre (79.2/sq mi) The town is located on lake Saimaa. Together with Savonlinna, it is one of the largest towns in the South Savonia region and one of the concentrations in the region's hospital districts.

The Vuoksi is a river running through the northernmost part of the Karelian Isthmus from Lake Saimaa in southeastern Finland to Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia. The river enters Lake Ladoga in three branches, an older main northern branch at Priozersk (Käkisalmi), a smaller branch a few kilometers to the north of it, and a new southern branch entering 50 kilometers (31 mi) further southeast as Burnaya River, which has become the main stream in terms of water discharge. Since 1857, the old northern distributaries drain only the lower reaches of the Vuoksi basin and are not fed by Lake Saimaa. The northern and southern branches actually belong to two separate river systems, which at times get isolated from each other in dry seasons.
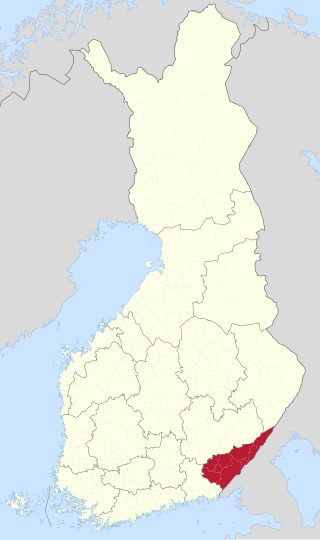
South Karelia is a region of Finland. It borders the regions of Kymenlaakso, South Savo and North Karelia, as well as Russia.

Lake Inari is the largest lake in Sápmi and the third-largest lake in Finland. It is located in the northern part of Lapland, north of the Arctic Circle. The lake is 117–119 metres (384–390 ft) above sea level, and is regulated at the Kaitakoski power plant in Russia. The freezing period normally extends from November to early June.

The Saimaa Canal is a transportation canal that connects lake Saimaa with the Gulf of Finland near Vyborg, Russia. The canal was built from 1845 to 1856 and opened on 7 September 1856 . It was overhauled and widened in 1963–1968.

The Arctic char or Arctic charr is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes, as well as Arctic and subarctic coastal waters in the Holarctic.

The Saimaa ringed seal is a subspecies and glacial relict of ringed seal. They are among the most endangered seals in the world, having a total population of only about 400 individuals. The only existing population of these seals is found in Lake Saimaa, Finland. They have lived in complete isolation from other ringed seal species for around 9,500 years and have diverged into a morphologically and ecologically different subspecies of ringed seal. The population is descended from ringed seals that were separated from the rest when the land rose after the last ice age. This seal, along with the Ladoga seal and the Baikal seal, is one of the few living freshwater seals.

Kuopio Airport is an airport in Rissala, Siilinjärvi, Finland, about 14 kilometres (9 mi) north of Kuopio city centre. It is the fifth busiest airport in Finland, as measured by the number of passengers (ca. 235,411.

Finnish Lakeland or Finnish lake district is the largest of the four landscape regions into which the geography of Finland is divided.

Haukivesi is a lake in southeastern Finland and a part of the Saimaa lake system. Haukivesi is the central basin of the system, collecting 80% of the water that eventually flows into Lake Ladoga through River Vuoksi. Its area is 562.31 square kilometres (217.11 sq mi) (8th). Like other lakes in the system, it has a convoluted shoreline with numerous islands and is divided into a number of smaller regions (selkä) such as Siitinselkä, Saviluoto, Tahkoselkä, Vuoriselkä, Kuokanselkä, Kuivaselkä, Heposelkä, Peonselkä, Tuunaanselkä, Hiekonselkä, Varparannanselkä, and Iso-Haukivesi. Haukivesi stretches from Varkaus to Savonlinna in a northeast–southwest direction. The northern part is shallow, at less than 20 metres (66 ft), but deepens toward the southeast, up to 60 metres (200 ft) at Kuivaselkä.

Kermajärvi is a medium-sized lake in the Vuoksi main catchment area. It is located in the region of Southern Savonia in Heinävesi. It is the country's 53rd largest lake with an area of 85.57 square kilometres (33.04 sq mi) and consists of a wide open lake with plenty of islands in both northwest and southeast parts of it and several long, narrow bays in both ends.
In biogeography and paleontology, a relict is a population or taxon of organisms that was more widespread or more diverse in the past. A relictual population is a population currently inhabiting a restricted area whose range was far wider during a previous geologic epoch. Similarly, a relictual taxon is a taxon which is the sole surviving representative of a formerly diverse group.
Yövesi is a sub-lake of the lake Saimaa in eastern Finland. It is located in Mikkeli municipality in the Southern Savonia region. Part of the Saimaa lake system, it borders on the system of Pihlajavesi to the east. The deepest point of the whole Saimaa is in Yövesi, in Käenniemenselkä open area. The Astuvansalmi rock paintings are situated in the northern shore of Yövesi.

The wildlife of Finland is affected by prevailing environmental conditions. The phytogeography of Finland is shared between the Arctic, central European, and northern European provinces of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. The territory of Finland can be subdivided into three ecoregions: the Scandinavian and Russian taiga, Sarmatic mixed forests, and Scandinavian montane birch forest and grasslands. Taiga covers most of Finland from northern regions of southern provinces to the north of Lapland. On the southwestern coast, south of the Helsinki-Rauma line, forests are mixed as is more typical in the Baltic region. In the extreme north of Finland, near the tree line and Arctic Ocean, montane birch forests are common.


















