
The Usarp Mountains is a major Antarctic mountain range, lying westward of the Rennick Glacier and trending N-S for about 190 kilometres (118 mi). The feature is bounded to the north by Pryor Glacier and the Wilson Hills. Its important constituent parts include Welcome Mountain, Mount Van der Hoeven, Mount Weihaupt, Mount Stuart, Mount Lorius, Smith Bench, Mount Roberts, Pomerantz Tableland, Daniels Range, Emlen Peaks, Helliwell Hills and Morozumi Range.
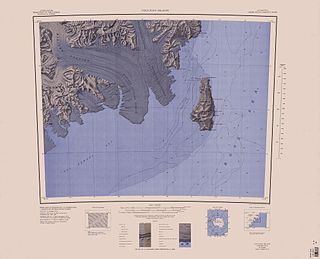
Borchgrevink Glacier is a large glacier in the Victory Mountains, Victoria Land, draining south between Malta Plateau and Daniell Peninsula, and thence projecting into Glacier Strait, Ross Sea, as a floating glacier tongue, the Borchgrevink Glacier Tongue, just south of Cape Jones. It was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1957–58, for Carsten Borchgrevink, leader of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900. Borchgrevink visited the area in February 1900 and first observed the seaward portion of the glacier.
Isfossnipa Peak is a peak 2 miles (3 km) southeast of Austvorren Ridge, surmounting the eastern part of the Neumayer Cliffs in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It was photographed from the air by the Third German Antarctic Expedition (1938–39). It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1949–1952), led by John Schjelderup Giæver, and from air photos by the Norwegian expedition (1958–59) and named "Isfossnipa".

Austreskorve Glacier is a broad glacier in the Mühlig-Hofmann Mountains which drains north from a position just east of the head of Vestreskorve Glacier and passes along the east side of Breplogen Mountain. It was mapped and named from surveys and from air photos by the Sixth Norwegian Antarctic Expedition (1956–60).
Ahlstad Hills is a group of rock hills just east of Cumulus Mountain in the Mühlig-Hofmann Mountains of Queen Maud Land. Plotted from surveys and air photos by the Sixth Norwegian Antarctic Expedition (1956–60), which gave it the name Ahlstadhottane.

Beakley Glacier is a glacier on the west side of the Duncan Peninsula on Carney Island, flowing north into the Amundsen Sea. It was delineated by the United States Geological Survey from aerial photos taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump in January 1947, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Vice Admiral W.M. Beakley, U.S. Navy, Deputy Chief of Naval Operations for Ship Operations and Readiness during the IGY period, 1957–58.
Urfjelldokka Valley is a broad ice-filled valley between Urfjell Cliffs and Skappelnabben Spur along the Kirwan Escarpment in Queen Maud Land. Mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by Norwegian-British-Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE) (1949–52) and additional air photos (1958–59). Named in association with Urfjell Cliffs.
Utrinden Point is a rock point at the northwest side of Kuven Hill, near the southwest end of the Kirwan Escarpment in Queen Maud Land. Mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by NGSAE (1949–52) and additional air photos (1958–59), and named Utrinden.
Kuvsletta Flat is a small, flattish, ice-covered area between Utrinden Point and Framranten Point, near the southwest end of the Kirwan Escarpment in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1949–52) and additional air photos (1958–59), and named Kuvsletta.
Kuven Hill is a prominent hill between Gommen Valley and Kuvsletta Flat, near the southwest end of the Kirwan Escarpment in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1949–52) and additional air photos (1958–59), and named Kuven.
Trollkjelen Crevasse Field is a crevasse field about 12 nautical miles (22 km) long in the Fimbul Ice Shelf, lying immediately off the northeast side of Trollkjelneset Headland in Queen Maud Land. Mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by Norwegian-British-Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE) (1949–52) and air photos by the Norwegian expedition (1958–59) and named Trollkjelen.
Domen Butte is a snow-topped butte with steep rock sides, just southwest of Hogskavlen Mountain in the Borg Massif of Queen Maud Land. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1949–52) and named Domen.

Peter Glacier is a short, broad glacier draining northeast into Jutulstraumen Glacier just east of Neumayer Cliffs and Melleby Peak in Queen Maud Land. Mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by Norwegian-British-Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE) (1949–52) and air photos by the Norwegian expedition (1958–59). Named for Peter Melleby who was in charge of sledge dogs with the NBSAE.
Mosby Glacier is a glacier 5 nautical miles (9 km) wide at its mouth, flowing in a southeasterly direction to the northwest corner of New Bedford Inlet, on the east coast of Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was discovered and photographed from the air in December 1940 by the United States Antarctic Service. During 1947 it was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne, who in conjunction with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) mapped its terminus from the ground. It was named by the FIDS for Hakon Mosby, a Norwegian meteorologist and oceanographer.
Lorentzen Peak is a peak 5 nautical miles (9 km) south of Vesleskarvet Cliff and 6 nautical miles west of Tommeliten Rock, on the west side of Ahlmann Ridge in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE) (1949–52) and air photos by the Norwegian expedition (1958–59), and was named for Bjarne Lorentzen, a cook with the NBSAE.
Heiser Ridge is a narrow rock ridge, 5 nautical miles (9 km) long, midway between the West Prongs and Hudson Ridge in the Neptune Range of the Pensacola Mountains in Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1956–66, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for James R. Heiser, a topographic engineer with the Neptune Range field party, summer 1963–64.
Mount Hemmingsen is a mountain at the northeast end of the Werner Mountains, located on the south side of Meinardus Glacier, 5 nautical miles (9 km) southwest of Court Nunatak, in Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Edvard A. Hemmingsen, a biologist at McMurdo Station in the summer of 1966–67, and at Palmer Station, 1967–68.

The Lyon Nunataks are a group of nunataks lying west of the Grossman Nunataks and 30 nautical miles (56 km) northwest of the Behrendt Mountains, in Palmer Land, Antarctica. They include Grossenbacher Nunatak, Holtet Nunatak, Christoph Nunatak and Isakson Nunatak. The group was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after Owen R. Lyon, hospital corpsman, U.S. Navy, chief petty officer in charge of Eights Station in 1965.







