Related Research Articles

The retina is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera.

Caenorhabditis elegans is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek caeno- (recent), rhabditis (rod-like) and Latin elegans (elegant). In 1900, Maupas initially named it Rhabditides elegans. Osche placed it in the subgenus Caenorhabditis in 1952, and in 1955, Dougherty raised Caenorhabditis to the status of genus.

Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and convert it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons. In higher organisms, the eye is a complex optical system which collects light from the surrounding environment, regulates its intensity through a diaphragm, focuses it through an adjustable assembly of lenses to form an image, converts this image into a set of electrical signals, and transmits these signals to the brain through complex neural pathways that connect the eye via the optic nerve to the visual cortex and other areas of the brain. Eyes with resolving power have come in ten fundamentally different forms, and 96% of animal species possess a complex optical system. Image-resolving eyes are present in molluscs, chordates and arthropods.

The visual system comprises the sensory organ and parts of the central nervous system which gives organisms the sense of sight as well as enabling the formation of several non-image photo response functions. It detects and interprets information from the optical spectrum perceptible to that species to "build a representation" of the surrounding environment. The visual system carries out a number of complex tasks, including the reception of light and the formation of monocular neural representations, colour vision, the neural mechanisms underlying stereopsis and assessment of distances to and between objects, the identification of a particular object of interest, motion perception, the analysis and integration of visual information, pattern recognition, accurate motor coordination under visual guidance, and more. The neuropsychological side of visual information processing is known as visual perception, an abnormality of which is called visual impairment, and a complete absence of which is called blindness. Non-image forming visual functions, independent of visual perception, include the pupillary light reflex and circadian photoentrainment.

Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a genetic disorder of the eyes that causes loss of vision. Symptoms include trouble seeing at night and decreasing peripheral vision. As peripheral vision worsens, people may experience "tunnel vision". Complete blindness is uncommon. Onset of symptoms is generally gradual and often begins in childhood.

A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential.

A planarian is one of many flatworms of the traditional class Turbellaria. It usually describes free-living flatworms of the order Tricladida (triclads), although this common name is also used for a wide number of free-living platyhelminthes. Planaria are common to many parts of the world, living in both saltwater and freshwater ponds and rivers. Some species are terrestrial and are found under logs, in or on the soil, and on plants in humid areas.

Rod cells are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in lower light better than the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Rods are usually found concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in peripheral vision. On average, there are approximately 92 million rod cells in the human retina. Rod cells are more sensitive than cone cells and are almost entirely responsible for night vision. However, rods have little role in color vision, which is the main reason why colors are much less apparent in dim light.

Pinealocytes are the main cells contained in the pineal gland, located behind the third ventricle and between the two hemispheres of the brain. The primary function of the pinealocytes is the secretion of the hormone melatonin, important in the regulation of circadian rhythms. In humans, the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus communicates the message of darkness to the pinealocytes, and as a result, controls the day and night cycle. It has been suggested that pinealocytes are derived from photoreceptor cells. Research has also shown the decline in the number of pinealocytes by way of apoptosis as the age of the organism increases. There are two different types of pinealocytes, type I and type II, which have been classified based on certain properties including shape, presence or absence of infolding of the nuclear envelope, and composition of the cytoplasm.

A depth gauge is an instrument for measuring depth below a reference surface. They include depth gauges for underwater diving and similar applications, and engineering instruments used to measure the depth of holes and indentations from a reference surface.
Transient receptor potential channels are a group of ion channels located mostly on the plasma membrane of numerous animal cell types. Most of these are grouped into two broad groups: Group 1 includes TRPC, TRPV, TRPVL, TRPM, TRPS, TRPN, and TRPA. Group 2 consists of TRPP and TRPML. Other less-well categorized TRP channels exist, including yeast channels and a number of Group 1 and Group 2 channels present in non-animals. Many of these channels mediate a variety of sensations such as pain, temperature, different kinds of tastes, pressure, and vision. In the body, some TRP channels are thought to behave like microscopic thermometers and used in animals to sense hot or cold. Some TRP channels are activated by molecules found in spices like garlic (allicin), chili pepper (capsaicin), wasabi ; others are activated by menthol, camphor, peppermint, and cooling agents; yet others are activated by molecules found in cannabis or stevia. Some act as sensors of osmotic pressure, volume, stretch, and vibration. Most of the channels are activated or inhibited by signaling lipids and contribute to a family of lipid-gated ion channels.

Melanopsin is a type of photopigment belonging to a larger family of light-sensitive retinal proteins called opsins and encoded by the gene Opn4. In the mammalian retina, there are two additional categories of opsins, both involved in the formation of visual images: rhodopsin and photopsin in the rod and cone photoreceptor cells, respectively.

Cyclic nucleotide–gated ion channels or CNG channels are ion channels that function in response to the binding of cyclic nucleotides. CNG channels are nonselective cation channels that are found in the membranes of various tissue and cell types, and are significant in sensory transduction as well as cellular development. Their function can be the result of a combination of the binding of cyclic nucleotides and either a depolarization or a hyperpolarization event. Initially discovered in the cells that make up the retina of the eye, CNG channels have been found in many different cell types across both the animal and the plant kingdoms. CNG channels have a very complex structure with various subunits and domains that play a critical role in their function. CNG channels are significant in the function of various sensory pathways including vision and olfaction, as well as in other key cellular functions such as hormone release and chemotaxis. CNG channels have also been found to exist in prokaryotes, including many spirochaeta, though their precise role in bacterial physiology remains unknown.

Horizontal cells are the laterally interconnecting neurons having cell bodies in the inner nuclear layer of the retina of vertebrate eyes. They help integrate and regulate the input from multiple photoreceptor cells. Among their functions, horizontal cells are believed to be responsible for increasing contrast via lateral inhibition and adapting both to bright and dim light conditions. Horizontal cells provide inhibitory feedback to rod and cone photoreceptors. They are thought to be important for the antagonistic center-surround property of the receptive fields of many types of retinal ganglion cells.
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), also called photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGC), or melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells (mRGCs), are a type of neuron in the retina of the mammalian eye. The presence of ipRGCs was first suspected in 1927 when rodless, coneless mice still responded to a light stimulus through pupil constriction, This implied that rods and cones are not the only light-sensitive neurons in the retina. Yet research on these cells did not advance until the 1980s. Recent research has shown that these retinal ganglion cells, unlike other retinal ganglion cells, are intrinsically photosensitive due to the presence of melanopsin, a light-sensitive protein. Therefore they constitute a third class of photoreceptors, in addition to rod and cone cells.

Many researchers have found the evolution of the eye attractive to study because the eye distinctively exemplifies an analogous organ found in many animal forms. Simple light detection is found in bacteria, single-celled organisms, plants and animals. Complex, image-forming eyes have evolved independently several times.

Uncoordinated-119 (Unc-119) is a protein that has been identified in C. elegans, humans, mice, zebrafish, rabbits, pig, calf, monkey, and protozoa. They have been classified in the GMP phophodiesterase, delta superfamily. Unc-119 proteins are categorized into their own family but are shown to be ancestrally related to PrBP and rhoGDI. It has been given many different names: Retinal Protein 4, HRG4, POC7 Centriolar Protein Homolog A, IMD13, POC7A, and RG4.

Cornelia Isabella "Cori" Bargmann is an American neurobiologist. She is known for her work on the genetic and neural circuit mechanisms of behavior using C. elegans, particularly the mechanisms of olfaction in the worm. She has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences and had been a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator at UCSF and then Rockefeller University from 1995 to 2016. She was the Head of Science at the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative from 2016 to 2022. In 2012 she was awarded the $1 million Kavli Prize, and in 2013 the $3 million Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences.

NeuN , a protein which is a homologue to the protein product of a sex-determining gene in Caenorhabditis elegans, is a neuronal nuclear antigen that is commonly used as a biomarker for neurons.
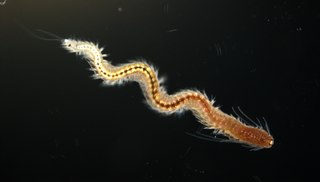
Platynereis dumerilii is a species of annelid polychaete worm. It was originally placed into the genus Nereis and later reassigned to the genus Platynereis. Platynereis dumerilii lives in coastal marine waters from temperate to tropical zones. It can be found in a wide range from the Azores, the Mediterranean, in the North Sea, the English Channel, and the Atlantic down to the Cape of Good Hope, in the Black Sea, the Red Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Sea of Japan, the Pacific, and the Kerguelen Islands. Platynereis dumerilii is today an important lab animal, it is considered as a living fossil, and it is used in many phylogenetic studies as a model organism.
References
- 1 2 Gong, Jianke; Yuan, Yiyuan; Ward, Alex; Kang, Lijun; Zhang, Bi; Wu, Zhiping; Peng, Junmin; Feng, Zhaoyang; Liu, Jianfeng; Xu, X. Z. Shawn (November 2016). "The C. elegans Taste Receptor Homolog LITE-1 Is a Photoreceptor". Cell. 167 (5): 1252–1263.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.053. ISSN 1097-4172. PMC 5388352 . PMID 27863243.
- ↑ "lite-1 (gene) - WormBase : Nematode Information Resource". wormbase.org. Retrieved 2020-05-05.
- ↑ November 2016, Laura Geggel 17 (17 November 2016). "Teensy, Eyeless Worms Have Completely New Light-Detecting Cells". livescience.com. Retrieved 2020-05-10.