Related Research Articles

The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and oldest specialised agency of the UN. The ILO has 187 member states: 186 out of 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.

Flag of convenience (FOC) is a business practice whereby a ship's owners register a merchant ship in a ship register of a country other than that of the ship's owners, and the ship flies the civil ensign of that country, called the flag state. The term is often used pejoratively, and although common, the practice is sometimes regarded as contentious.
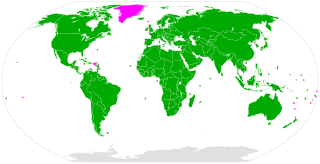
The Convention Concerning the Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labour, known in short as the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, was adopted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) in 1999 as ILO Convention No 182. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.
The Convention concerning the Rights of Association and Combination of Agricultural Workers is an International Labour Organization Convention adopted in 1921. The convention secures the rights of "association and combination" of agricultural workers to the same extent as those rights are extended to industrial workers.
Inspection of Emigrants Convention, 1926 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Invalidity, Old-Age and Survivors' Benefits Convention, 1967 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Significant levels of child labour exist in Lesotho. The 1997 Lesotho Labour Force Survey found that 4.6% of males who were working full-time, 14.1% of males who were working part-time and 1.3% of male job seekers in Lesotho were aged between 10 and 15 years. Many of these would have been involved in herding and those with part-time work were not necessarily earning an income but may well have been working on family land in subsistence agriculture.
Child labour in Namibia is not always reported. This involved cases of child prostitution as well as voluntary and forced agricultural labour, cattle herding and vending.
Labour Inspection Convention, 1947 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
The Convention concerning the Right of Association and the Settlement of Labour Disputes in Non-Metropolitan Territories is an International Labour Organization Convention on the rights of workers in non-metropoliton territories to form and be active in labour unions.
Minimum Wage Fixing Machinery (Agriculture) Convention, 1951 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Holidays with Pay (Agriculture) Convention, 1952 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
The Convention concerning Discrimination in Respect of Employment and Occupation or Discrimination Convention is an International Labour Organization Convention on anti-discrimination. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions. The convention requires states to enable legislation which prohibits all discrimination and exclusion on any basis including of race or colour, sex, religion, political opinion, national or social origin in employment and repeal legislation that is not based on equal opportunities.
Prevention of Accidents (Seafarers) Convention, 1970 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Labour Inspection (Seafarers) Convention, 1996 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
The Inspection du travail is a French specialized body of civil servants, charged of the surveillance of employment and labour law in firms, created in 1892 during the Third Republic.

The Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) is an International Labour Organization (ILO) convention, number 186, established in 2006 as the fourth pillar of international maritime law and embodies "all up-to-date standards of existing international maritime labour Conventions and Recommendations, as well as the fundamental principles to be found in other international labour Conventions". The other pillars are the SOLAS, STCW and MARPOL. The treaties applies to all ships entering the harbours of parties to the treaty (port states), as well as to all ships flying the flag of state party (flag states, as of 2021: over 91 per cent).
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating Work and the workplace. The International Labour Organization and the World Trade Organization have been the main international bodies involved in reforming labour markets. The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank have indirectly driven changes in labour policy by demanding structural adjustment conditions for receiving loans or grants. Issues regarding Conflict of laws arise, determined by national courts, when people work in more than one country, and supra-national bodies, particularly in the law of the European Union, has a growing body of rules regarding labour rights.
The right to sit refers to laws or policies granting workers the right to be granted suitable seating at the workplace. Jurisdictions that have enshrined "right to sit" laws or policies include the United Kingdom, Jamaica, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Uganda, Lesotho, Malaysia, Brazil, Israel, Ireland, the Indian states of Tamil Nadu and Kerala, the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador, and the British overseas territory of Gibraltar and Montserrat. Almost all states of the United States and Australia, as well as the majority of Canadian provinces passed right to sit legislation for women workers between 1881 and 1917. US states with current right to sit legislation include California, Florida, Massachusetts, Montana, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Wisconsin. A right to sit provision is included in the International Labour Organization's Hygiene Convention, 1964; the convention being ratified by 51 countries as of 2014. Local jurisdictions with right to sit laws include Portland, Oregon, St. Louis, Missouri and London's Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. Some jurisdictions, such as Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Idaho, Kentucky, Maine, Michigan, Missouri, Nevada, New Hampshire, Quebec, and Washington, D.C. have revoked their right to sit laws. Many right to sit laws originally contained gendered language specifying women workers only. Some jurisdictions maintain gendered laws, but many jurisdictions have amended their right to sit laws to be gender neutral.