Related Research Articles

The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the first and oldest specialised agencies of the UN. The ILO has 187 member states: 186 out of 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.
Labour laws, labour code or employment laws are those that mediate the relationship between workers, employing entities, trade unions, and the government. Collective labour law relates to the tripartite relationship between employee, employer, and union.
Labor rights or workers' rights are both legal rights and human rights relating to labor relations between workers and employers. These rights are codified in national and international labor and employment law. In general, these rights influence working conditions in the relations of employment. One of the most prominent is the right to freedom of association, otherwise known as the right to organize. Workers organized in trade unions exercise the right to collective bargaining to improve working conditions.
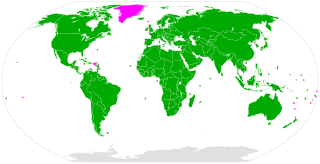
The Convention Concerning the Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labour, known in short as the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, was adopted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) in 1999 as ILO Convention No 182. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.

The Forced Labour Convention, the full title of which is the Convention Concerning Forced or Compulsory Labour, 1930 (No.29), is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions of the International Labour Organization. Its object and purpose is to suppress the use of forced labour in all its forms irrespective of the nature of the work or the sector of activity in which it may be performed. The Convention defines forced labour as "all work or service which is exacted from any person under the menace of any penalty and for which the said person has not offered himself voluntarily", with few exceptions like compulsory military service.
The Freedom of Association and Protection of the Right to Organise Convention (1948) No 87 is an International Labour Organization Convention, and one of eight conventions that form the core of international labour law, as interpreted by the Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work.
Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Occupational Health Services Convention, 1985 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Chemicals Convention, 1990 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Safety and Health in Mines Convention, 1995 is an International Labour Organization Convention. It was adopted at the 82nd International Labour Conference (ILC) of the International Labour Organization (ILO). The ILO is an agency under the United Nations that deals with international labor issues while promoting workers rights and opportunities. One of ILO's goals is to hold annual labor conventions to create legally binding contracts for participating nations to ratify. During the Safety and Health in Mines Convention (C176), it was recognized that there are inherent hazards in the mining workplace, and a need for a convention was mandatory.
Labour standards in the World Trade Organization are binding rules, which form a part of the jurisprudence and principles applied within the rule making institutions of the World Trade Organization (WTO). Labour standards play an implicit, but not an overt role within the WTO, however it forms a prominent issue facing the WTO today, and has generated a wealth of academic debate.

The Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) is an International Labour Organization (ILO) convention, number 186, established in 2006 as the fourth pillar of international maritime law and embodies "all up-to-date standards of existing international maritime labour Conventions and Recommendations, as well as the fundamental principles to be found in other international labour Conventions". The other pillars are the SOLAS, STCW and MARPOL. The treaties applies to all ships entering the harbours of parties to the treaty (port states), as well as to all ships flying the flag of state party (flag states, as of 2021: over 91 per cent).
Child labour refers to the full-time employment of children under a minimum legal age. In 2003, an International Labour Organization (ILO) survey reported that one in every ten children in the capital above the age of seven was engaged in child domestic labour. Children who are too young to work in the fields work as scavengers. They spend their days rummaging in dumps looking for items that can be sold for money. Children also often work in the garment and textile industry, in prostitution, and in the military.
Child labor in the Philippines is the employment of children in hazardous occupations below the age of fifteen (15), or without the proper conditions and requirements below the age of fifteen (15), where children are compelled to work on a regular basis to earn a living for themselves and their families, and as a result are disadvantaged educationally and socially. So to make it short, it is called child labor when it is forced.
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating Work and the workplace. The International Labour Organization and the World Trade Organization have been the main international bodies involved in reforming labour markets. The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank have indirectly driven changes in labour policy by demanding structural adjustment conditions for receiving loans or grants. Issues regarding Conflict of laws arise, determined by national courts, when people work in more than one country, and supra-national bodies, particularly in the law of the European Union, have a growing body of rules regarding labour rights.
The First International Congress of Working Women (ICWW), convened by the Women's Trade Union League of America from October 28 to November 6, 1919, was a meeting of labor feminists from around the world. The ICWW planned to share their proposals for addressing women's labor concerns at the First International Labor Conference (ILC) of 1919. ICWW delegates agreed upon a list of resolutions, some of which were taken up by the ILC's Commission on the Employment of Women and resulted in the passage of the Maternity Protection Convention, 1919.
Migrant workers in the Gulf Cooperation Council region involves the prevalence of migrant workers in the Kingdom of Bahrain, the State of Kuwait, the Sultanate of Oman, the State of Qatar, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Together, these six countries form the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), established in 1981. The GCC cooperates on issues related to economy and politics, and the subject of migrant workers constitutes a substantial part of the council's collaboration. All of the GCC countries are dependent on migrant labor to bolster and stimulate economic growth and development, as the GCC countries possess an abundance of capital while the domestic labor capacity is low. Although migrant workers in the Persian Gulf region amount to no more than 10% of all migrants worldwide, they constitute a significant part of the populations of their host countries.
Labour rights in Azerbaijan are substantially constrained. Labor rights activists face repression in Azerbaijan. Azerbaijani law nominally allows the formation of labor unions and the right to strike, but in practice, most unions collaborate with the authoritarian regime, many categories of workers are prohibited from striking, and most major industries are dominated by state-owned enterprises where the government sets working conditions.

The right to sit refers to laws or policies granting workers the right to be granted suitable seating at the workplace. Jurisdictions that have enshrined "right to sit" laws or policies include Mexico, France, Spain, Argentina, the United Kingdom, Jamaica, South Africa, Eswatini, Cameroon, Tanzania, Uganda, Lesotho, Malaysia, Brazil, Israel, Ireland, Zambia, Guyana, the Indian states of Tamil Nadu and Kerala, the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador, and the British overseas territory of Gibraltar and Montserrat. Almost all states of the United States and Australia, as well as the majority of Canadian provinces passed right to sit legislation for women workers between 1881 and 1917. US states with current right to sit legislation include California, Florida, Massachusetts, Montana, New Jersey, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Wisconsin. A right to sit provision is included in the International Labour Organization's Hygiene Convention, 1964; the international treaty being ratified by 52 countries as of 2023. EU-OSHA recommends suitable seating as a best practice. Local jurisdictions with right to sit laws include Portland, Oregon, St. Louis, Missouri, and London's Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea.
References
- 1 2 3 International Labour Organization (1947). "C081 - Labour Inspection Convention, 1947 (No. 81)". NORMLEX - Information System on International Labour Standards. Retrieved 10 January 2024.
- 1 2 International Labour Organization (1995). "P081 - Protocol of 1995 to the Labour Inspection Convention, 1947". NORMLEX - Information System on International Labour Standards. Retrieved 10 January 2024.
- ↑ "International Labour Standards on Labour inspection". www.ilo.org. Retrieved 10 January 2024.
- ↑ International Labour Organization (2024). "Ratifications of P081 - Protocol of 1995 to the Labour Inspection Convention, 1947". NORMLEX - Information System on International Labour Standards. Retrieved 10 January 2024.