
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg.

Russia is the largest country in the world, covering over 17,125,191 km2 (6,612,073 sq mi), and encompassing more than one-eighth of Earth's inhabited land area. Russia extends across eleven time zones, and has the most borders of any country in the world, with sixteen sovereign nations.

Lake Baikal is the deepest rift lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Republic of Buryatia to the southeast.
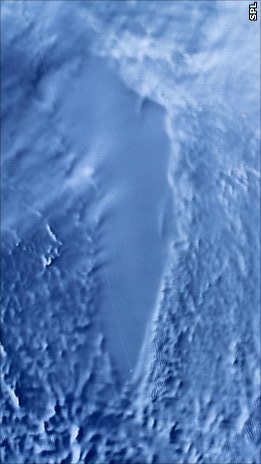
Lake Vostok is the largest of Antarctica's 675 known subglacial lakes. Lake Vostok is located at the southern Pole of Cold, beneath Russia's Vostok Station under the surface of the central East Antarctic Ice Sheet, which is at 3,488 m (11,444 ft) above mean sea level. The surface of this fresh water lake is approximately 4,000 m (13,100 ft) under the surface of the ice, which places it at approximately 500 m (1,600 ft) below sea level.
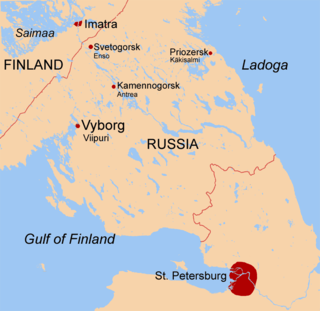
The Karelian Isthmus is the approximately 45–110-kilometre-wide (30–70 mi) stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the westernmost point of Lake Ladoga, Pekonlahti. If the Karelian Isthmus is defined as the entire territory of present-day Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast to the north of the Neva and also a tiny part of the Republic of Karelia, the area of the isthmus is about 15,000 km2 (5,800 sq mi).

Issyk-Kul or Ysyk-Köl is an endorheic saline lake in the western Tianshan Mountains in eastern Kyrgyzstan, just south of a dividing range separating Kyrgyzstan from Kazakhstan. It is the eighth-deepest lake in the world, the eleventh-largest lake in the world by volume, the deepest lake whose deepest point is above sea level, and the third-largest saline lake. Issyk-Kul means "warm lake" in the Kyrgyz language; although it is located at a lofty elevation of 1,607 metres (5,272 ft) and subject to severe cold during winter, it rarely freezes over due to high salinity.

Lake Onega is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic Sea, and is the second-largest lake in Europe after Lake Ladoga, slightly smaller than Lebanon. The lake is fed by about 50 rivers and is drained by the Svir.

Lake Peipus is the largest trans-boundary lake in Europe, lying on the international border between Estonia and Russia.

Tver Oblast is a federal subject of Russia. Its administrative center is the city of Tver. From 1935 to 1990, it was known as Kalinin Oblast. Population: 1,353,392 (2010 Census).

Leningrad Oblast is a federal subject of Russia. The oblast has an area of 84,500 square kilometres (32,600 sq mi) and a population of 2,000,997 ; up from 1,716,868 recorded in the 2010 Census. Leningrad Oblast is highly industrialized. Its administrative center and largest city is Gatchina.

Lake Balkhash, also spelt Lake Balqash, is a lake in southeastern Kazakhstan, one of the largest lakes in Asia and the 15th largest in the world. It is located in the eastern part of Central Asia and sits in the Balkhash-Alakol Basin, an endorheic (closed) basin. The basin drains seven rivers, the primary of which is the Ili, bringing most of the riparian inflow; others, such as the Karatal, bring surface and subsurface flow. The Ili is fed by precipitation, largely vernal snowmelt, from the mountains of China's Xinjiang region.

Karelia is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia, Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia and Finland.

The Volkhov is a river in Novgorodsky and Chudovsky Districts of Novgorod Oblast and Kirishsky and Volkhovsky Districts of Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia. The Volkhov, which forms part of the basin of the Neva, is the only outflow of Lake Ilmen, and connects it with Lake Ladoga. The length of the Volkhov is 224 kilometres (139 mi), and the area of its drainage basin is 80,200 square kilometres (31,000 sq mi). The city of Veliky Novgorod, the towns of Kirishi, Volkhov and Novaya Ladoga, and the historically important village of Staraya Ladoga are located along the Volkhov.

The Ysyk-Köl Region is one of the regions of Kyrgyzstan. Its capital is Karakol. It is surrounded by Almaty Region, Kazakhstan to the north, Chüy Region to the west, Naryn Region to the southwest, and Xinjiang, China to the southeast. It takes its name from Lake Issyk-Kul, the world's second-largest high altitude lake. Its total area is 43,735 km2 (16,886 sq mi). The resident population of the region was 501,933 as of January 2021. The region has a sizeable Russian minority.
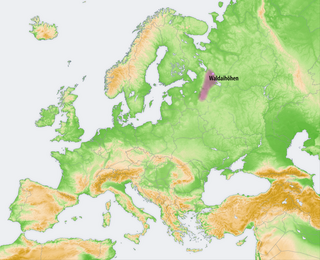
The Valdai Hills, sometimes shortened to Valdai, are an upland region in the north-west of central European Russia running north–south, about midway between Saint Petersburg and Moscow, spanning Leningrad, Novgorod, Tver, Pskov, and Smolensk Oblasts.

Lake Khanka or Lake Xingkai, is a freshwater lake on the border between Primorsky Krai, Russia and Heilongjiang province, Northeast China.

Transbaikal, Trans-Baikal, Transbaikalia, or Dauria is a mountainous region to the east of or "beyond" (trans-) Lake Baikal in Far Eastern Russia.

Uvs Lake Basin is an endorheic basin located on the territorial border of Mongolia and Tuva, a republic of the Russian Federation. The basin is part of the Central Asian Internal Drainage Basin and is named after Uvs Lake, a large saline lake situated in the western part of its drainage basin, and is one of the last remnants of the mammoth steppes. Uvs Lake is a shallow lake with an area of 3,350 km2 (1,290 sq mi). Its entire basin, which includes several smaller lakes, is 70,000 km2 (27,000 sq mi).

The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake and sometimes referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau. It covers a surface area of 371,000 km2 (143,000 sq mi), an area approximately equal to that of Japan, with a volume of 78,200 km3 (19,000 cu mi). It has a salinity of approximately 1.2%, about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast.

The Monster of Lake Tota is a legendary aquatic animal known in many works as: diablo ballena, lit. 'devil whale'. The monster is an inhabitant of Lake Tota in present-day Colombia, according to the Muisca, who inhabited the Altiplano Cundiboyacense. The earliest reference in modern history was made by the conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada. He described the monster as "A fish with a black head like an ox and larger than a whale" and Antonio de Alcedo, 1788)). The monster was also defined as "a monstrous fish", "a black monster", and even as "the Dragon" and as a "divine animal archetype" (2012).





















