
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America or the Laurentian Great Lakes, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the upper mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. They are Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario and are in general on or near the Canada–United States border. Hydrologically, there are four lakes, because lakes Michigan and Huron join at the Straits of Mackinac. The Great Lakes Waterway enables travel by water between the lakes.

Lake Erie is the fourth-largest lake of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has the shortest average water residence time. At its deepest point Lake Erie is 210 feet deep.

Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume and the third-largest by surface area, after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that of Lake Huron through the narrow Straits of Mackinac, giving it the same surface elevation as its easterly counterpart; the two are technically a single lake.
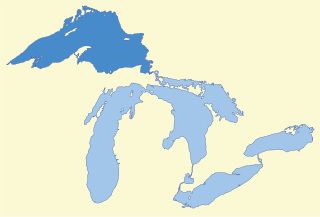
Lake Superior is the largest and northernmost of the Great Lakes of North America, and among freshwater lakes, it is the world's largest by surface area and the third-largest by volume. It holds 10% of the world's surface fresh water. It is shared by Ontario, Canada to the north, and states in the United States in other directions: Minnesota to the west, and Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to the south. Lake Superior is the most northerly and most westerly of the Great Lakes chain, and the highest in elevation. It drains into Lake Huron via St. Mary's River.

Michigan is a state in the Great Lakes region of the upper Midwestern United States. Its name derives from a gallicized variant of the original Ojibwe word ᒥᓯᑲᒥ, meaning 'large water' or 'large lake'. With a population of nearly 10.1 million and a total area of nearly 97,000 sq mi (250,000 km2), Michigan is the 10th-largest state by population, the 11th-largest by area, and the largest east of the Mississippi River. Its capital is Lansing, and its largest city is Detroit. Metro Detroit is among the nation's most populous and largest metropolitan economies.

Ontario is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada's most populous province, with 38.3 percent of the country's population, and is the second-largest province by total area. Ontario is Canada's fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation's capital city, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto, which is also Ontario's provincial capital.

Utah is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Colorado to the east, Wyoming to the northeast, Idaho to the north, Arizona to the south and Nevada to the west. It also touches a corner of New Mexico in the southeast. Of the fifty U.S. states, Utah is the 13th-largest by area; with a population over three million, it is the 30th-most-populous and 11th-least-densely populated. Urban development is mostly concentrated in two areas: the Wasatch Front in the north-central part of the state, which is home to roughly two-thirds of the population and includes the capital city, Salt Lake City; and Washington County in the south, with more than 170,000 residents. Most of the western half of Utah lies in the Great Basin.

Earvin "Magic" Johnson Jr. is an American former professional basketball player and former president of basketball operations of the Los Angeles Lakers of the National Basketball Association (NBA). Often regarded as the best point guard of all time, Johnson played 13 seasons for the Lakers and was honored as one of the 50 Greatest Players in NBA History in 1996. After winning championships in high school and college, Johnson was selected first overall in the 1979 NBA draft by the Lakers. He won a championship and an NBA Finals Most Valuable Player Award in his rookie season, and won four more championships with the Lakers during the 1980s. Johnson retired abruptly in 1991 after announcing that he had contracted HIV, but returned to play in the 1992 All-Star Game, winning the All-Star MVP Award. After protests from his fellow players, he retired again for four years, but returned in 1996, at age 36, to play 32 games for the Lakers before retiring for the third and final time.

Salt Lake City is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Utah, as well as the seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With an estimated population of 200,567 in 2019, the city is the core of the Salt Lake City metropolitan area, which has a population of 1,222,540. Salt Lake City is further situated within a larger metropolis known as the Salt Lake City–Ogden–Provo Combined Statistical Area, a corridor of contiguous urban and suburban development stretched along a 120-mile (190 km) segment of the Wasatch Front, comprising a population of 2,606,548, making it currently the 22nd largest in the nation. It sits at the central core of the larger of only two major urban areas located within the Great Basin.

Lake Baikal is a rift lake located in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryatia to the southeast. Lake Baikal is the world's largest freshwater lake by volume, containing 22 to 23% of the world's fresh surface water. It contains 23,615.39 km3 (5,670 cu mi) of fresh water, which is more water than all of the North American Great Lakes combined. Lake Baikal has a maximum depth of 1,642 m (5,387 ft), and is the world's deepest lake. It is among the world's clearest lakes and is the world's oldest lake, at 25–30 million years. Lake Baikal is also the world's seventh-largest lake by surface area.

The Los Angeles Lakers are an American professional basketball team based in Los Angeles. The Lakers compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the league's Western Conference Pacific Division. The Lakers play their home games at Staples Center, an arena shared with the NBA's Los Angeles Clippers, the Los Angeles Sparks of the Women's National Basketball Association, and the Los Angeles Kings of the National Hockey League. The Lakers are one of the most successful teams in the history of the NBA, and have won 17 NBA championships, tied with the Boston Celtics for the most in NBA history.

Lake Tahoe is a large freshwater lake in the Sierra Nevada of the United States. Lying at 6,225 ft (1,897 m), it straddles the state line between California and Nevada, west of Carson City. Lake Tahoe is the largest alpine lake in North America, and at 122,160,280 acre⋅ft (150.7 km3) it trails only the five Great Lakes as the largest by volume in the United States. Its depth is 1,645 ft (501 m), making it the second deepest in the United States after Crater Lake in Oregon.

Kobe Bean Bryant was an American professional basketball player. A shooting guard, he spent his entire 20-year career with the Los Angeles Lakers in the National Basketball Association (NBA). Widely regarded as one of the greatest basketball players of all time, Bryant won five NBA championships, was an 18-time All-Star, a 15-time member of the All-NBA Team, a 12-time member of the All-Defensive Team, the 2008 NBA Most Valuable Player (MVP), and a two-time NBA Finals MVP. Bryant also led the NBA in scoring twice, and ranks fourth in league all-time regular season and postseason scoring. He was posthumously voted into the Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame in 2020.

Swan Lake, Op. 20, is a ballet composed by Russian composer Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky in 1875–76. Despite its initial failure, it is now one of the most popular ballets of all time.

An endorheic basin is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes or swamps, permanent or seasonal, that equilibrate through evaporation. They are also called closed or terminal basins or internal drainage systems or basins. Endorheic regions contrast with exorheic regions. Endorheic water bodies include some of the largest lakes in the world, such as the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water.

Philip Douglas Jackson is an American former professional basketball player, coach, and executive in the National Basketball Association (NBA). A power forward, Jackson played 12 seasons in the NBA, winning NBA championships with the New York Knicks in 1970 and 1973. Jackson was the head coach of the Chicago Bulls from 1989 to 1998, leading them to six NBA championships. He then coached the Los Angeles Lakers from 1999 to 2004 and again from 2005 to 2011; the team won five league titles under his leadership. Jackson's 11 NBA titles as a coach surpassed the previous record of nine set by Red Auerbach. He also holds the NBA record for the most combined championships, winning a total of 13 as a player and a coach.

Metta Sandiford-Artest is an American former professional basketball player. He was known as Ron Artest before legally changing his name to Metta World Peace in 2011 and later to Metta Sandiford-Artest in May 2020.

A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, apart from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although like the much larger oceans, they form part of Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. They are generally larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which are usually flowing in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams.



















