Related Research Articles
In telecommunications, RS-232 or Recommended Standard 232 is a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a DTE such as a computer terminal, and a DCE, such as a modem. The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, the meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The current version of the standard is TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange, issued in 1997. The RS-232 standard had been commonly used in computer serial ports and is still widely used in industrial communication devices.

Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cables, connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply (interfacing) between computers, peripherals and other computers. A broad variety of USB hardware exists, including 14 different connector types, of which USB-C is the most recent.

In computing, a serial port is a serial communication interface through which information transfers in or out sequentially one bit at a time. This is in contrast to a parallel port, which communicates multiple bits simultaneously in parallel. Throughout most of the history of personal computers, data has been transferred through serial ports to devices such as modems, terminals, various peripherals, and directly between computers.

In computing, a parallel port is a type of interface found on early computers for connecting peripherals. The name refers to the way the data is sent; parallel ports send multiple bits of data at once, as opposed to serial communication, in which bits are sent one at a time. To do this, parallel ports require multiple data lines in their cables and port connectors and tend to be larger than contemporary serial ports, which only require one data line.
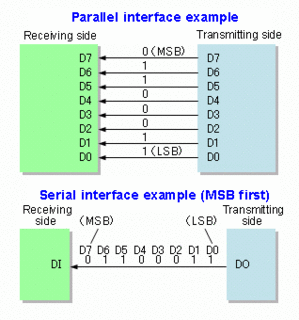
In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels.

Electronic test equipment is used to create signals and capture responses from electronic devices under test (DUTs). In this way, the proper operation of the DUT can be proven or faults in the device can be traced. Use of electronic test equipment is essential to any serious work on electronics systems.

Null modem is a communication method to directly connect two DTEs using an RS-232 serial cable. The name stems from the historical use of RS-232 cables to connect two teleprinter devices or two modems in order to communicate with one another; null modem communication refers to using a crossed-over RS-232 cable to connect the teleprinters directly to one another without the modems. It is also used to serially connect a computer to a printer, since both are DTE, and is known as a Printer Cable.
The Parallel Line Internet Protocol (PLIP) is a computer networking protocol for direct computer-to-computer communications using the parallel port normally used for connections to a printer.

IEEE 1284 is a standard that defines bi-directional parallel communications between computers and other devices. It was originally developed in the 1970s by Centronics, and was widely known as the Centronics port, both before and after its IEEE standardization.

The Atari Portfolio is an IBM PC-compatible palmtop PC, released by Atari Corporation in June 1989. This makes it the world's first palmtop computer.
Direct Cable Connection (DCC) is a feature of Microsoft Windows that allows a computer to transfer and share files with another computer, via a connection using either the serial port, parallel port or the infrared port of each computer. It is well-suited for computers that do not have an ethernet adapter installed, although DCC in Windows XP can be configured to use one if available.

A wireless router is a device that performs the functions of a router and also includes the functions of a wireless access point. It is used to provide access to the Internet or a private computer network. Depending on the manufacturer and model, it can function in a wired local area network, in a wireless-only LAN, or in a mixed wired and wireless network.
A terminal server connects devices with a serial port to a local area network (LAN). Products marketed as terminal servers can be very simple devices that do not offer any security functionality, such as data encryption and user authentication. The primary application scenario is to enable serial devices to access network server applications, or vice versa, where security of the data on the LAN is not generally an issue. There are also many terminal servers on the market that have highly advanced security functionality to ensure that only qualified personnel can access various servers and that any data that is transmitted across the LAN, or over the Internet, is encrypted. Usually, companies that need a terminal server with these advanced functions want to remotely control, monitor, diagnose and troubleshoot equipment over a telecommunications network.

A serial cable is a cable used to transfer information between two devices using a serial communication protocol. The form of connectors depends on the particular serial port used. A cable wired for connecting two DTEs directly is known as a null modem cable.

A digital subscriber line (DSL) modem is a device used to connect a computer or router to a telephone line which provides the digital subscriber line (DSL) service for connection to the Internet, which is often called DSL broadband. The modem connects to a single computer or router, through an Ethernet port, USB port, or is installed in a computer PCI slot.

Xircom, Inc. was based in Thousand Oaks, California, with manufacturing facilities located in Penang, Malaysia and international offices throughout Europe and Asia Pacific. They were one of the first companies to develop network computing products for notebook computers. Products included computer memory cards, LAN adapters, modems, and remote access server products. The company's products enabled notebook users to share information over a network connection. During fiscal 1999, the company introduced 56K modems in the MiniPCI form factor. In September 1999, the company acquired Rex PC Card Organizer product line. During fiscal 2000, the company acquired Omnipoint Technologies, Inc. and Entrega Technologies Inc. Branded products accounted for 65% of fiscal 2000 revenues and OEM products, 35%. In 2001, Intel acquired Xircom and in early 2003 laid off most of Xircom's Thousand Oaks employees.

Windows Easy Transfer is a specialized file transfer program developed by Microsoft that allows users of the Windows operating system to transfer personal files and settings from a computer running an earlier version of Windows to a computer running a newer version.
Laplink PCmover is PC migration software developed by Laplink Software. Introduced in 2005, as the successor to Laplink, PCmover comes in a variety of versions that provide the ability to move or restore all selected files, folders, settings, user profiles and programs from an old PC to a new one, an old operating system to a new one, or an old hard drive to a new one. Microsoft has partnered with Laplink on multiple occasions and recommends PCmover for automatically moving programs, files and profile setting to new Windows 10 PCs.
Commodore 64 disk/tape emulation and data transfer comprises hardware and software for Commodore 64 disk & tape emulation and for data transfer between either Commodore 64 (C64), Commodore (1541) disk drive or Commodore tape deck and newer computers.
Laplink was a proprietary piece of software developed by Mark Eppley and sold by Traveling Software, which is now LapLink Software, Inc. First available in 1983, LapLink was used to synchronize, copy, or move, files between two PCs, in an era before local area networks, using the parallel port and a LapLink cable or serial port and a null modem cable or USB and a USB adhoc network cable.