Related Research Articles

Dual wielding is the technique of using two weapons, one in each hand for training or combat. It is not a common combat practice. Although historical records of dual wielding in war are limited, there are numerous weapon-based martial arts that involve the use of a pair of weapons. The use of a companion weapon is sometimes employed in European martial arts and fencing, such as a parrying dagger. Miyamoto Musashi, a Japanese swordsman and ronin, was said to have conceived of the idea of a particular style of swordsmanship involving the use of two swords.

A gladiator was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their lives and their legal and social standing by appearing in the arena. Most were despised as slaves, schooled under harsh conditions, socially marginalized, and segregated even in death.

A trident is a three-pronged spear. It is used for spear fishing and historically as a polearm.

Swordsmanship or sword fighting refers to the skills and techniques used in combat and training with any type of sword. The term is modern, and as such was mainly used to refer to smallsword fencing, but by extension it can also be applied to any martial art involving the use of a sword. The formation of the English word "swordsman" is parallel to the Latin word gladiator, a term for the professional fighters who fought against each other and a variety of other foes for the entertainment of spectators in the Roman Empire. The word gladiator itself comes from the Latin word gladius, which is a type of sword.

The murmillo was a type of gladiator during the Roman Imperial age. The murmillo-class gladiator was adopted in the early Imperial period to replace the earlier Gallus, named after the warriors of Gaul. As the Gauls inhabiting Italy had become well integrated with the Romans by the time of the reign of Augustus, it became undesirable to portray them as enemy outsiders; the Gallus-class gladiator thus had to be retired.

A secutor was a class of gladiator in ancient Rome. Thought to have originated around 50 AD, the secutor was armed similarly to the Murmillo gladiator and like the Murmillo, was protected by a heavy shield. A secutor usually carried a short sword, a gladius, or a dagger. The secutor was specially trained to fight a retiarius, a type of lightly armoured gladiator armed with a trident and net.

A retiarius was a Roman gladiator who fought with equipment styled on that of a fisherman: a weighted net, a three-pointed trident, and a dagger (pugio). The retiarius was lightly armoured, wearing an arm guard (manica) and a shoulder guard (galerus). Typically, his clothing consisted only of a loincloth (subligaculum) held in place by a wide belt, or of a short tunic with light padding. He wore no head protection or footwear.

The gladiatrix is the female equivalent of the gladiator of ancient Rome. Like their male counterparts, gladiatrices fought each other, or wild animals, to entertain audiences at various games and festivals. Very little is known about them. They seem to have used much the same equipment as male gladiators, but were heavily outnumbered by them, and were almost certainly considered an exotic rarity by their audiences. They seem to have been introduced during the very late republic and early empire, and were officially banned as unseemly from 200 AD onwards. Their existence is known only through a few accounts written by members of Rome's elite, and a very small number of inscriptions.
Among Ancient Romans, bestiarii were those who went into combat with beasts, or were exposed to them. It is conventional to distinguish two categories of bestiarii: the first were those condemned to death via the beasts and the second were those who faced them voluntarily, for pay or glory. The latter are sometimes erroneously called gladiators; to their contemporaries, however, the term gladiator referred specifically to one who fought other men. The contemporary term for those who made a career out of participating in arena "hunts" was venatores.

A hoplomachus was a type of gladiator in ancient Rome, armed to resemble a Greek hoplite. The hoplomachus would wear a bronze helmet, a manica on his right arm, loincloth (subligaculum), heavy padding on his legs, and a pair of high greaves reaching to mid-thigh. His weapons were the spear and a short sword. He was often pitted against the murmillo, perhaps as a re-enactment of Rome's wars in Greece and the Hellenistic East. The name hoplomachus means 'armored fighter'. The small, round shield was as much a weapon as a sword or spear, not unlike the original hoplites, who used it primarily for defensive purposes, but also employed it in their charges, using it to ram their opponents at the onset of a fight. They wore no shoes so the sand would chafe their feet, presenting them a greater challenge.

The inaugural games were held, on the orders of the Roman Emperor Titus, to celebrate the completion in AD 80 of the Colosseum, then known as the Flavian Amphitheatre. Vespasian began construction of the amphitheatre around AD 70 and it was completed by his son Titus, who became emperor following Vespasian's death in AD 79. Titus' reign began with months of disasters – including the eruption of Mount Vesuvius, a fire in Rome, and an outbreak of plague – he inaugurated the completion of the structure with lavish games that lasted for more than one hundred days, perhaps in an attempt to appease the Roman public and the gods.

The Gladiator Mosaic is a famous set of 5 large mosaics of gladiators and venators and two smaller ones. The mosaics are dated to the first half of the 4th century and are now installed in the Salone of the Galleria Borghese in Rome. They were discovered in 1834 on the Borghese estate at Torrenova, on the Via Casilina outside Rome. Prince Francesco Borghese Aldobrandini requested the excavations be completed. It is believed to have decorated a cryptoporticus of an inner peristylum for a large domus. The mosaics were removed from excavations and restored by Gaetano Ruspi and Filippo Scaccia in 1839. These panels reinvigorated the Borghese Collection after it had shrunk following the sale of much of the collection to Napoleon I.

A Samnite was a Roman gladiator who fought with equipment styled on that of a warrior from Samnium: a short sword (gladius), a rectangular shield (scutum), a greave (ocrea), and the helmet. Warriors armed in such a way were the earliest gladiators in the Roman games. They appeared in Rome shortly after the defeat of Samnium in the 4th century BC, apparently adopted from the victory celebrations of Rome's allies in Campania. By arming low-status gladiators in the manner of a defeated foe, Romans mocked the Samnites and appropriated martial elements of their culture.
The scissor was a type of Roman gladiator. Very little is known about scissores besides the name, which means 'cutter, cleaver, render'.

Pollice Verso is an 1872 painting by French artist Jean-Léon Gérôme, featuring the eponymous Roman gesture directed to the winning gladiator.
The dimachaeri were a type of Roman gladiator that fought with two swords. The name is the Latin-language borrowing of the Greek word διμάχαιρος meaning "bearing two knives".
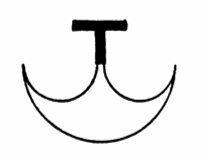
The arbelas was a type of ancient Roman gladiator. The word is a hapax legomenon, occurring only in the Oneirocritica of Artemidorus, a Greek work on dream interpretation that discusses the symbolism of various gladiator types. It may be related to the Greek word arbelos (ἄρβηλος), a cobbler's semicircular blade used to cut leather similar to an ulu.
Italian martial arts include all those unarmed and armed fighting arts popular in Italy between the Bronze age until the 19th century AD. It involved the usage of weapons. Each weapon is the product of a specific historical era. The swords used in Italian martial arts range from the Bronze daggers of the Nuragic times to the gladius of the Roman legionaries to swords which were developed during the renaissance, the baroque era and later. Short blades range from medieval daggers to the liccasapuni Sicilian duelling knife.

The Cavillargues medallion is a terracotta relief medallion or plaque of the 2nd or 3rd century, 16 centimetres (6.3 in) across, made under the Roman Empire and found in modern France. It depicts a gladiatorial combat between a retiarius and a secutor. The medallion has been studied by American historian Anthony Corbeill and he believes it shows a games official signalling pollicēs premere, the granting of mercy to fighters whose combat ends in a draw.
References
- Baker, Alan (2002). The Gladiator: The Secret History of Rome's Warrior Slaves. Da Capo Press. ISBN 0-306-81185-5.
- Cowper, H. S. (1906). The Art of Attack: Being a Study in the Development of Weapons and Appliances of Offence, from the Earliest Times to the Age of Gunpowder. Ulverston, Lancashire: W. Holmes, Ltd., Printers.
- Junkelmann, Marcus (2000). "Familia Gladiatoris: The Heroes of the Amphitheatre", Gladiators and Caesars: The Power of Spectacle in Ancient Rome. University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-22798-0.
- Tegg, Thomas, ed. (1829). "Laquearius", The London Encyclopædia, or Universal Dictionary of Science, Art, Literature, and Practical Mechanics, Comparing a Popular View of the Present State of Knowledge . London: Thomas Tegg.