
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates, and it connects the knee with the ankle bones. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane or centre-line. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of the leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body next to the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The ulnar collateral ligament is a thick triangular band at the medial aspect of the elbow uniting the distal aspect of the humerus to the proximal aspect of the ulna.

The olecranon from the Greekolene meaning elbow and kranon meaning head is the large, thick, curved bony eminence of the ulna, a long bone in the forearm that projects behind the elbow. It forms the most pointed portion of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit. The olecranon serves as a lever for the extensor muscles that straighten the elbow joint.

The interphalangeal joints of the hand are the hinge joints between the phalanges of the fingers that provide flexion towards the palm of the hand.

The lateral meniscus is a fibrocartilaginous band that spans the lateral side of the interior of the knee joint. It is one of two menisci of the knee, the other being the medial meniscus. It is nearly circular and covers a larger portion of the articular surface than the medial. It can occasionally be injured or torn by twisting the knee or applying direct force, as seen in contact sports.
The knee examination, in medicine and physiotherapy, is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with knee pain or a history that suggests a pathology of the knee joint.

The stifle joint is a complex joint in the hind limbs of quadruped mammals such as the sheep, horse or dog. It is the equivalent of the human knee and is often the largest synovial joint in the animal's body. The stifle joint joins three bones: the femur, patella, and tibia. The joint consists of three smaller ones: the femoropatellar joint, medial femorotibial joint, and lateral femorotibial joint.
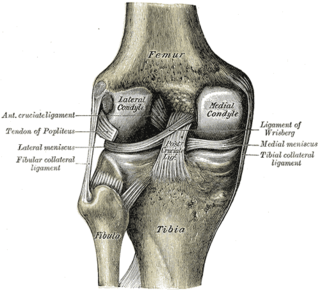
The fibular collateral ligament is a ligament located on the lateral (outer) side of the knee, and thus belongs to the extrinsic knee ligaments and posterolateral corner of the knee.

The lower extremity of the humerus is flattened from before backward, and curved slightly forward; it ends below in a broad, articular surface, which is divided into two parts by a slight ridge.

The radial collateral ligament (RCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), or external lateral ligament is a ligament in the elbow on the side of the radius.

The interphalangeal joints of the foot are between the phalanx bones of the toes in the feet.

The lateral collateral ligament of ankle joint are ligaments of the ankle which attach to the fibula.

The unhappy triad, also known as a blown knee among other names, is an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and meniscus. Analysis during the 1990s indicated that this 'classic' O'Donoghue triad is actually an unusual clinical entity among athletes with knee injuries. Some authors mistakenly believe that in this type of injury, "combined anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligament disruptions that were incurred during athletic endeavors" always present with concomitant medial meniscus injury. However, the 1990 analysis showed that lateral meniscus tears are more common than medial meniscus tears in conjunction with sprains of the ACL.
Collateral ligament can refer to:

The knee bursae are the fluid-filled sacs and synovial pockets that surround and sometimes communicate with the knee joint cavity. The bursae are thin-walled, and filled with synovial fluid. They represent the weak point of the joint, but also provide enlargements to the joint space. They can be grouped into either communicating and non-communicating bursae or, after their location – frontal, lateral, or medial.

The ulnar collateral ligament is a rounded cord, attached above to the end of the styloid process of the ulna, and dividing below into two fasciculi, one of which is attached to the medial side of the triquetral bone, the other to the pisiform and flexor retinaculum.

In human anatomy, the radial (RCL) and ulnar (UCL) collateral ligaments of the metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) of the hand are the primary stabilisers of the MCP joints. They have two parts: the cord-like collateral ligaments proper located more dorsally and the accessory collateral ligaments located more volarly. They enable us to spread our fingers with an open hand but not with the hand closed into a fist.
Collateral ligament of ankle joint may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.














