Related Research Articles

The Statute of Westminster 1931 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that sets the basis for the relationship between the Commonwealth realms and the Crown.

The Westminster system or Westminster model is a type of parliamentary government that incorporates a series of procedures for operating a legislature. This concept was first developed in England.
An open file format is a file format for storing digital data, defined by an openly published specification usually maintained by a standards organization, and which can be used and implemented by anyone. Open file format is licensed with open license. For example, an open format can be implemented by both proprietary and free and open-source software, using the typical software licenses used by each. In contrast to open file formats, closed file formats are considered trade secrets. However, the actual image used by an open file format may still be copyrighted or trademarked.

The Constitution of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico is the controlling government document of Puerto Rico. It is composed of nine articles detailing the structure of the government as well as the function of several of its institutions. The document also contains an extensive and specific bill of rights. It was ratified by Puerto Rico's electorate in a referendum on March 3, 1952, and on July 25, 1952, Governor Luis Muñoz Marín proclaimed that the constitution was in effect. July 25 is known as Constitution Day.

Lewis Howard Latimer was an African-American inventor and patent draftsman. His inventions included an evaporative air conditioner, an improved process for manufacturing carbon filaments for light bulbs, and an improved toilet system for railroad cars. In 1884, he joined the Edison Electric Light Company where he worked as a draftsman and wrote the first book on electric lighting. The Lewis H. Latimer House, his landmarked former residence, is located near the Latimer Projects at 34-41 137th Street in Flushing, Queens, New York City.

The Massachusetts House of Representatives is the lower house of the Massachusetts General Court, the state legislature of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. It is composed of 160 members elected from 14 counties each divided into single-member electoral districts across the Commonwealth. The House of Representatives convenes at the Massachusetts State House in Boston.

Latimer Road is a London Underground station in North Kensington, in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. It is on the Circle and Hammersmith & City lines between Wood Lane and Ladbroke Grove stations and is in Travelcard Zone 2.

The Government of Western Australia, formally referred to as Her Majesty's Government of Western Australia, is the Australian state democratic administrative authority of Western Australia. It is also commonly referred to as the WA Government or the Western Australian Government. The Government of Western Australia, a parliamentary constitutional monarchy, was formed in 1890 as prescribed in its Constitution, as amended from time to time. Since the Federation of Australia in 1901, Western Australia has been a state of the Commonwealth of Australia, and the Constitution of Australia regulates its relationship with the Commonwealth. Under the Australian Constitution, Western Australia ceded legislative and judicial supremacy to the Commonwealth, but retained powers in all matters not in conflict with the Commonwealth.

The Government of New South Wales, also known as the NSW Government, is the Australian state democratic administrative authority of New South Wales. It is currently held by a coalition of the Liberal Party and the National Party. The Government of New South Wales, a parliamentary constitutional monarchy, was formed in 1856 as prescribed in its Constitution, as amended from time to time. Since the Federation of Australia in 1901, New South Wales has been a state of the Commonwealth of Australia, and the Constitution of Australia regulates its relationship with the Commonwealth. Under the Australian Constitution, New South Wales, as with all states, ceded legislative and judicial supremacy to the Commonwealth, but retained powers in all matters not in conflict with the Commonwealth.

The Federation of Australia was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia, and Western Australia agreed to unite and form the Commonwealth of Australia, establishing a system of federalism in Australia. The colonies of Fiji and New Zealand were originally part of this process, but they decided not to join the federation. Following federation, the six colonies that united to form the Commonwealth of Australia as states kept the systems of government that they had developed as separate colonies, but they also agreed to have a federal government that was responsible for matters concerning the whole nation. When the Constitution of Australia came into force, on 1 January 1901, the colonies collectively became states of the Commonwealth of Australia.
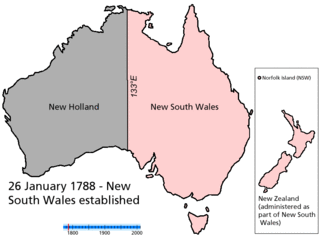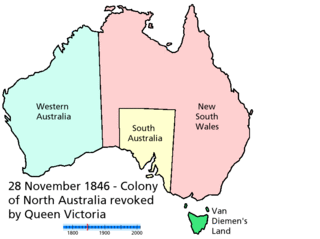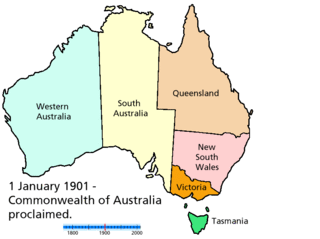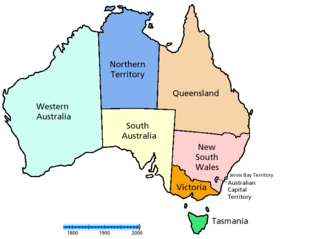
Proposals for new Australian states have been numerous since the late 19th and early 20th centuries; however, to date, no states have been added to Australia since Federation in 1901. Many proposals have suggested an Aboriginal state which would resemble the Inuit territory of Nunavut in Canada, while others have suggested incorporating New Zealand, Papua New Guinea and East Timor. Other proposals suggest making the Northern Territory and/or Australian Capital Territory states.

The Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Duties' are sections of the Constitution of India that prescribe the fundamental obligations of the states to its citizens and the duties and the rights of the citizens to the State. These sections are considered vital elements of the constitution, which was developed between 1949 by the Constituent Assembly of India.

The Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942 is an act of the Australian Parliament that formally adopted sections 2–6 of the Statute of Westminster 1931, an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom enabling the total legislative independence of the various self-governing Dominions of the British Empire. With its enactment, Westminster relinquished nearly all of its authority to legislate for the Dominions, effectively making them de jure sovereign nations.

The criteria for membership in the Commonwealth of Nations, which apply to current and prospective member states, have been altered by a series of documents issued over the past eighty-two years.

The monarchy of Australia is Australia's form of government embodied by the Australian sovereign and head of state. The Australian monarchy is a constitutional monarchy, modelled on the Westminster system of parliamentary government, while incorporating features unique to the Constitution of Australia.
Solon Nikitas was a distinguished Cypriot judge and jurist. Born in Limassol on 1.10.1937, where he lived his early years. His family then moved to Famagusta and he graduated from the Gymnasium of Famagusta with distinction and being awarded the Palamas Prize. Working for a short time at the Board of Commerce, he then went to England where he studied law and was called to the Bar (Lincoln's). From 1961 he practiced law in Nicosia. On 10.9.1971 he was appointed Judge of the District Court of Famagusta, subsequently serving at the District Court of Nicosia. On 10.10.1980 he was appointed Senior District Judge and on 1.1.1982 President of District Court, serving at the District Court of Nicosia and at the District Court of Larnaca-Famagusta. On 19.11.1988 he was appointed Judge of the Supreme Court. He left the Court on 30.4.2003, upon his appointment as Attorney-General. He resigned from that position in May 2005 in connection with a judgment of the Supreme Court, considering, as he stated in his announcement, that the case “is inextricably interwoven with the very essence of the administration of justice, the principles of the rule of law and the democratic principle of the separation of powers. It is also related to the existence, the endurance and the quality of institutions in a free and democratic society”.

The monarchy of Jamaica is a constitutional system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign and head of state of Jamaica. The terms Crown in Right of Jamaica, Her Majesty in Right of Jamaica, or The Queen in Right of Jamaica may also be used to refer to the entire executive of the government of Jamaica. Though the Jamaican Crown has its roots in the British Crown, it has evolved to become a distinctly Jamaican institution, represented by its own unique symbols.
The Commonwealth Local Government Forum (CLGF) is a global local government organisation, bringing together local authorities, their national associations and the ministries responsible for local government in the member countries of the Commonwealth. CLGF works with national and local governments to support the development of democratic values and good local governance and is the associated organisation officially recognised by Commonwealth Heads of Government as the representative body for local government in the Commonwealth.
The Universal Declaration on Animal Welfare (UDAW) is a proposed inter-governmental agreement to recognise that animals are sentient, to prevent cruelty and reduce suffering, and to promote standards on the welfare of animals such as farm animals, companion animals, animals in scientific research, draught animals, wildlife and animals in recreation.

The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations amongst member states.