Related Research Articles

Paraguay, officially the Republic of Paraguay, is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. It has a population of around 7.4 million, nearly 3 million of whom live in the capital and largest city of Asunción, and its surrounding metro area.
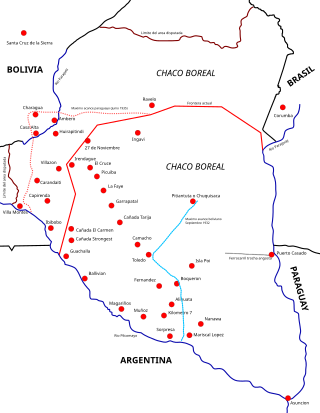
The Chaco War was fought from 1932 to 1935 between Bolivia and Paraguay, over the control of the northern part of the Gran Chaco region of South America, which was thought to be rich in oil. The war is also referred to as La Guerra de la Sed in literary circles since it was fought in the semi-arid Chaco. The bloodiest interstate military conflict fought in South America in the 20th century, it was fought between two of its poorest countries, both of which had lost territory to neighbours in 19th-century wars.

Formosa Province is a province in northeastern Argentina, part of the Gran Chaco Region. Formosa's northeast end touches Asunción, Paraguay, and the province borders the provinces of Chaco and Salta to its south and west, respectively. The capital is Formosa.

Chaco, officially the Province of Chaco, is one of the 23 provinces in Argentina. Its capital and largest city, is Resistencia. It is located in the north-east of the country.

Corrientes, officially the Province of Corrientes is a province in northeast Argentina, in the Mesopotamia region. It is surrounded by : Paraguay, the province of Misiones, Brazil, Uruguay, and the provinces of Entre Rios, Santa Fe and Chaco.

Presidente Hayes is a department in Paraguay. The capital is the city of Villa Hayes. The department was named after U.S. President Rutherford B. Hayes, who awarded the territory to Paraguay while arbitrating a boundary dispute between Paraguay and Argentina after the Paraguayan War.

The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region. This land is sometimes called the Chaco Plain.
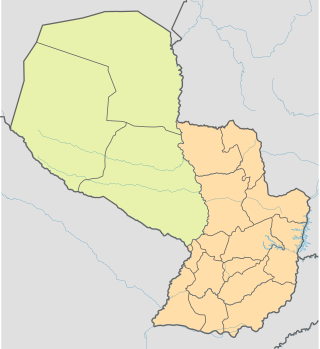
The Paraguayan Chaco or Región Occidental is a semi-arid region in Paraguay, with a very low population density. The area is being rapidly deforested. Consisting of more than 60% of Paraguay's land area, but with less than 3% of the population, the Chaco is one of the most sparsely inhabited areas in South America.

Encarnación is a district and the capital city of Itapúa Department in Paraguay, located at the south-east of the department, on the right-hand (western) shore of the Paraná River, opposite Posadas, Argentina. The city has an area of 274 km2 and a population of 93,497, and the Greater Encarnacion area has a population of over 220,000 according to a 2020 estimate. Encarnación is the third-largest city of Paraguay. The city was originally named Nuestra Señora de la Anunciación de Itapúa, and is considered the capital of summer by most of its inhabitants.

Cándido Pastor Bareiro Caballero was President of Paraguay from 27 November 1878 to 4 September 1880 and the leading politician of the post-war decade.
Villa Hayes is a city in Paraguay, and is the capital of Presidente Hayes Department.

Club Presidente Hayes is a Paraguayan association football club from Tacumbú, a section of Asunción, Paraguay. The club is also known colloquially by its nicknames The Yankees and The Little Star. They play regularly in Asuncion's Kiko Reyes Stadium as part of the Paraguayan Soccer League. The club was founded in 1907 and participated in their first international tournament in the 1953 Copa Montevideo. It is one of several entities in Paraguay that were named in honor of Rutherford B. Hayes, the 19th President of the United States. Hayes, who was required to arbitrate an Argentine-Paraguayan territorial dispute in the Gran Chaco after the War of the Triple Alliance, decided in favour of Paraguay. The club is the former home of Paraguayans Néstor Benítez, Teófilo Barrios, Tomás Guzmán, Julio Valentín González and José Ariel Núñez, and foreigners Riki Kitawaki, Bryan Lopez, and Victor Cristaldo
{{Infobox Ethnic group |group = German Paraguayans |image = |population = 320,000 |popplace = Asunción, Itapúa Department and Boquerón Department. |langs = Guaraní, Castellano ([[]]), [[ |rels = ChristianityRoman Catholic and Protestantism), Judaism |related = German diaspora, German-Chileans, German-Argentinians, German-Brazilian, German Uruguayan, German Americans }}

The Treaty of the Triple Alliance was a treaty that allied the Empire of Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay against Paraguay. Signed in 1865, after the outbreak of the Paraguayan War, its articles prescribed the allies' actions both during and after the war. The war led to the near-annihilation of Paraguay.
Benjamín Aceval is a city in the Department of Presidente Hayes in Paraguay. The city is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Benjamín Aceval.

José Falcón is a district in Presidente Hayes Department of Paraguay, located 48 km North of Asuncion, which one can go from, through the Route 12.
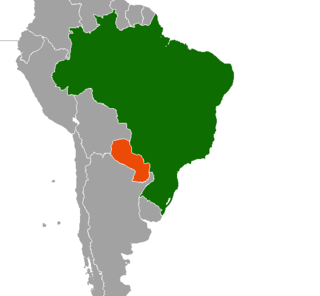
Brazil–Paraguay relations are foreign relations between Brazil and Paraguay.

Historically, the migratory history of Paraguay has been ambiguous, since it has had periods of large scale emigration as well as large waves of immigrants, primarily from Europe.

The Machain–Irigoyen Treaty was a border treaty signed in Buenos Aires on 3 February 1876 between Paraguay and Argentina. Concluded in the aftermath of the Paraguayan War, it was signed by Facundo Machaín and Bernardo de Irigoyen.
The Hito Esmeralda is a tripoint where Argentina, Bolivia and Paraguay meet. This geographical point is at the edge of Pilcomayo River, at an altitude of 200 m, with coordinates of 22°13′31″S62°38′11″W.
References
- ↑ "Paraguay celebrates U.S.A.'s President Hayes". nydailynews.com. Associated Press.
- ↑ Color, ABC. "Los entretelones del laudo Hayes - Edicion Impresa - ABC Color".
