| Monastery information | |
|---|---|
| Other names | The Augustinian Hermits of Leicester |
| Order | Austin Friars |
| Established | 1254 |
| Disestablished | 1538 |
| Dedicated to | St Catherine |
| Diocese | Lincoln |
| People | |
| Important associated figures | Thomas, 2nd Earl of Lancaster |
| Site | |
| Coordinates | 52°38′00″N1°08′40″W / 52.633362°N 1.144428°W Coordinates: 52°38′00″N1°08′40″W / 52.633362°N 1.144428°W |
| Visible remains | None |
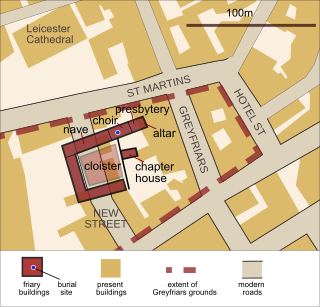
Leicester Austin Friary is a former Augustinian Friary in Leicester, England.
Austin Friars is a coeducational independent day school located in Carlisle, England. The Senior School provides secondary education for 350 boys and girls aged 11–18. There are 150 children aged 4–11 in the Junior School and the Nursery has places for 16 children aged 3–4. Founded by the Augustinian friars in 1951, it is one of the network of Augustinian schools in other parts of the world and welcomes pupils of all denominations.

Leicester is a city and unitary authority area in the East Midlands of England, and the county town of Leicestershire. The city lies on the River Soar and close to the eastern end of the National Forest.

England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to the west and Scotland to the north-northwest. The Irish Sea lies west of England and the Celtic Sea lies to the southwest. England is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight.