
Binn is a municipality in the district of Goms in the canton of Valais in Switzerland.

Hutchinsonite is a sulfosalt mineral of thallium, arsenic and lead with formula (Tl,Pb)2As5S9. Hutchinsonite is a rare hydrothermal mineral.

Lorándite is a thallium arsenic sulfosalt with the chemical formula: TlAsS2. Though rare, it is the most common thallium-bearing mineral. Lorandite occurs in low-temperature hydrothermal associations and in gold and mercury ore deposits. Associated minerals include stibnite, realgar, orpiment, cinnabar, vrbaite, greigite, marcasite, pyrite, tetrahedrite, antimonian sphalerite, arsenic and barite.

Seligmanite is a rare mineral, with the chemical formula PbCuAsS3. Originally described from the Lengenbach Quarry, Valais Canton, Switzerland; it has also been found in the Raura district, Lima Region, Peru; at Tsumeb, Oshikoto Region, Namibia; and at the Sterling Mine, Sussex County, New Jersey, US.

George Frederick Herbert Smith CBE was a British mineralogist who worked for the British Museum. He discovered the mineral paratacamite in 1906, and developed a jeweller's refractometer for the rapid identification of gems. The minerals smithite and herbertsmithite are named after him, as is Herbert's rock-wallaby.

Hyalophane or jaloallofane is a crystalline mineral, part of the feldspar group of tectosilicates. It is considered a barium-rich potassium feldspar. Its chemical formula is (K,Ba)[Al(Si,Al)Si2O8], and it has a hardness of 6 to 6+1⁄2. The name hyalophane comes from the Greek hyalos, meaning "glass", and phanos meaning "to appear".

Jordanite is a sulfosalt mineral with chemical formula Pb14(As,Sb)6S23 in the monoclinic crystal system, named after the German scientist H. Jordan (1808–1887) who discovered it in 1864.

Cafarsite is a rare calcium iron arsenite mineral. Manganese and titanium occur with iron in the formula.

The Binn Valley is a valley of the Alps, located on the north side of the Lepontine Alps in the Swiss canton of Valais. The valley is drained by the Binna, a tributary of the Rhone, at Grengiols. The valley is named after Binn, the main settlement. Other villages or localities are Ausserbinn, Heiligkreuz and Fäld.

Baumhauerite (Pb3As4S9) is a rare lead sulfosalt mineral. It crystallizes in the triclinic system, is gray-black to blue-gray and its lustre is metallic to dull. Baumhauerite has a hardness of 3.
Dương Đức is a commune (xã) and village in Lạng Giang District, Bắc Giang Province, in northeastern Vietnam.

Marrite (mar'-ite) is a mineral with the chemical formula PbAgAsS3. It is the arsenic equivalent of freieslebenite (PbAgSbS3), but also displays close polyhedral characteristics with sicherite and diaphorite. Marrite was first described in 1905, and was named in honor of geologist John Edward Marr (1857–1933) of Cambridge, England.
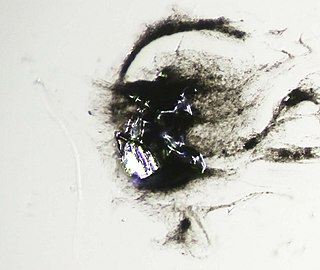
Gabrielite is an extremely rare thallium sulfosalt mineral with a chemical formula of Tl6Ag3Cu6(As,Sb)9S21 or Tl2AgCu2As3S7.
Guettardite is a rare arsenic-antimony lead sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula Pb(Sb,As)2S4. It forms gray black metallic prismatic to acicular crystals with monoclinic symmetry. It is a dimorph of the triclinic twinnite.
Heptasartorite is a very rare mineral with formula Tl7Pb22As55S108. It belongs to sartorite homologous series. It is related to other recently approved minerals of the series: enneasartorite and hendekasartorite. All three minerals come from a quarry in Lengenbach, Switzerland, which is famous of thallium minerals. Chemically similar minerals include edenharterite and hutchinsonite.

Enneasartorite is a very rare mineral with formula Tl6Pb32As70S140. It belongs to sartorite homologous series. It is related to other recently approved minerals of the sartorite series: hendekasartorite and heptasartorite. All come from Lengenbach quarry in Switzerland, which is famous for thallium sulfosalts. Enneasartorite is chemically similar to edenharterite and hutchinsonite.

Hendekasartorite is a very rare thallium sulfosalt mineral with formula Tl2Pb48As82S172. It is one of recently approved new members of sartorite homologous series, by enneasartorite and heptasartorite. All new members come from Lengenbach quarry in Switzerland, prolific in terms of thallium sulfosalt minerals. Hendekasartorite is chemically similar to edenharterite and hutchinsonite.
Heinrich Adolph Baumhauer was a German chemist and mineralogist.

Sartorite is a lead arsenic sulfide with the chemical formula PbAs2S4 and as type locality the Lengenbach Quarry in Legenbach, Binnental, Valais, Switzerland. Historically, sartorite has been thought isomorphic to chalcostibite, emplectite, and zinckenite, but was definitively distinguished from the others in 1939.

Smithite is a sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula AgAsS2. It was first described by mineralogist R H Solly in 1905, in samples from the Lengenbach quarry near Binn, Switzerland, and was named for Herbert Smith, who was an assistant in the department of mineralogy of the British Museum. Smithite is a dimorph of trechmannite.
















