
The Antarctic is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole.

The Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands is an Australian external territory comprising a volcanic group of mostly barren Antarctic islands, about two-thirds of the way from Madagascar to Antarctica. The group's overall land area is 372 km2 (144 sq mi) and it has 101.9 km (63 mi) of coastline. Discovered in the mid-19th century, the islands lie on the Kerguelen Plateau in the Indian Ocean and have been an Australian territory since 1947.

Penguins are a group of aquatic flightless birds from the family Spheniscidae of the order Sphenisciformes. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is found north of the Equator. Highly adapted for life in the ocean water, penguins have countershaded dark and white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch with their bills and swallow whole while swimming. A penguin has a spiny tongue and powerful jaws to grip slippery prey.

Krill(Euphausiids) are small and exclusively marine crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word krill, meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish.

Antarctic flora are a distinct community of vascular plants which evolved millions of years ago on the supercontinent of Gondwana. Presently, species of Antarctica flora reside on several now separated areas of the Southern Hemisphere, including southern South America, southernmost Africa, New Zealand, Australia, and New Caledonia. Joseph Dalton Hooker was the first to notice similarities in the flora and speculated that Antarctica had served as either a source or a transitional point, and that land masses now separated might formerly have been adjacent.

The Antarctic fur seal is one of eight seals in the genus Arctocephalus, and one of nine fur seals in the subfamily Arctocephalinae. Despite what its name suggests, the Antarctic fur seal is mostly distributed in Subantarctic islands and its scientific name is thought to have come from the German vessel SMS Gazelle, which was the first to collect specimens of this species from Kerguelen Islands.

The Antarctic Floristic Kingdom, also the Holantarctic Kingdom, is a floristic kingdom that includes most areas of the world south of 40°S latitude. It was first identified by botanist Ronald Good, and later by Armen Takhtajan. The Antarctic Floristic Kingdom is a classification in phytogeography, different from the Antarctic realm classification in biogeography, and from Antarctic flora genera/species classifications in botany.

Leotia viscosa, commonly known as chicken lips, as well as jelly baby and green jelly drops, is a species of mushroom in the Leotiaceae family. Its stipe is yellow, and the cap is green. The cap comes in a variety of shapes. The edibility of this mushroom is unknown. It grows under oak trees or on dead logs.

Antarctica is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of 14,200,000 km2 (5,500,000 sq mi). Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of 1.9 km (1.2 mi).

Cochlicopa lubrica is a species of small air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Cochlicopidae.
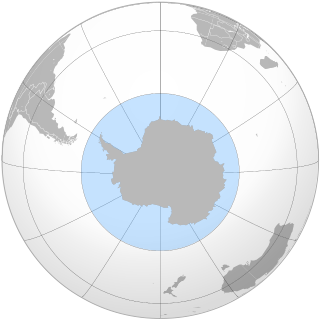
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of 20,327,000 km2 (7,848,000 sq mi), it is the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions, smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian oceans, and larger than the Arctic Ocean.

Lygephila is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Gustaf Johan Billberg in 1820.

Mount Banda Banda, a mountain of the Mid North Coast region of New South Wales, Australia, is situated 320 kilometres (200 mi) from Sydney within the Willi Willi National Park. Banda Banda can be seen on the north-western horizon from Port Macquarie, as well as on the south-western horizon 39 km from the town of Kempsey. At 1,258 metres (4,127 ft) AHD it is the highest mountain in the region.

Bharati is a permanent Antarctic research station commissioned by India. It is India's third Antarctic research facility and one of two active Indian research stations, alongside Maitri. India's first committed research facility, Dakshin Gangotri, is being used as a supply base. India has demarcated an area beside Larsemann Hills at 69°S, 76°E for construction. The research station has been operational since 18 March 2012, though it is still being run on trial basis and formal launch is awaited. Since its completion, India has become one of nine nations to have multiple stations within the Antarctic Circle. Bharati's research mandate focuses on oceanographic studies and the phenomenon of continental breakup. It also facilitates research to refine the current understanding of the Indian subcontinent's geological history. News sources have referred to the station as "Bharathi", "Bharti" and "Bharati".

Leotia lubrica, commonly referred to as a jelly baby, is a species of fungus in the family Leotiaceae. L. lubrica was first validly described by Giovanni Antonio Scopoli, but it was later transferred to Leotia by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon. Its relationship with other members of the genus, of which it is the type species, is complicated.

Odostomia lubrica is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Pyramidellidae, the pyrams and their allies.

The wildlife of Antarctica are extremophiles, having adapted to the dryness, low temperatures, and high exposure common in Antarctica. The extreme weather of the interior contrasts to the relatively mild conditions on the Antarctic Peninsula and the subantarctic islands, which have warmer temperatures and more liquid water. Much of the ocean around the mainland is covered by sea ice. The oceans themselves are a more stable environment for life, both in the water column and on the seabed.

Lygephila lubrica is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Christian Friedrich Freyer in 1842. It is found from the Zaporizhia region of Ukraine to the Rostov, Samara and Povolzhie regions to the Ural of Russia through Kazakhstan, the Russian Altai to northern Mongolia.

Trachelobdella lubrica is a species of marine leech in the family Piscicolidae. It is a parasite of fish and has a worldwide distribution in the equatorial belt. It was first described in 1840 by the German zoologist Adolph Eduard Grube, the type locality being Palermo, Sicily, in the Mediterranean Sea.
Theora lubrica is a bivalve mollusc endemic to the Northwest Pacific, including northern Japan, southern Russia and Hong Kong. It was introduced into harbours around the North Island of New Zealand around 1972, and has since spread to the upper South Island. It has also been introduced to California, Australia, the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Sea.

















