
Otorhinolaryngology ( oh-toh-RYE-noh-LAR-ən-GOL-ə-jee, abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology – head and neck surgery, or ear, nose, and throat, is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management and reconstruction of cancers and benign tumors of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck.

The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso and provides the mobility and movements of the head. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments; vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve.
Mirizzi's syndrome is a rare complication in which a gallstone becomes impacted in the cystic duct or neck of the gallbladder causing compression of the common hepatic duct, resulting in obstruction and jaundice. The obstructive jaundice can be caused by direct extrinsic compression by the stone or from fibrosis caused by chronic cholecystitis (inflammation). A cholecystocholedochal fistula can occur.

The omohyoid muscle is a muscle that depresses the hyoid. It is located in the front of the neck, and consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. The omohyoid muscle is proximally attached to the scapula and distally attached to the hyoid bone, stabilising it. Its superior belly serves as the most lateral member of the infrahyoid muscles, located lateral to both the sternothyroid muscles and the thyrohyoid muscles.

The digastric muscle is a small muscle located under the jaw. The term "digastric muscle" refers to this specific muscle. However, other muscles that have two separate muscle bellies include the suspensory muscle of duodenum, omohyoid, occipitofrontalis.
A Zenker's diverticulum, also pharyngeal pouch, is a diverticulum of the mucosa of the human pharynx, just above the cricopharyngeal muscle. It is a pseudo diverticulum.
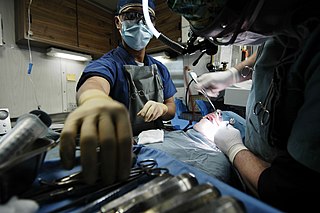
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the oral cavity, head and neck, mouth, and jaws, as well as facial cosmetic surgery.

The neck dissection is a surgical procedure for control of neck lymph node metastasis from squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the head and neck. The aim of the procedure is to remove lymph nodes from one side of the neck into which cancer cells may have migrated. Metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma into the lymph nodes of the neck reduce survival and is the most important factor in the spread of the disease. The metastases may originate from SCC of the upper aerodigestive tract, including the oral cavity, tongue, nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx, as well as the thyroid, parotid and posterior scalp.

Louis Hubert Farabeuf, French surgeon who is said to have introduced hygiene in French medical schools. His statue dominates the central court of the National School of Medicine in Paris whose main amphitheater is also named after him. Farabeuf wrote some short surgical booklets (précis) and designed several medical instruments that are still in use today.

The submandibular triangle corresponds to the region of the neck immediately beneath the body of the mandible.
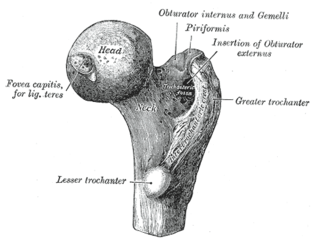
The femoral neck is a flattened pyramidal process of bone, connecting the femoral head with the femoral shaft, and forming with the latter a wide angle opening medialward.

The surgical neck of the humerus is a constriction below the tubercles of the greater tubercle and lesser tubercle, and above the deltoid tuberosity.
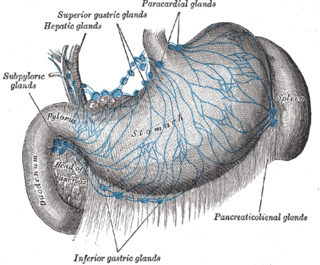
The hepatic lymph nodes consist of the following groups:
Migraine surgery is a surgical operation undertaken with the goal of reducing or preventing migraines. Migraine surgery most often refers to surgical decompression of one or several nerves in the head and neck which have been shown to trigger migraine symptoms in many migraine sufferers. Following the development of nerve decompression techniques for the relief of migraine pain in the year 2000, these procedures have been extensively studied and shown to be effective in appropriate candidates. The nerves that are most often addressed in migraine surgery are found outside of the skull, in the face and neck, and include the supra-orbital and supra-trochlear nerves in the forehead, the zygomaticotemporal nerve and auriculotemporal nerves in the temple region, and the greater occipital, lesser occipital, and third occipital nerves in the back of the neck. Nerve impingement in the nasal cavity has additionally been shown to be a trigger of migraine symptoms.
Farabeuf's triangle is the triangular space in the upper portion of the neck where the bifurcation of the carotid artery can be seen. It is limited: the rear: the jugular vein; internal below and beyond: the facial vein; above and beyond: the hypoglossal nerve. This triangle serves as a reference to locate surgery elements that are in the carotid triangle.
The Pirogov triangle is an area in the human neck formed by the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle, the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle, and the hypoglossal nerve. The triangle was named after Russian surgeon and scientist Nikolay Pirogov who performed a first description of that anatomic area of the neck. The lingual artery can be found in the Pirogov triangle underneath the fibers of the hyoglossus muscle.

The submental space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space located between the mylohyoid muscle superiorly, the platysma muscle inferiorly, under the chin in the midline. The space coincides with the anatomic region termed the submental triangle, part of the anterior triangle of the neck.
Béclard's triangle is an area whose boundaries are the posterior border of the hyoglossus, the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and the greater horn of the hyoid bone.













