
The Soviet–Afghan War was a protracted armed conflict fought in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from 1979 to 1989. It saw extensive fighting between the Soviet Union and the Afghan mujahideen after the former militarily intervened in, or launched an invasion of, Afghanistan to support the local pro-Soviet government that had been installed during Operation Storm-333. Most combat operations against the mujahideen took place in the Afghan countryside, as the country's urbanized areas were entirely under Soviet control.
The Army of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, also referred to as the Islamic Emirate Army and the Afghan Army, is the land force branch of the Armed Forces of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. The roots of an army in Afghanistan can be traced back to the early 18th century when the Hotak dynasty was established in Kandahar followed by Ahmad Shah Durrani's rise to power. It was reorganized in 1880 during Emir Abdur Rahman Khan's reign. Afghanistan remained neutral during the First and Second World Wars. From the 1960s to the early 1990s, the Afghan Army was equipped by the Soviet Union.

Ali Ahmad Jalali is an Afghan politician, diplomat, and academic. Jalali served as the Minister of Interior from January 2003 to September 2005. He has also been a distinguished professor at the Near East South Asia Center for Strategic Studies (NESA) at the National Defense University in Washington, D.C. In August 2021, amid the collapse of the US-backed Afghan government, Jalali was rumored to become the leader of the Taliban-controlled interim Afghan government, which he has denied on Twitter as "fake news."
Operation Magistral was a Soviet Army military operation during the Soviet–Afghan War that began in late November 1987 and ended in early January 1988.

The Panjshir offensives were a series of battles from 1980 to 1985 between the Soviet Army and groups of Afghan mujahideen under Ahmad Shah Massoud. The goal of these offensives was control of the strategic Panjshir Valley in Afghanistan, during the Soviet–Afghan War of the 1980s.
The Battles of Zhawar were fought during the Soviet–Afghan War between Soviet Army units, and their allies of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan against Afghan mujahideen groups. The Soviets' objective was to destroy the Mujahideen logistic base situated at Zhawar, 3 kilometers from the Pakistani border.

Khost (Matun) District is situated in the central and eastern part of Khost Province, Afghanistan. The district center is the town of Khost. Khost Airfield is situated 2 miles (3.2 km) southeast of the town of Khost.

The Democratic Republic of Afghanistan was the government of Afghanistan between 1978 and 1992. It was recognised diplomatically by only eight countries which were allies of the Soviet Union. It was ideologically close to and economically and militarily dependent on the Soviet Union, and was a major belligerent of the Afghan Civil War.
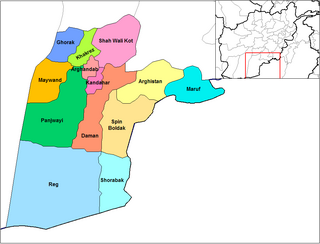
The Battle of Arghandab was an offensive launched by Afghan government forces, supported by Soviet troops, against mujahideen strongholds in the Arghandab District of Kandahar Province, Afghanistan, in 1987. The operation ended in failure, and the government forces withdrew after suffering heavy losses.

The siege of Urgun was a military engagement that took place during the Soviet–Afghan War. Between August 1983 and January 1984 Mujahideen forces laid siege to the town of Urgun, which was defended by a garrison of troops loyal to the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan. The mujahideen tried to take the town by storm using tanks, but despite making initial progress, they were eventually driven back and the siege was lifted.
Lor Koh is a mountain, 2,492 metres high, southeast of the city of Farah in western Afghanistan.
Walakan is a village in Kandahar Province, in southern Afghanistan. It is situated 5 miles southwest of Kandahar, 1 mile west of Karezak. Walakan is said to have been one of four villages given to the original Parsiwan inhabitants. Walakan, along with Zalakhan is said to have been part of sector which the Soviets left unguarded during the war.
Alishang is a village, river and a fertile valley of Laghman Province, and also the district headquarters of Mihtarlam District, in eastern Afghanistan. It lies about 40 km northwest of Jalalabad.
Bagram District is a district of Parwan Province, Afghanistan. Its seat lies at Bagram, which lies about 60 kilometers north of the capital of Kabul. It borders Kabul District to the south, Shinwari District to the east, and Chaharikar District to the north.
Kokari-Sharshari or Kakari and Sharshari was a fortified supply depot in western Afghanistan, operated by mujaheddin as a logistic base in the 1980s during the Soviet invasion and at least up to 1990.

Iliyas Daudi is a former Soviet and Russian military serviceman, best known for being one of few veterans of the Soviet–Afghan War who was awarded the title Hero of Russian Federation.

The Bear Went Over the Mountain: Soviet Combat Tactics in Afghanistan is a 1996 non-fiction book translated and edited by American military scholar and author Lester W. Grau. The book is translated from a study initially published by the Frunze Military Academy in 1991 titled "Combat Actions of Soviet Forces in the Republic of Afghanistan" and subtitled "A Thematic Collection of Tactical Examples." Grau received the original Russian language text from the Department of the History of the Military Art at the Frunze academy. With their permission he translated, included commentary, and published his results as this book.

The Other Side of the Mountain: Mujahadeen Tactics in the Soviet-Afghan War is a 1998 non-fiction book written by former Afghan Army Colonel Ali Ahmad Jalali and American military scholar Lester W. Grau.
A battalion tactical group, abbreviated as BTG, is a combined-arms manoeuvre unit deployed by the Russian Army that is kept at a high level of readiness. A BTG typically comprises a battalion of two to four companies reinforced with air-defence, artillery, engineering, and logistical support units, formed from a garrisoned army brigade. A tank company and rocket artillery typically reinforce such groupings. BTGs formed the mainstay of Russia's military intervention in Ukraine from 2013 to 2015, particularly in the War in Donbas.









