
The 2005 Liberian general election was held on 11 October 2005, with a runoff election for the presidency held on 8 November of that year. The presidency, as well as all seats in the House of Representatives and Senate were up for election. The election marked the end of the political transition following Liberia's second civil war and had been stipulated in the Accra Comprehensive Peace Agreement of 2003. Ellen Johnson Sirleaf, former World Bank employee and Liberian finance minister, won the presidential contest and became the first democratically elected female African head of state in January 2006.

The Legislature of Liberia is the bicameral legislature of the government of Liberia. It consists of a Senate – the upper house, and a House of Representatives – the lower house, modeled after the United States Congress. Sessions are held at the Capitol Building in Monrovia. Legislature of Liberia is considered one of the three branches of government based on the Article III of the Constitution of Liberia that stipulates all three branches ought to be equal and coordinated based on the Principle of checks and balances.

The House of Representatives is the lower chamber of the bicameral legislative branch of Liberia, and together with the Senate comprises the Legislature of Liberia. The number of seats is fixed by law at 73, with each county being apportioned a number of seats based on its percentage of the national population. House members represent single-member districts within the counties drawn up by the National Elections Commission and serve six-year terms. The House meets at the Capitol Building in Monrovia.

The Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislative branch of Liberia, and together with the House of Representatives comprises the Legislature of Liberia. Each of the fifteen counties are equally represented by two senators, elected to serve staggered nine-year terms. The Senate meets at the Capitol Building in Monrovia.

The Samuel Kanyon Doe Sports Stadium is a multi-purpose stadium in Monrovia, Liberia built in 1986. It is used mostly for football matches and has an athletics track, though it has also been used for a reggae concert, political rallies, IDP refuge, and Ebola treatment. The largest stadium in Liberia, its spectator capacity is 35,000.

A general election was held in the Philippines on May 13, 2013. It was a midterm election—the officials elected will be sworn in on June 30, 2013, midway through President Benigno Aquino III's term of office.

A presidential election was held in Guinea in 2010. It was held under the two-round system: the first round took place on 27 June 2010, and the second round on 7 November, after an initial date of 18 July and many other postponements. Alpha Condé was declared the winner, with 52.52% of the votes in the second round. He assumed office on 21 December 2010.

Presidential and parliamentary elections were held in Madagascar on 20 December 2013, following a first round of presidential elections on 25 October. The presidential elections in December were a runoff between Jean Louis Robinson and Hery Rajaonarimampianina, the top two candidates to emerge from the first round of voting in October. The official results of the second round were announced on 7 January 2014 with Rajaonarimampianina proclaimed the victor with nearly 54% of the vote.
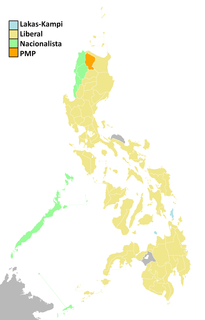
Election to the Senate of the Philippines was held on Monday, May 10, 2010. This is to elect 12 of the 24 seats in the Senate. Together with those elected in 2007, they will comprise the 15th Congress. The senators elected in 2007 will serve until June 30, 2013, while the senators elected in this election will serve up to June 30, 2016. The 2010 presidential election, elections to the House of Representatives as well as local elections will occur on the same date. The Philippines uses plurality-at-large voting for seats in the Senate: the twelve candidates with the highest number of votes wins the twelve seats up for election.

Jean-Marie Doré was a Guinean politician who was the Prime Minister of Guinea from January 2010 until December 2010. Doré, who was the President of the Union for the Progress of Guinea (UPG), was an opposition leader for years before being chosen to head a transitional government that was in place during the preparation and conduct of the 2010 presidential election.

Parliamentary elections were held in Nigeria on 9 April 2011.
Barangay elections was held on Monday, October 28, 2013. The election shall elect the Punong Barangay, more commonly known as barangay captains, and members of the Sangguniang Barangay, or barangay council, in 42,028 barangays throughout the Philippines whose terms start on November 30, 2013. Barangays are the smallest local government unit in the Philippines.
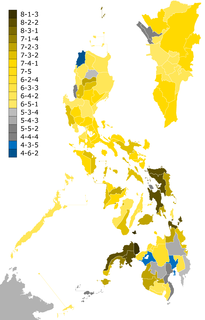
The 2016 election of members to the Senate of the Philippines was the 32nd election of members to the Senate of the Philippines. The seats of 12 senators elected in 2010 were filled during this election. The winners in this election joined the winners of the 2013 election to form the 17th Congress of the Philippines. The senators elected in 2013 will serve until June 30, 2019, while the senators elected in this election will serve up to June 30, 2022.
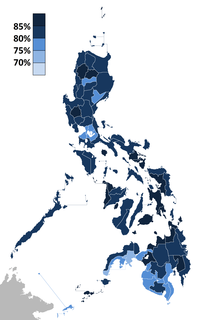
A general election in the Philippines took place on May 9, 2016, for executive and legislative branches for all levels of government – national, provincial, and local, except for the barangay officials.

An Ebola virus epidemic in Sierra Leone occurred in 2014, along with the neighbouring countries of Guinea and Liberia. On March 18, 2014 Guinean health officials announce the outbreak of a mysterious hemorrhagic fever "which strikes like lightning." It was identified as Ebola virus disease and spread to Sierra Leone by May 2014. The disease is thought to have originated when a child in a bat-hunting family contracted the disease in Guinea in December 2013. Consumption of African bushmeat, including rats, bats, and monkeys, is commonplace in Sierra Leone and West Africa in general.

An epidemic of Ebola virus disease occurred in Liberia from 2014 to 2015, along with the neighbouring countries of Guinea and Sierra Leone. The first cases of virus were reported by late March 2014. The Ebola virus, a biosafety level four pathogen, is an RNA virus discovered in 1976.
Barangay elections in the Philippines were held on May 14, 2018. The election shall elect the Punong Barangay, more commonly known as barangay captains, and members of the Sangguniang Barangay, or barangay council, in 41,948 barangays (villages) throughout the country whose terms start in June 30, 2018. Barangays are the smallest local government unit in the Philippines.

General elections were held in the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 30 December 2018, to determine a successor to President Joseph Kabila, as well as for the 500 seats of the National Assembly and 715 provincial council seats. It was announced on 10 January 2019 that Félix Tshisekedi (UDPS) won with 38.6% of the vote, defeating another opposition candidate, Martin Fayulu, and Emmanuel Ramazani Shadary, backed by the ruling party PPRD. Fayulu alleged that the vote was rigged against him in a deal made by Tshisekedi and outgoing President Kabila, challenging the result in the DRC's Constitutional Court. Different election observers, including those from the country's Roman Catholic Church, also cast doubt on the official result. Nonetheless on 20 January the Court rejected his appeal and declared Tshisekedi as the winner. Parties supporting President Kabila won the majority of seats in the National Assembly. Félix Tshisekedi was sworn in as the 5th President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 24 January 2019, making it the first peaceful transition of power in the country since it became independent from Belgium in 1960.

General elections were held in Nigeria on 23 February 2019 to elect the President, Vice President, House of Representatives and the Senate. The elections had initially been scheduled for 16 February, but the Election Commission postponed the vote by a week at 03:00 on the original polling day, citing logistical challenges in getting electoral materials to polling stations on time. In some places, the vote was delayed until 24 February due to electoral violence. Polling in some areas was subsequently delayed until 9 March, when voting was carried out alongside gubernatorial and state assembly elections.


















