Related Research Articles

St Benet's Abbey, also known as St Benet's at Holme or St Benet Hulme, was a medieval monastery of the Order of Saint Benedict situated at Cow Holm in Horning, Norfolk, England. It lay on the River Bure within the Broads. St Benet is a medieval English version of the name of St Benedict of Nursia, hailed as the founder of western monasticism. At the period of the Dissolution of the Monasteries the abbey's possessions were in effect seized by the crown and assigned to the diocese of Norwich. Though the monastery was supposed to continue as a community, within a few years at least the monks had dispersed. Today there remain only ruins.

Edmund the Martyr was king of East Anglia from about 855 until his death.

Bury St Edmunds, commonly referred to locally as Bury is a cathedral as well as market town and civil parish in the West Suffolk district, in the county of Suffolk, England. The town is best known for Bury St Edmunds Abbey and St Edmundsbury Cathedral. Bury is the seat of the Diocese of St Edmundsbury and Ipswich of the Church of England, with the episcopal see at St Edmundsbury Cathedral. In 2011 it had a population of 45,000. The town, originally called Beodericsworth, was built on a grid pattern by Abbot Baldwin around 1080. It is known for brewing and malting and for a British Sugar processing factory, where Silver Spoon sugar is produced. The town is the cultural and retail centre for West Suffolk and tourism is a major part of the economy.
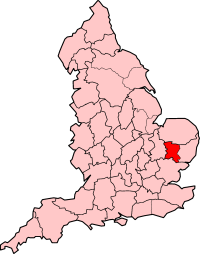
West Suffolk was an administrative county of England created in 1889 from part of the county of Suffolk. It survived until 1974 when it was rejoined with East Suffolk. Its county town was Bury St Edmunds.
Frederick William Augustus Hervey, 8th Marquess of Bristol, is a British peer.

Abbotsbury Abbey, dedicated to Saint Peter, was a Benedictine monastery in the village of Abbotsbury in Dorset, England. The abbey was founded in the 11th century by King Cnut's thegn Orc and his wife Tola, who handsomely endowed the monastery with lands in the area. The abbey prospered and became a local centre of power, controlling eight manor houses and villages. During the later Middle Ages, the abbey suffered much misfortune. In the time of the dissolution of the monasteries, the last abbot surrendered the abbey and the site became the property of Sir Giles Strangways.
This article describes the history of Suffolk, the English county.

The Abbey of Bury St Edmunds was once among the richest Benedictine monasteries in England, until its dissolution in 1539. It is in the town that grew up around it, Bury St Edmunds in the county of Suffolk, England. It was a centre of pilgrimage as the burial place of the Anglo-Saxon martyr-king Saint Edmund, killed by the Great Heathen Army of Danes in 869. The ruins of the abbey church and most other buildings are merely rubble cores, but two very large medieval gatehouses survive, as well as two secondary medieval churches built within the abbey complex.

Long Melford, colloquially and historically also referred to as Melford, is a large village and civil parish in the Babergh district, in the county of Suffolk, England. It is on Suffolk's border with Essex, which is marked by the River Stour, 3 miles (4.8 km) from Sudbury, approximately 16 miles (26 km) from Colchester and 14 miles (23 km) from Bury St Edmunds. It is one of Suffolk's "wool towns" and is a former market town. The parish also includes the hamlets of Bridge Street and Cuckoo Tye. In 2011 the parish had a population of 3918.

Culford is a village and civil parish about 4 miles (6 km) north of Bury St Edmunds and 62 miles (100 km) north east of London in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk, England.

Alpheton is a village and civil parish in the Babergh district of Suffolk, England. Located on the A134 road about six miles north of Sudbury, in 2005 it had a population of 260, reducing to 256 at the 2011 Census. According to Eilert Ekwall the meaning of the village name is the homestead of Aelfled.

Suffolk County Council is the upper-tier local authority for the county of Suffolk, England. It is run by 75 elected county councillors representing 63 divisions. It is a member of the East of England Local Government Association.
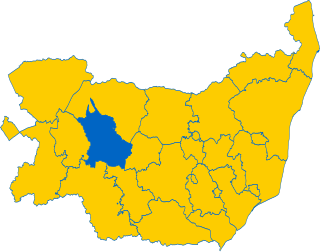
Thedwastre was a hundred of the county of Suffolk, England covering an area of 40,362 acres (163.34 km2). It formed part of the Liberty of Saint Edmund, under the jurisdiction of the abbots of Bury St Edmunds.
Abbot of Bury St. Edmunds was the title used by the head of the Benedictine monastery Bury St. Edmunds Abbey in the county of Suffolk, England. The following table lists the abbots from the foundation of the abbey in 1020 until its dissolution in 1539.

Thorpe Morieux is a small village and civil parish in Suffolk, England. It is 10 miles south-east of Bury St Edmunds and 10 miles north east of Sudbury.

Lawshall is a village and civil parish in Suffolk, England. Located around a mile off the A134 between Bury St Edmunds and Sudbury, it is part of Babergh district. The parish has nine settlements comprising the three main settlements of The Street, Lambs Lane and Bury Road along with the six small hamlets of Audley End, Hanningfield Green, Harrow Green, Hart's Green, Hibb's Green and Lawshall Green.

Groton is a village and civil parish in the Babergh district, Suffolk, England, located around a mile north of the A1071 between Hadleigh and Sudbury. In 2021 the parish had a population of 299.

Timworth is a village and civil parish 65 mi (105 km) north east of London and 26 mi (42 km) east of Cambridge in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England. Located around two miles north of Bury St Edmunds, its 2005 population was 50. At the 2011 Census the appropriate Postal Code showed the population as being included in Ampton.
Baldwin was a French monk and royal physician. He became a monk in France before coming to England to serve as King Edward the Confessor's doctor. He served as a prior before becoming abbot of Bury St Edmunds in 1065. As abbot he promoted the cult of Edmund the Martyr and secured the abbey's independence from the bishops of Thetford. He continued to serve as royal physician to two more kings of England and also rebuilt parts of the abbey before dying around 1097.
Stoke-by-Clare Priory was a Benedictine monastery in Stoke-by-Clare, in Suffolk, an alien priory, dependent on Bec Abbey, in Normandy. Reinstituted in 1124, the Priory was suppressed in 1415.
References
- ↑ "St Edmundsbury Local History – Home mapping using QGIS". www.stedmundsburychronicle.co.uk.
- ↑ "History of Bury St Edmunds Abbey". English Heritage. English Heritage . Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- 1 2 Green, Angela (1967). "The Stewardship of the eight and a half hundred". Suffolk Institute of Archaeology.
- ↑ Lilian J. Redstone. "The Liberty of St. Edmund" (PDF). suffolkinstitute.pdfsrv.co.uk. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ↑ Commission, Record (1812–18). Hundred Rolls (vol II ed.). p. 143.
- ↑ Calder, Julian (2000). Keepers of the Kingdom: The Ancient Offices of Britain. Cassell Illustrated. pp. 15–16. ISBN 1-84188-073-6.
- ↑ "Distinguished Families Bristol". www.burkespeerage.com.