
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally influence gene expression.
The 5′ untranslated region is the region of an mRNA that is directly upstream from the initiation codon. This region is important for the regulation of translation of a transcript by differing mechanisms in viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes. While called untranslated, the 5′ UTR or a portion of it is sometimes translated into a protein product. This product can then regulate the translation of the main coding sequence of the mRNA. In many organisms, however, the 5′ UTR is completely untranslated, instead forming complex secondary structure to regulate translation.

Leptospira is a genus of spirochaete bacteria, including a small number of pathogenic and saprophytic species. Leptospira was first observed in 1907 in kidney tissue slices of a leptospirosis victim who was described as having died of "yellow fever."
An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. In eukaryotic translation, initiation typically occurs at the 5' end of mRNA molecules, since 5' cap recognition is required for the assembly of the initiation complex. The location for IRES elements is often in the 5'UTR, but can also occur elsewhere in mRNAs.
Ribosome shunting is a mechanism of translation initiation in which ribosomes bypass, or "shunt over", parts of the 5' untranslated region to reach the start codon, enabling viruses to have more information than usual in an mRNA molecule. Some viral RNAs have been shown to use ribosome shunting as a more efficient form of translation during certain stages of viral life cycle or when translation initiation factors are scarce. Some viruses known to use this mechanism include adenovirus, Sendai virus, human papillomavirus, duck hepatitis B pararetrovirus, rice tungro bacilliform viruses, and cauliflower mosaic virus. In these viruses the ribosome is directly translocated from the upstream initiation complex to the start codon (AUG) without the need to unwind RNA secondary structures.
Cis-regulatory elements (CREs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology.

EF-Tu is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochrondria as TUFM.

Cobalamin riboswitch is a cis-regulatory element which is widely distributed in 5' untranslated regions of vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) related genes in bacteria. Riboswitches are metabolite binding domains within certain messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that serve as precision sensors for their corresponding targets. Allosteric rearrangement of mRNA structure is mediated by ligand binding, and this results in modulation of gene expression or translation of mRNA to yield a protein. Cobalamin in the form of adenosylcobalamin (Ado-CBL) is known to repress expression of proteins for vitamin B12 biosynthesis via a post-transcriptional regulatory mechanism that involves direct binding of Ado-CBL to 5' UTRs in relevant genes, preventing ribosome binding and translation of those genes. Before proof of riboswitch function, a conserved sequence motif called the B12 box was identified that corresponds to a part of the cobalamin riboswitch, and a more complete conserved structure was identified. Variants of the riboswitch consensus have been identified.

The FMN riboswitch is a highly conserved RNA element that is found frequently in the 5'-untranslated regions of prokaryotic mRNAs that encode for flavin mononucleotide (FMN) biosynthesis and transport proteins. This element is a metabolite-dependent riboswitch that directly binds FMN in the absence of proteins. In Bacillus subtilis, the riboswitch controls gene expression by causing premature transcription termination within the 5' untranslated region of the ribDEAHT operon and precluding access to the ribosome-binding site of ypaA mRNA.

The repression of heat shock gene expression (ROSE) element is an RNA element found in the 5' UTR of some heat shock protein's mRNAs. The ROSE element is an RNA thermometer that negatively regulates heat shock gene expression. The secondary structure is thought to be altered by temperature, thus it is an RNA thermometer. This structure blocks access to the ribosome binding site at normal temperatures. During heat shock however, the structure changes freeing the ribosome binding site and allowing expression to occur.

HIV ribosomal frameshift signal is a ribosomal frameshift (PRF) that human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) uses to translate several different proteins from the same sequence.
A ribosome binding site, or ribosomal binding site (RBS), is a sequence of nucleotides upstream of the start codon of an mRNA transcript that is responsible for the recruitment of a ribosome during the initiation of translation. Mostly, RBS refers to bacterial sequences, although internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) have been described in mRNAs of eukaryotic cells or viruses that infect eukaryotes. Ribosome recruitment in eukaryotes is generally mediated by the 5' cap present on eukaryotic mRNAs.
Trans-regulatory elements (TRE) are DNA sequences encoding upstream regulators, which may modify or regulate the expression of distant genes. Trans-acting factors interact with cis-regulatory elements to regulate gene expression. TRE mediates expression profiles of a large number of genes via trans-acting factors. While TRE mutations affect gene expression, it is also one of the main driving factors for evolutionary divergence in gene expression.
Ribosomal frameshifting, also known as translational frameshifting or translational recoding, is a biological phenomenon that occurs during translation that results in the production of multiple, unique proteins from a single mRNA. The process can be programmed by the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA and is sometimes affected by the secondary, 3-dimensional mRNA structure. It has been described mainly in viruses, retrotransposons and bacterial insertion elements, and also in some cellular genes.
Rev is a transactivating protein that is essential to the regulation of HIV-1 protein expression. A nuclear localization signal is encoded in the rev gene, which allows the Rev protein to be localized to the nucleus, where it is involved in the export of unspliced and incompletely spliced mRNAs. In the absence of Rev, mRNAs of the HIV-1 late (structural) genes are retained in the nucleus, preventing their translation.

The msiK RNA motif describes a conserved RNA structure discovered using bioinformatics. The RNA is always found in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of genes annotated as msiK, and is therefore hypothesized to be an RNA-based cis-regulatory element that regulates these genes.

FourU thermometers are a class of non-coding RNA thermometers found in Salmonella. They are named 'FourU' due to the four highly conserved uridine nucleotides found directly opposite the Shine-Dalgarno sequence on hairpin II (pictured). RNA thermometers such as FourU control regulation of temperature via heat shock proteins in many prokaryotes. FourU thermometers are relatively small RNA molecules, only 57 nucleotides in length, and have a simple two-hairpin structure.
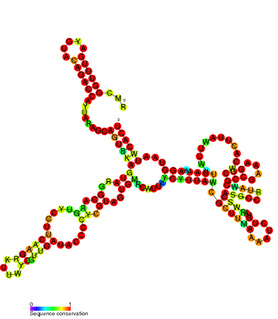
cspA mRNA 5' UTR is the untranslated region of the cspA gene, which is important in the cold shock response in Enterobacteriales such as E. coli. The 5' UTR element acts as an RNA thermometer, regulating the expression of cspA in response to temperature. By regulating temperature, cspA proteins carry out the vital function of homeostasis.

An RNA thermometer is a temperature-sensitive non-coding RNA molecule which regulates gene expression. RNA thermometers often regulate genes required during either a heat shock or cold shock response, but have been implicated in other regulatory roles such as in pathogenicity and starvation.
Leptospira kirschneri is a Gram negative, obligate aerobe species of spirochete bacteria named for University of Otago bacteriologist Dr. Leopold Kirschner. It is a member of the genus Leptospira. The species is pathogenic and can cause leptospirosis, most commonly in pigs.










