Related Research Articles
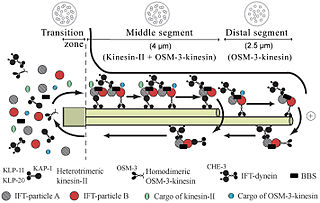
Intraflagellar transport or IFT is a bidirectional motility along axonemal microtubules that is essential for the formation (ciliogenesis) and maintenance of most eukaryotic cilia and flagella. It is thought to be required to build all cilia that assemble within a membrane projection from the cell surface. Plasmodium falciparum cilia and the sperm flagella of Drosophila are examples of cilia that assemble in the cytoplasm and do not require IFT. The process of IFT involves movement of large protein complexes called IFT particles or trains from the cell body to the ciliary tip and followed by their return to the cell body. The outward or anterograde movement is powered by kinesin-2 while the inward or retrograde movement is powered by cytoplasmic dynein 2/1b. The IFT particles are composed of about 20 proteins organized in two subcomplexes called complex A and B.
Ciliary neurotrophic factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CNTF gene.
EVC is a gene associated with Ellis-van Creveld syndrome. It overlaps with the CRMP1 gene.

X-linked retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator is a GTPase-binding protein that in humans is encoded by the RPGR gene. The gene is located on the X-chromosome and is commonly associated with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP). In photoreceptor cells, RPGR is localized in the connecting cilium which connects the protein-synthesizing inner segment to the photosensitive outer segment and is involved in the modulation of cargo trafficked between the two segments.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 (MAP3K1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP3K1 gene.

Exostosin glycosyltransferase-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EXT2 gene.

Epsilon-sarcoglycan is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SGCE gene.

Phosphatidylinositol N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase subunit A is the catalytic subunit of the phosphatidylinositol N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase enzyme, which in humans is encoded by the PIGA gene.

DNA-binding protein RFX5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RFX5 gene.

Centrosomal protein of 290 kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP290 gene. CEP290 is located on the Q arm of chromosome 12.

Inversin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the INVS gene.

Dynein intermediate chain 1, axonemal is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAI1 gene.

Cytokine receptor-like factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRLF1 gene.

Nephrocystin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPHP4 gene.

Bestrophin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BEST2 gene.

Dynein heavy chain 11, axonemal is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAH11 gene.

Bardet–Biedl syndrome 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BBS9 gene.

Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 50 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRRC50 gene.

Radial spoke head protein 9 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RSPH9 gene.
The BBSome is an octameric protein complex. It is a component of the basal body and is involved in trafficking cargos to the primary cilium. The BBSome is a complex of seven Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS) proteins: BBS1, BBS2, BBS4, BBS5, BBS7, BBS8 and BBS9. In addition the BBSome contains the BBIP10 protein. Mutation in each of this eight BBSome genes causes a severe multiorganic syndrome (BBS) presenting in most cases by retinal dystrophy, obesity, renal anomalies, post-axial polydactyly, and developmental delay.
References
- 1 2 Zhang H, Takeda H, Tsuji T, Kamiya N, Rajderkar S, Louie K, et al. (September 2015). "Generation of Evc2/Limbin global and conditional KO mice and its roles during mineralized tissue formation". Genesis. 53 (9): 612–626. doi:10.1002/dvg.22879. PMC 4731321 . PMID 26219237.
- ↑ Takeda H, Takami M, Oguni T, Tsuji T, Yoneda K, Sato H, et al. (August 2002). "Positional cloning of the gene LIMBIN responsible for bovine chondrodysplastic dwarfism". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (16): 10549–54. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9910549T. doi: 10.1073/pnas.152337899 . PMC 124971 . PMID 12136126.