
The Common Desktop Environment (CDE) is a desktop environment for Unix and OpenVMS, based on the Motif widget toolkit. It was part of the UNIX 98 Workstation Product Standard, and was for a long time the Unix desktop associated with commercial Unix workstations. It helped to influence early implementations of successor projects such as KDE and GNOME, which largely replaced CDE following the turn of the century.

The X Window System is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.

Oracle Solaris is a proprietary Unix operating system offered by Oracle for SPARC and x86-64 based workstations and servers. Originally developed by Sun Microsystems as Solaris, it superseded the company's earlier SunOS in 1993 and became known for its scalability, especially on SPARC systems, and for originating many innovative features such as DTrace, ZFS and Time Slider. After the Sun acquisition by Oracle in 2010, it was renamed Oracle Solaris.

In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphical shell. The desktop environment was seen mostly on personal computers until the rise of mobile computing. Desktop GUIs help the user to easily access and edit files, while they usually do not provide access to all of the features found in the underlying operating system. Instead, the traditional command-line interface (CLI) is still used when full control over the operating system is required.

The ROX Desktop is a discontinued graphical desktop environment for the X Window System. It is based on the ROX-Filer which is a drag and drop spatial file manager. It is free software released under the GNU General Public License. The environment was inspired by the user interface of RISC OS. The name "ROX" comes from "RISC OS on X". Programs can be installed or removed easily using Zero Install, a decentralized software installation system.
Computer accessibility refers to the accessibility of a computer system to all people, regardless of disability type or severity of impairment. The term accessibility is most often used in reference to specialized hardware or software, or a combination of both, designed to enable the use of a computer by a person with a disability or impairment.

Anjuta was an integrated development environment written for the GNOME project. It had support for C, C++, Java, JavaScript, Python and Vala programming language. In May 2022, the project was archived due to a lack of maintainers. Since October 2022 the project's former homepage no longer exists and the domain is owned by an SBOBET, an Indonesian gambling website. It has been superseded by GNOME Builder.

TrueOS is a discontinued Unix-like, server-oriented operating system built upon the most recent releases of FreeBSD-CURRENT.

Assistive Technology Service Provider Interface (AT-SPI) is a platform-neutral framework for providing bi-directional communication between assistive technologies (AT) and applications. It is the de facto standard for providing accessibility to free and open desktops, like Linux or OpenBSD, led by the GNOME Project.
A compositing manager, or compositor, is software that provides applications with an off-screen buffer for each window. The compositing manager composites the window buffers into an image representing the screen and writes the result into the display memory. A compositing window manager is a window manager that is also a compositing manager.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license.

Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is a free and open-source virtualization module in the Linux kernel that allows the kernel to function as a hypervisor. It was merged into the mainline Linux kernel in version 2.6.20, which was released on February 5, 2007. KVM requires a processor with hardware virtualization extensions, such as Intel VT or AMD-V. KVM has also been ported to other operating systems such as FreeBSD and illumos in the form of loadable kernel modules.

The history of free and open-source software begins at the advent of computer software in the early half of the 20th century. In the 1950s and 1960s, computer operating software and compilers were delivered as a part of hardware purchases without separate fees. At the time, source code—the human-readable form of software—was generally distributed with the software, providing the ability to fix bugs or add new functions. Universities were early adopters of computing technology. Many of the modifications developed by universities were openly shared, in keeping with the academic principles of sharing knowledge, and organizations sprung up to facilitate sharing.

Orca is a free and open-source, flexible, extensible screen reader from the GNOME project for individuals who are blind or visually impaired. Using various combinations of speech synthesis and braille, Orca helps provide access to applications and toolkits that support AT-SPI.

GNOME originally an acronym for GNU Network Object Model Environment, is a free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems.

Cinnamon is a free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems, which was originally based on GNOME 3, but follows traditional desktop metaphor conventions.
Comparison of user features of operating systems refers to a comparison of the general user features of major operating systems in a narrative format. It does not encompass a full exhaustive comparison or description of all technical details of all operating systems. It is a comparison of basic roles and the most prominent features. It also includes the most important features of the operating system's origins, historical development, and role.
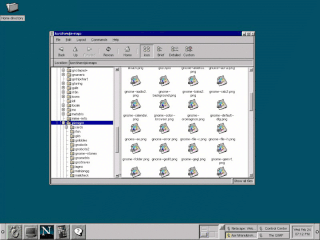
GNOME 1 is the first major release of the GNOME desktop environment. Its primary goal was to provide a consistent user-friendly environment in conjunction with the X Window System. It was also a modern and free and open source software alternative to older desktop environments such as the Common Desktop Environment (CDE), but also to the K Desktop Environment (KDE). Each desktop environment was built-upon then proprietary-licensed widget toolkits, whereas GNOME's goal from the onset, was to be freely-licensed, and utilize the GTK toolkit instead.















